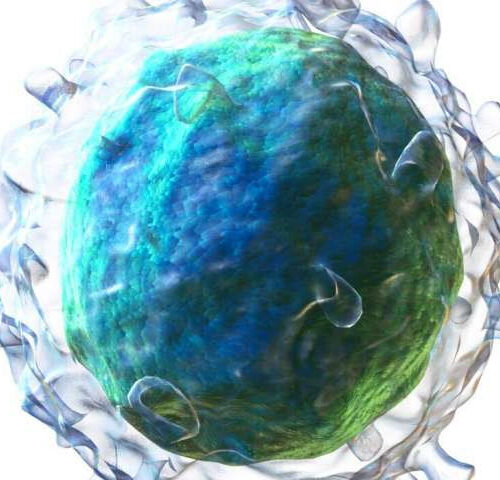
by Allison Hydzik, University of Pittsburgh 3D rendering of a B cell. Credit: Blausen.com staff (2014). “Medical gallery of Blausen Medical 2014”. WikiJournal of Medicine 1 (2). The immune system’s B cells have the unique distinction of being the only cells in the human body that evolve, in real time—and an international team of scientists announced...
New drugs to fight COVID-19 developed
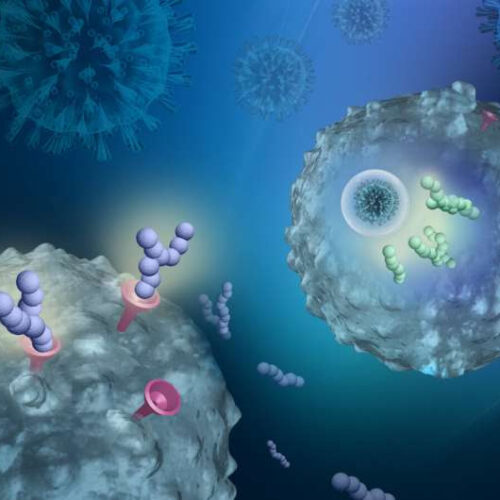
by QIMR Berghofer Medical Research Institute The illustration depicts two peptide drugs to target SARS-CoV-2. The SARS-CoV-2 spike protein uses the ACE2 receptor (pink funnel) to bind to and invade cells. With the first peptide drug (purple balls), the virus latches onto the cloaking peptides (purple balls, which protect ACE2), which they mistake for ACE2 receptor on...
Neuroscientists uncover a novel means of interneuronal communication using extracellular vesicles
by Marissa Shapiro, Miquéla Thornton, Vanderbilt University Credit: Public Domain An international collaboration led by Vanderbilt researchers has found that a novel form of brain cell communication may influence brain function. The discovery was uncovered by Natalí L. Chanaday, postdoctoral scholar, A. Alejandro Vilcaes, assistant professor at the Universidad Nacional de Córdoba in Argentina and Ege...
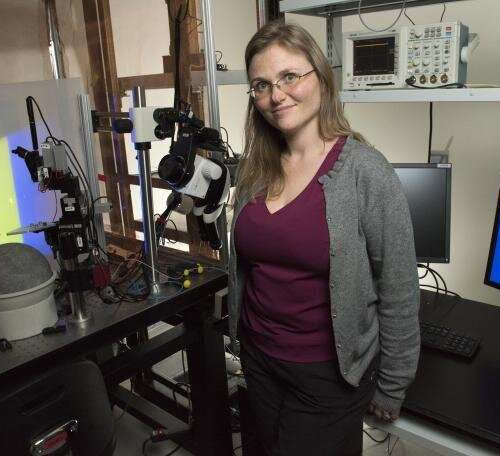
Study shows flickering lights and sound could be new weapon against Alzheimer’s
by Georgia Institute of Technology Annabelle Singer. Credit: Georgia Institute of Technology For the past few years, Annabelle Singer and her collaborators have been using flickering lights and sound to treat mouse models of Alzheimer’s disease, and they’ve seen some dramatic results. Now they have results from the first human feasibility study of the flicker treatment,...
Scientists Drove Mice to Bond by Zapping Their Brains With Light
By Virginia Hughes Mice with tiny devices implanted in their brains showed a great affinity to one another in an experiment when the signals were synchronized. Credit: Northwestern University Late one evening last March, just before the coronavirus pandemic shut down the country, Mingzheng Wu, a graduate student at Northwestern University, plopped two male mice into...
