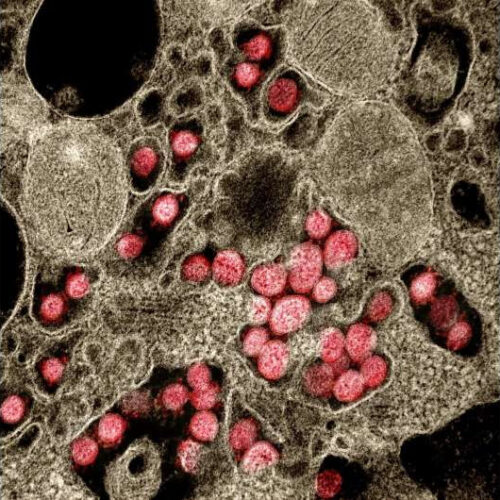
by American Association for Thoracic Surgery Transmission electron micrograph of SARS-CoV-2 virus particles isolated from a patient. Credit: NIAID A new study, presented today at the AATS 101st Annual Meeting, found that severely ill COVID-19 patients treated with ECMO did not suffer worse long-term outcomes than other mechanically-ventilated patients. The multidisciplinary team included cardio thoracic...
DNA building blocks regulate inflammation
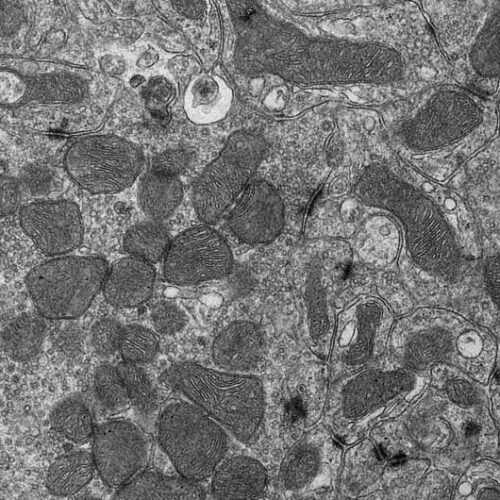
by Max Planck Society Electron micrograph of mitochondria in a nerve cell. Credit: Hans-Georg Sprenger Electron micrograph of mitochondria in a nerve cell. Credit: Hans-Georg Sprenger Mitochondria are the energy suppliers of our body cells. These tiny cell components have their own genetic material, which triggers an inflammatory response when released into the interior of the...
Multi-drug resistant infection about to evolve within cystic fibrosis patients
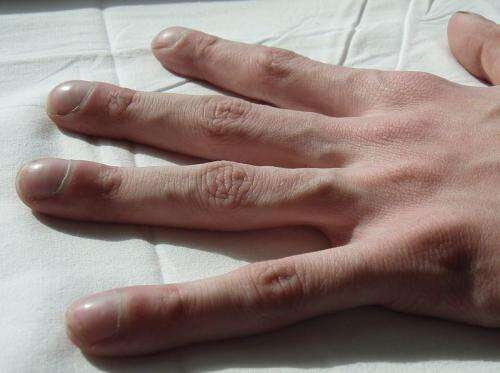
by University of Cambridge “Clubbing” of the fingers is a classic features of Cystic Fibrosis, although not present in many patients. Credit: Jerry Nick, M.D./ Wikipedia Scientists have been able to track how a multi-drug resistant organism is able to evolve and spread widely among cystic fibrosis patients—showing that it can evolve rapidly within an individual...
New technology could allow more cancer patients to benefit from immunotherapy
Professor Naoto Hirano of the Temerty Faculty of Medicine and collaborators have developed a new technology that rigorously and robustly identifies the immune cells that are capable of recognizing and eliminating cancer cells. The findings, published in Nature Biotechnology, pave the way for novel immunotherapies to help more patients, regardless of their genetic ancestry, live longer and healthier lives....
Cancer-linked mutation accelerates growth of abnormal stroke-causing brain blood vessels
Researchers have discovered an explanation for why cerebral cavernous malformations (CCMs)—clusters of dilated blood vessels in the brain—can suddenly grow to cause seizures or stroke. Specifically, they found that a specific, acquired mutation in a cancer-causing gene (PIK3CA) could exacerbate existing CCMs in the brain. Furthermore, repurposing an already existing anticancer drug showed promise in mouse...
Targeting Tumors with Nanoworms
Drugs and vaccines circulate through our vascular system reacting according to their chemical and structural nature. In some cases, their destination is diffuse. In other cases, like cancer treatments, the intended target is highly localized. The effectiveness of a medicine —and how much is needed and the amount of side-effects it causes —are a function...
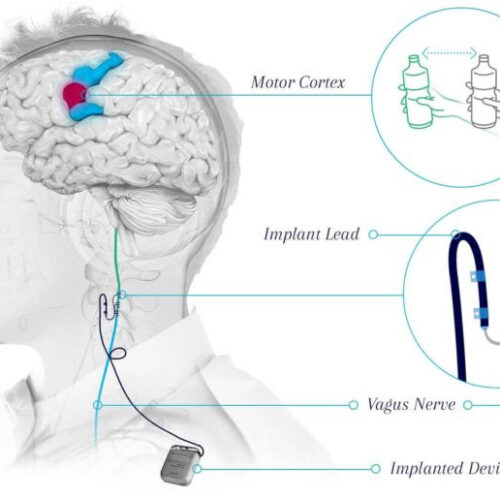
Surgical procedure may help restore hand and arm function after stroke
Every year, more than 795,000 people in the United States have a stroke. Of these, approximately 80% lose arm function and as many as 50-60% of this population still experience problems six months later. Traditionally, stroke patients try to regain motor function through physical rehabilitation, where patients re-learn pre-stroke skills, such as eating motions and grasping. However, most...
Study strengthens links between red meat and heart disease
The research is presented at ESC Preventive Cardiology 2021, an online scientific congress of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and published in the journal Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicine. Study author Dr Zahra Raisi-Estabragh from Queen Mary’s William Harvey Research Institute said: “Previous studies have shown links between greater red meat consumption and increased risk of heart attacks or dying...
Treatment found to improve cognitive function in patients with fragile X syndrome
RUSH UNIVERSITY MEDICAL CENTER An experimental treatment produced improvements in cognitive function and language in patients with fragile X syndrome, according to study results published on April 29 in Nature Medicine. Fragile X syndrome (known as FXS for short) is the most common known genetic cause of autism and the most common cause of inherited intellectual...
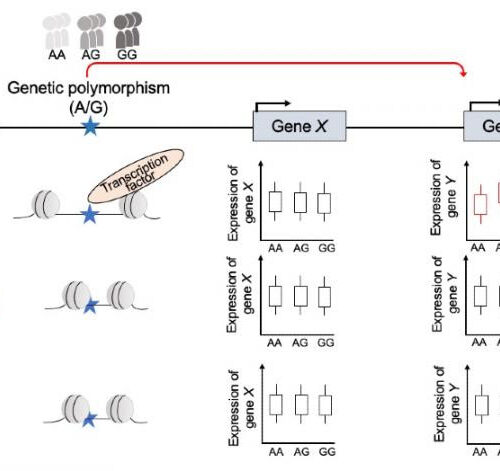
New atlas of genetic function maps complexities of immune system and immune diseases
UNIVERSITY OF TOKYO IMAGE: Each person only has one genome, but different parts of the genome are active in different cell types. In the example above, a region of regulatory DNA (blue star) is active only in Cell A. This regulatory DNA controls expression level of Gene Y. Different people have different variations of that...