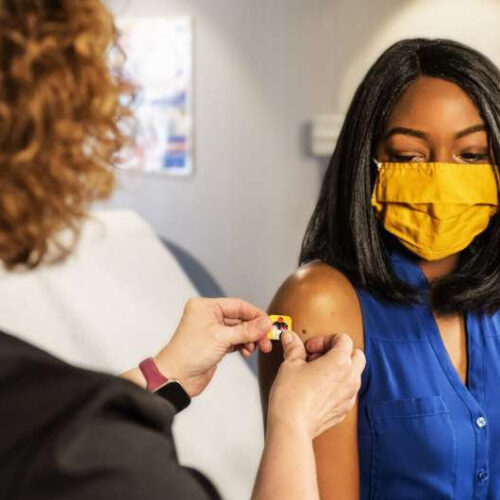
by Carlos Andres López, New Mexico State University Credit: Unsplash/CC0 Public Domain New research from a New Mexico State University professor shows hesitancy toward the COVID-19 vaccine is much more prevalent among Hispanic and Black adults in the United States when compared to the overall hesitancy rate for the general American population. Jagdish Khubchandani, professor of public health...
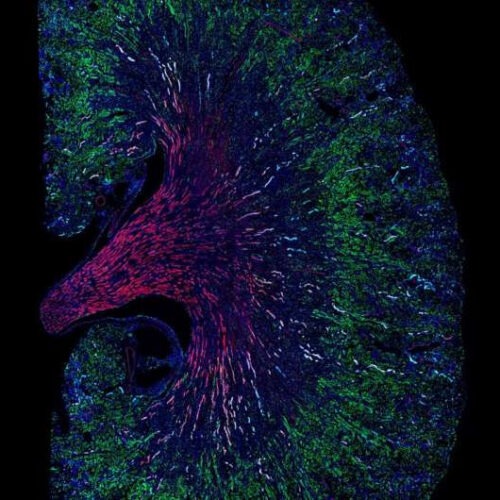
The same cell type can help or hinder kidney repair after acute injury
by Keck School of Medicine of USC A mouse kidney one month after acute kidney injury. Cells that proliferated in response to the injury are shown in green. Credit: Louisa M. S. Gerhardt/McMahon Lab The USC Stem Cell laboratory of Andy McMahon has identified a type of injured cell that might contribute to the transition from...
COVID-19 outpatient thrombosis prevention trial ends early
by Brigham and Women’s Hospital Credit: CC0 Public Domain A year ago, investigators set out to study whether symptomatic COVID-19 outpatients should be given anticoagulant or antiplatelet therapy to prevent clots that were reported among some patients with COVID-19. The data collected to date, through a randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled trial sponsored by the National Heart, Lung,...
Access to peer support combined with telehealth being studied to combat PTSD
by Alexis Shelly, University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston Even with access to telemedicine, many PTSD patients do not finish their treatment. A new study from UTHealth is pairing evidence-based psychotherapy with peer support to address this problem. Credit: Rogelio Castro/UTHealth The military mantra of “no man left behind” is being applied to help...
Rare neurological disorder documented following COVID-19 vaccination
by Wiley Credit: Pixabay/CC0 Public Domain In two separate articles in the Annals of Neurology, clinicians in India and England report cases of a rare neurological disorder called Guillain-Barré syndrome after individuals were vaccinated against COVID-19. Both reports describe an unusual variant of Guillain-Barré syndrome characterized by prominent facial weakness. Seven cases were reported from a regional medical center...
Old vaccines for COVID-19: Tetanus, diphtheria show promise
A history of diphtheria and tetanus vaccination may partly explain why some people with COVID-19 do not require hospitalization. David Greedy/Getty Images Tetanus and diphtheria vaccines may produce protective effects against COVID-19. Preliminary data finds severe disease outcomes significantly reduced among people who have received vaccines. Scientists say that the vaccines could be achieving this...
