In a landmark study, a team led by researchers at the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania has discovered—and filmed—the molecular details of how a cell, just before it divides in two, shuffles important internal components called mitochondria to distribute them evenly to its two daughter cells. The finding, published in Nature, is principally a...
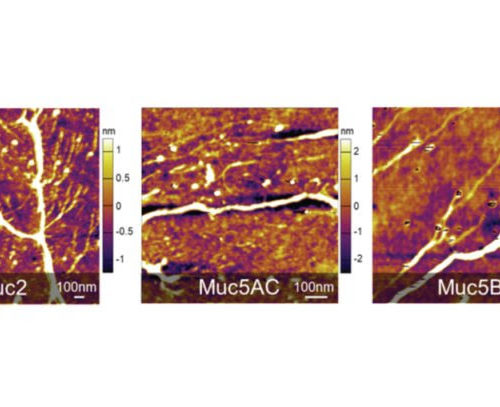
Synthetic mucus can mimic the real thing
More than just a sign of illness, mucus is a critical part of our body’s defenses against disease. Every day, our bodies produce more than a liter of the slippery substance, covering a surface area of more than 400 square meters to trap and disarm microbial invaders. Mucus is made from mucins — proteins that...
Mount Sinai study reveals genetic and cellular mechanisms of Crohn’s disease
THE MOUNT SINAI HOSPITAL / MOUNT SINAI SCHOOL OF MEDICINE Mount Sinai researchers have identified genetic and cellular mechanisms of Crohn’s disease, providing new insights for future treatments that could offer a tailored approach to patients with the chronic inflammatory disease, according to a study published in Nature on March 31. The researchers found that blocking the common cytokine receptor subunit...
Harvard researchers identify mechanism for regenerating hair follicle stem cells
HARVARD UNIVERSITY Harvard University researchers have identified the biological mechanism of how chronic stress impairs hair follicle stem cells, confirming long-standing observations that stress might lead to hair loss. In a mouse study published in the journal Nature, the researchers found that a major stress hormone causes hair follicle stem cells to stay in an extended resting...
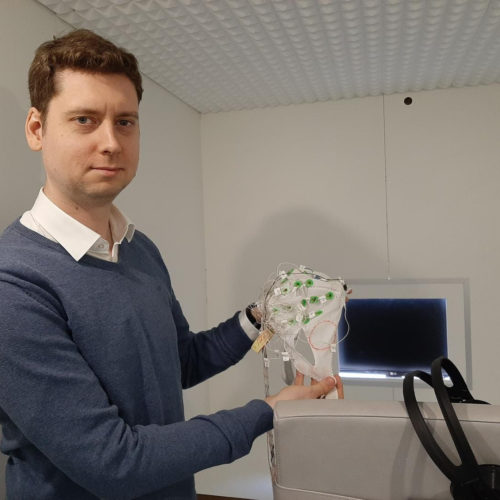
Scientists from Russia and Germany measured how the brain learn new words
URAL FEDERAL UNIVERSITY IMAGE: YURI PAVLOV AND GERMANY COLLEAGUES ARE STUDYING THE BRAIN SIGNALS OF PEOPLE IN A VEGETATIVE STATE. CREDIT: URFU / NADEZHDA PAVLOVA. Researchers from University of Tübingen (Tübingen, Germany) and Ural Federal University (Ekaterinburg, Russia) have developed and experimentally tested new method to understand how the brain builds associations between previously unrelated words....