AbbVie’s last stand: How an Icelandic billionaire’s biosimilar has one final shot to dethrone Humira
Zachary BrennanSenior Editor When AbbVie CEO Richard Gonzalez sat before the House Committee on Oversight last week, calmly fending off questions about his mega-blockbuster Humira and its fortress of patents, the fate of any competition entering the US market before 2023 seemed all but sealed. But what none of the representatives nor their 57-page report...
Can antibiotics treat human diseases in addition to bacterial infections?
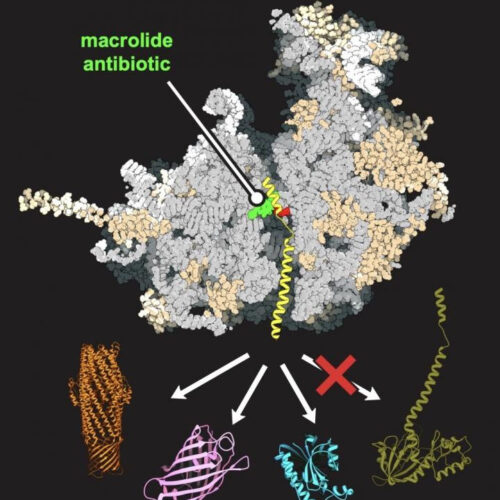
UNIVERSITY OF ILLINOIS AT CHICAGO IMAGE: AN ANTIBIOTIC (GREEN), BOUND IN THE HUMAN-LIKE YEAST RIBOSOME (GRAY), ALLOWS FOR SYNTHESIS OF SOME PROTEINS (REPRESENTED IN ORANGE, PURPLE, AND BLUE) BUT NOT OTHERS (DARK GREEN). CREDIT: MAXIM SVETLOV/UIC According to researchers at the University of Illinois Chicago, the antibiotics used to treat common bacterial infections, like pneumonia and sinusitis,...
One step closer to nasal spray drug delivery for Parkinson’s disease
by University of York Credit: Pixabay/CC0 Public Domain Scientists at the University of York have made significant progress in the development of a nasal spray treatment for patients with Parkinson’s disease. Researchers have developed a new gel that can adhere to tissue inside the nose alongside the drug levodopa, helping deliver treatment directly to the brain. Levodopa is...
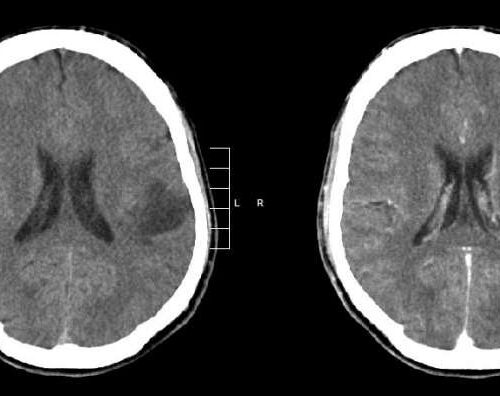
How ‘paralyzed’ immune cells can be reactivated against brain tumors
by German Cancer Research Center Glioma of the left parietal lobe. CT scan with contrast enhancement. Credit: Mikhail Kalinin/CC BY-SA 3.0 Brain tumor cells with a certain common mutation reprogram invading immune cells. This leads to the paralysis of the body’s immune defense against the tumor in the brain. Researchers from Heidelberg, Mannheim and Freiburg discovered this mechanism, and at...
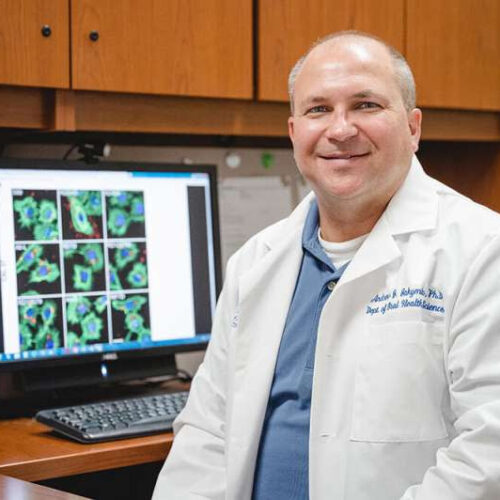
Chemical changes to peptide siRNA-carrier enhance gene silencing for future cancer drugs
by Caroline Wallace, Medical University of South Carolina Dr. Andrew Jakymiw and his team found a peptide carrier with heightened potential to deliver a cancer therapeutic for oral cancer. Credit: Marquel Coaxum MUSC Hollings Cancer Center researchers are exploring the use of peptide carriers for the delivery of small RNA drugs as a novel treatment for cancer. The...