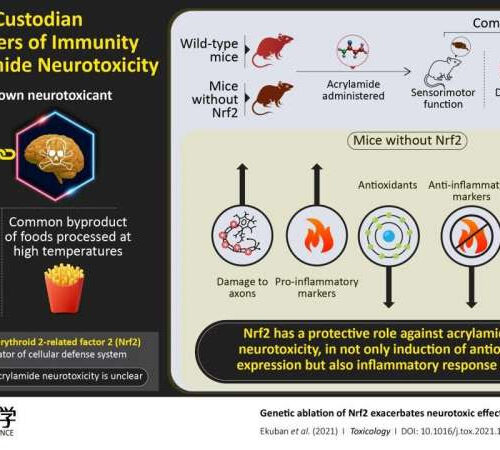
Nrf2: The custodian regulating oxidative stress and immunity against acrylamide toxicity
by Tokyo University of Science Genetic ablation of Nrf2 exacerbates neurotoxic effects of acrylamide in mice. Credit: Tokyo University of Science Acrylamide is a toxic chemical compound that affects the nervous system. It is widely used in industries such as paper production, plastics, and wastewater management, and is also a byproduct of commonly-used food processing methods,...
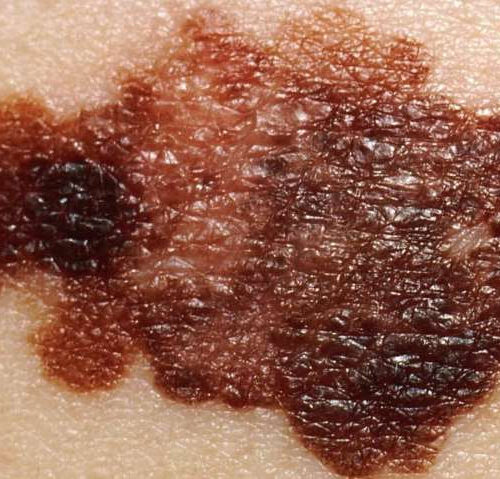
‘Suffocating’ cancer: Improved melanoma immunotherapy
by Luxembourg Institute of Health Credit: Wikimedia Commons/National Cancer Institute Hypoxia, or the inadequate oxygenation of a tissue, is a condition occurring frequently in all solid tumors such as melanoma skin cancer. Melanoma cells are not only able to survive oxygen deprivation, but also to use it to their own advantage by hijacking the anti-tumor...
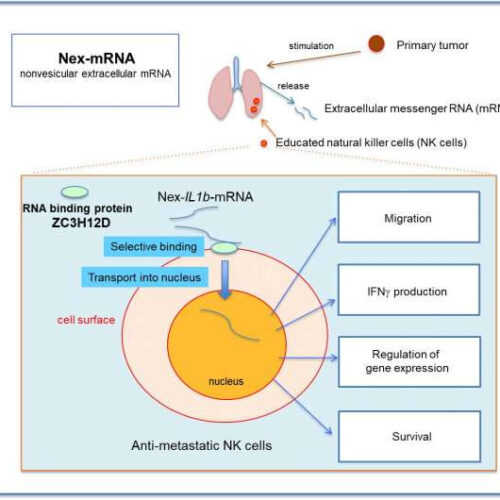
Extracellular mRNA transported to the nucleus shows translation-independent function
by Shinshu University The tumor-associated nex-IL1β-mRNA was introduced to the nucleus in a ZC3H12D protein-dependent manner. Then, the transport into the nucleus may elicit various functions. Credit: Sachie Hiratsuka, Shinshu University A research group led by Professor Sachie Hiratsuka, of the Institute for Biomedical Research, Shinshu University, has found that a specific sequence of messenger...
NEW DRUG TARGET REVEALS POTENTIAL TO STOP C. DIFF INFECTION
C. difficile infection (CDI) is the most frequent cause of healthcare-acquired gastrointestinal infections and death in developed countries. Published in Nature Communications, the study reveals the first 3D structure of the C. difficile toxin B (TcdB) in complex with a chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan 4 (CSPG4), a human receptor. “TcdB is one of two homologous C....