by Diane Nazaroff, University of New South Wales Researchers hope the technology to detect the PD-L1 biomarker in a blood sample will be available in the next five years. Credit: National Cancer Institute/Unsplash Researchers at UNSW Sydney have found a way to detect a very low amount of a cancer biomarker in undiluted blood in just 15 minutes,...
Newly discovered epigenetic regulatory mechanisms involved in multiple myeloma growth
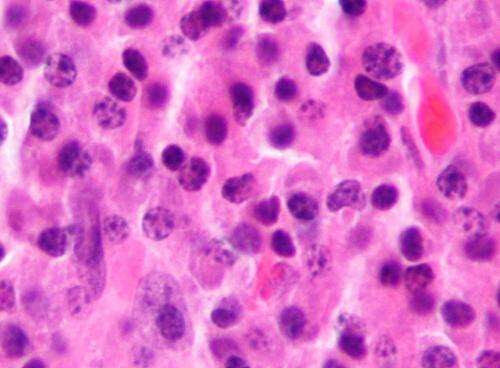
lby Kumamoto University Micrograph of a plasmacytoma, the histologic correlate of multiple myeloma. H&E stain. Credit: Wikipedia/CC BY-SA 3.0 An international team of researchers from Japan, the US and the UK has analyzed the function of the histone demethylase KDM5A in multiple myeloma, one of the three major hematological cancers, and clarified the mechanism by which it...
After setbacks, Sanofi/GlaxoSmithKline COVID vaccine performs well in early trial
by Ernie Mundell and Robin Foster Sanofi and GlaxoSmithKline announced Monday that their coronavirus vaccine candidate produced powerful responses in a preliminary trial that followed an earlier setback in the vaccine’s development. In selected data that has not yet been published in a peer-reviewed journal, the vaccine “triggered strong immune response amongst adults of all...
Lipid droplets help protect kidney cells from damage
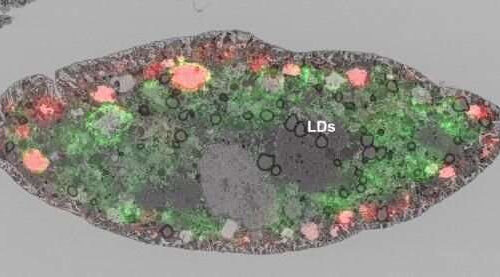
by The Francis Crick Institute Credit: The Francis Crick Institute Researchers at the Francis Crick Institute have found out how microscopic structures called lipid droplets may help to prevent a high-fat diet causing kidney damage. The work in fruit flies, published in PLoS Biology opens up a new research avenue for developing better treatments for chronic...
Scientists find new way of predicting COVID-19 vaccine efficacy
by Kirby Institute for Infection and Immunity in Society Credit: Pixabay/CC0 Public Domain The early immune response in a person who has been vaccinated for COVID-19 can predict the level of protection they will have to the virus over time, according to analysis from Australian mathematicians, clinicians, and scientists, and published today in Nature Medicine. The researchers from...
New combination immunotherapy plus ART expand innate cells critical to controlling HIV
by Emory University Credit: Pixabay/CC0 Public Domain Yerkes National Primate Research Center researchers in collaboration with Institut Pasteur have determined combination immunotherapy of Interleukin-21 (IL-21) and interferon alpha (IFNα) when added to antiviral therapy (ART) is effective in generating highly functional natural killer (NK) cells that can help control and reduce simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV) in...
Pirfenidone reduces scar tissue in patients with heart failure
by American College of Cardiology Credit: Unsplash/CC0 Public Domain Patients with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction who took the antifibrotic drug pirfenidone saw a significant reduction in a marker of heart muscles carring compared with patients who received a placebo, based on findings from an early-phase trial presented at the American College of Cardiology’s 70th...
Vitamin B3 as a possible treatment for glaucoma
by Karolinska Institutet Credit: Unsplash/CC0 Public Domain Glaucoma involves a high risk of losing sight. Researchers at Karolinska Institutet and St. Erik Eye Hospital, among others, have now studied the effects of nicotinamide, the amide of vitamin B₃, on animal and cell models for glaucoma. The study, published in Redox Biology, may be a future neuroprotective therapy in...
Engineered organism could diagnose Crohn’s disease flareups
by Rice University Rice University researchers engineered a strain of the gut bacteria E. coli to detect gastrointestinal acidosis. The organism produces fluorescent molecules that allow researchers to see it with standard optical equipment. Under normal conditions (left) it produces molecules that glow red. When it encounters acidic conditions (right), it glows green, and the brightness...
Researchers identify 64 regions of the genome that increase risk for bipolar disorder
by The Mount Sinai Hospital Credit: CC0 Public Domain In the largest genetic study of bipolar disorder to date, researchers have identified 64 regions of the genome containing DNA variations that increase risk of bipolar disorder—more than double the number previously identified. The research team also found overlap in the genetic bases of bipolar disorder and other psychiatric disorders. Furthermore, the study supports...