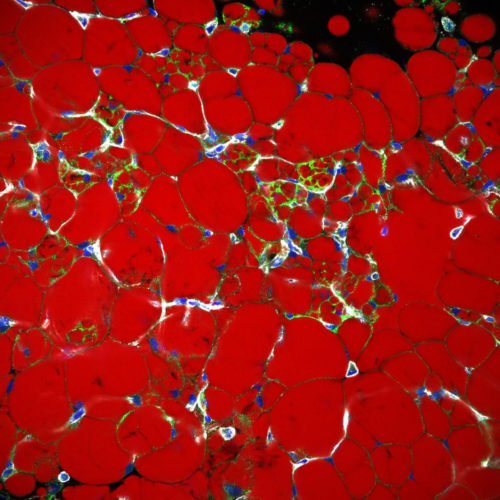
New approach for the development of a drug treatment for obesity and the resulting diseases
DEUTSCHES ZENTRUM FUER DIABETESFORSCHUNG DZD IMAGE: BEIGE ADIPOCYTES WITHIN WHITE ADIPOSE TISSUE (BEIGE ADIPOCYTES STAINED WITH UCP-1 IN GREEN. LIPIDS ARE STAINED IN RED AND F-ACTIN OUTLINING CELLS ESPECIALLY BLOOD VESSELS IN GREY, DNA IST BLUE). CREDIT: RUTH KARLINA The protein Asc-1 regulates whether fat-burning beige or fat-storing white adipocytes are formed, which can have...
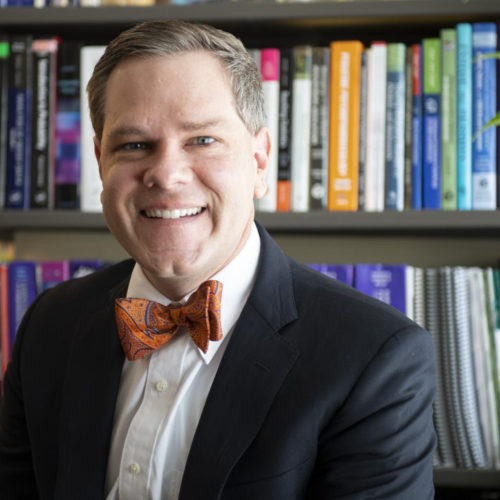
Pumping the ‘brain brake’ in pediatric anxiety
UNIVERSITY OF CINCINNATI IMAGE: JEFFREY STRAWN, MD, ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR AND ANXIETY EXPERT IN THE DEPARTMENT OF PSYCHIATRY AND BEHAVIORAL NEUROSCIENCE AT UC, WHO IS THE SENIOR AUTHOR ON THIS STUDY AND IS ALSO A PHYSICIAN AT CINCINNATI CHILDREN’S HOSPITAL MEDICAL CENTER AND UC HEALTH. CREDIT: COLLEEN KELLEY/UNIVERSITY OF CINCINNATI As with any complex machine, sometimes...
Targeted opioid that hones in on inflamed tissues stops colitis pain without side effects
NEW YORK UNIVERSITY A targeted opioid that only treats diseased tissues and spares healthy tissues relieves pain from inflammatory bowel disease without causing side effects, according to new research published in the journal Gut. The study, led by researchers at New York University College of Dentistry and Queen’s University in Ontario, was conducted in mice with colitis,...
New hydrogel that cuts in half recovery time from muscle injuries
UNIVERSITAT POLITÈCNICA DE VALÈNCIA IMAGE: PATRICIA RICO AND ANA RODRÍGUEZ (UPV-CIBERBBN) CREDIT: UPV A team from the Universitat Politècnica de València (UPV) and the CIBER Bioengineering, Biomaterials and Nanomedicine (CIBER-BBN) has designed and tested, at a preclinical level, a new biomaterial for the treatment and recovery of muscle injuries. It is a boron-loaded alginate hydrogel,...
Repurposing tocilizumab in scleroderma patients may prevent early lung disease
MICHIGAN MEDICINE – UNIVERSITY OF MICHIGAN Research led by Michigan Medicine’s Scleroderma Program and published in Arthritis & Rheumatology found that tocilizumab, a FDA-approved anti-inflammatory drug used to combat rheumatoid arthritis, can prevent lung disease in patients with systemic sclerosis if detected early enough in the disease course. Systemic sclerosis is an autoimmune disease and the most serious form...