MAY 19TH, 2021 CONN HASTINGS Researchers at City of Hope, a research center based in California, and Griffith University in Australia have collaborated to create a new experimental anti-viral therapy that can treat COVID-19. The therapeutic consists of small interfering RNA (siRNA) molecules encapsulated within lipid nanoparticles. When delivered into the bloodstream, the nanoparticles travel to the lungs. There,...
Novel immune checkpoints have applications for cancer, autoimmune disease treatment
UNIVERSITY OF CONNECTICUT IMAGE: LAIJUN LAI, RESEARCH PROFESSOR IN THE COLLEGE OF AGRICULTURE, HEALTH AND NATURAL RESOURCES AT THE UNIVERSITY OF CONNECTICUT. CREDIT: UCONN PHOTO The immune system is a complex balancing act; if it overreacts or underreacts to foreign molecules, there can be serious health consequences. For cancer patients, tumor progression is often accompanied...
Type 2 diabetes medication shown to benefit asthma patients
VANDERBILT UNIVERSITY MEDICAL CENTER IMAGE: KATHERINE CAHILL, MD, MEDICAL DIRECTOR OF CLINICAL ASTHMA RESEARCH IN THE DIVISION OF ALLERGY, PULMONARY, AND CRITICAL CARE MEDICINE AT VANDERBILT UNIVERSITY MEDICAL CENTER. CREDIT: VANDERBILT UNIVERSITY MEDICAL CENTER Type 2 diabetes patients who also have asthma are benefitting from a diabetes medication, typically given to help the pancreas produce...
New therapy shows promise in future treatment of multiple myeloma
by Peter MacCallum Cancer Centre Credit: National Cancer Institute \ Dana-Farber Harvard Cancer Center A preclinical study has found multiple myeloma is highly sensitive to a newly developed experimental therapy, according to research published today by Peter Mac scientists. Multiple myeloma is a type of blood cancer that originates in plasma cells, immune cells in the bone...
Drug could be promising new option against eczema
by Ernie Mundell and Robert Preidt A pill called upadacitinib, already approved for treating rheumatoid arthritis, might also ease another common immunological condition—eczema. In two phase 3 clinical trials, patients with moderate to severe eczema showed rapid and significant improvements after taking the drug, said researchers at Mount Sinai in New York City. The clinical trials were funded by the dug’s...
Neutrons show a connection between lithium concentration and depression
by Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich Credit: Pixabay/CC0 Public Domain Depressive disturbances are among the most frequent illnesses worldwide. The causes are complex and to date only partially understood. The trace element lithium appears to play a role. Using neutrons, a Munich based research team has now proved that the distribution of lithium in the brains of depressive...
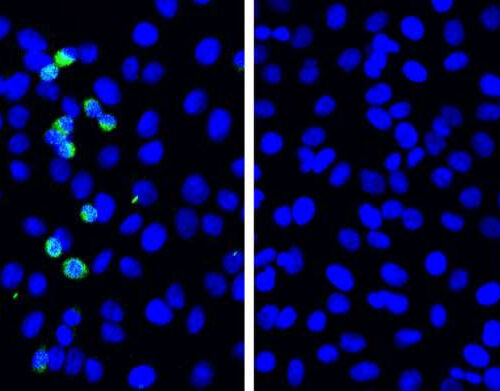
A novel defense mechanism for SARS-CoV-2 discovered
by Hokkaido University SARS-CoV-2 replication is suppressed by RIG-I. When pulmonary cells that do not express RIG-I (left) are exposed to SARS-CoV-2, viral spike proteins (green) are detected as soon as 5 days (72 hours) after exposure. In normal cells (right), SARS-CoV-2 replication is suppressed (Taisho Yamada, et al. Nature Immunology. May 11, 2021). Credit: Taisho...
Plant-produced COVID-19 vaccine shows potent immunogenic profile in humans
By Dr. Sanchari Sinha Dutta, Ph.D. May 20 2021 An interim report on a phase 2 clinical trial indicates both the safety and efficacy of a plant-produced virus-like particle vaccine candidate against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The vaccine candidate has shown an acceptable safety profile and high potency in inducing humoral and cellular immune...
COMPOUND MAY PREVENT ARRHYTHMIA SIDE EFFECT
Many drugs that are effective against cancer, infections, and other diseases, can induce a lengthening of the heart’s electrical event, or action potential, as an adverse side effect. This can render these drugs unsafe or too risky for patients. According to the American Heart Association, heart arrhythmias contribute to about 200,000 to 300,000 sudden deaths a...
An illuminating possibility for stroke treatment: Nano-photosynthesis
Blocked blood vessels in the brains of stroke patients prevent oxygen-rich blood from getting to cells, causing severe damage. Plants and some microbes produce oxygen through photosynthesis. What if there was a way to make photosynthesis happen in the brains of patients? Now, researchers reporting in ACS’ Nano Letters have done just that in cells and in mice, using...