UNIVERSITY OF NORTH TEXAS HEALTH SCIENCE CENTER IMAGE: DR. O’BRYANT ANNOUNCED THE AVAILABILITY OF THE RESEARCH DATA IN AN ARTICLE PUBLISHED JUNE 21 IN ALZHEIMER’S & DEMENTIA: DIAGNOSIS, ASSESSMENT & DISEASE MONITORING, A NATIONAL JOURNAL PUBLISHED BY THE ALZHEIMER’S ASSOCIATION. CREDIT: HSC A growing trove of data to help scientists understand the biology of Alzheimer’s...
Stopping the onset and progression of intractable immune diseases
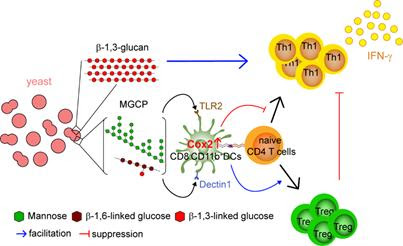
POHANG UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY (POSTECH) IMAGE: SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM DEPICTING ANTI-INFLAMMATORY RESPONSE MECHANISMS MEDIATED BY MGCP. CREDIT: POSTECH The development of therapeutic drugs for inflammatory bowel disease, an intractable immune disease, and multiple sclerosis – an autoimmune disorder – is gaining traction. A research team from the Department of Life Sciences at POSTECH and a joint research team...
When pandemic hit, some people wanted more sexual activity
UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH IMAGE: DIRECTOR OF THE UROLOGIC ONCOLOGY PROGRAM, UPMC HILLMAN CANCER CENTER, AND PROFESSOR, PITT’S DEPARTMENT OF UROLOGY. CREDIT: BENJAMIN DAVIES PITTSBURGH, June 25, 2021 – It is widely assumed that Americans’ sexual activity took a nosedive during the early chaotic months of the coronavirus pandemic. But a new study from the University...
Muscling up with nanoparticle-based anti-inflammatory therapy
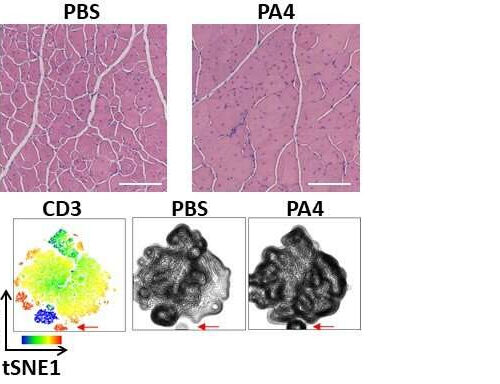
by Benjamin Boettner, Harvard University The images on top show representative muscle histology with increased muscle fiber area (pink) and improved morphology (fewer damaged fibers, white spaces) two weeks after mice with DMD were treated with a single dose of IL-4 NPs (PA4), compared to the PBS negative control. Scale bar, 300um. The images on the...
Genetic study of liver cancer reveals new drug target
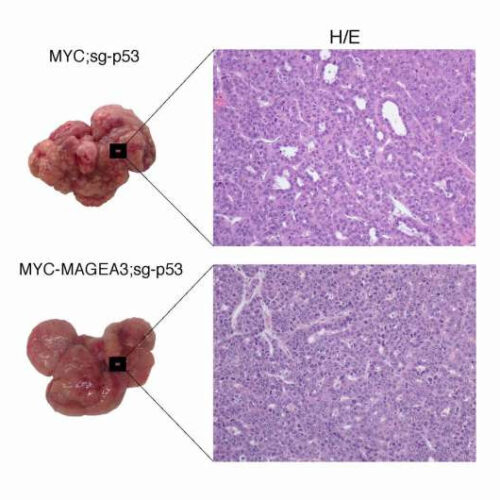
by Public Library of Science Histological pictures of aggressive hepatic tumors obtained from transgenic mice (using tail vein injection of transposable genetic elements) with induced overexpression of MAGEA3. Credit: Craig AJ et al., 2021, PLOS Genetics Drugs targeting the gene MAGEA3 may help block the growth of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), the most common type of primary...
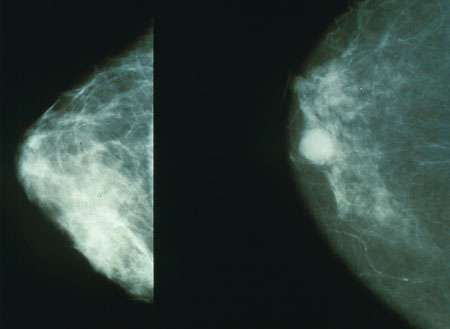
Researchers identify how most common breast cancer becomes resistant to treatment
by City of Hope National Medical Center Mammograms showing a normal breast (left) and a breast with cancer (right). Credit: Public Domain City of Hope, a world-renowned cancer research and treatment center, has identified how cancer cells in patients with early-stage breast cancer change and become resistant to hormone or combination therapies, according to a new study published...
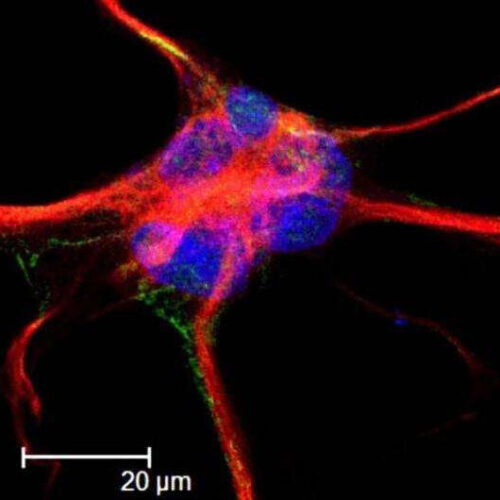
Researchers find the adhesions that build the brain’s networks
by Karl Leif Bates, Duke University School of Nursing This is an astrocyte, labeled with GFAP (red), Focal Adhesion Kinase (FAK) green, and nuclear stain To-Pro (blue). Credit: Nathan S. Ivey at TNPRC. Via Wikipedia. The brain’s neurons tend to get most of the scientific attention, but a set of cells around them called astrocytes—literally, star-shaped...
Research shines light on how cells recover from threats, may lead to new insights into Alzheimer’s and ALS
by Brian Andrew Maxwell, The Conversation Ubiquitin tags in cells serve different functions depending on stress conditions. Credit: Michael Hughes, CC BY-ND Our bodies contain a special protein tag that plays a role in how cells recover from specific threats to their survival, according to new research I co-authored. Understanding how this process works may be key to future...
Study shows potential dangers of sweeteners
by Anglia Ruskin University Credit: CC0 Public Domain New research has discovered that common artificial sweeteners can cause previously healthy gut bacteria to become diseased and invade the gut wall, potentially leading to serious health issues. The study, published in the International Journal of Molecular Sciences, is the first to show the pathogenic effects of some of the most widely used artificial...
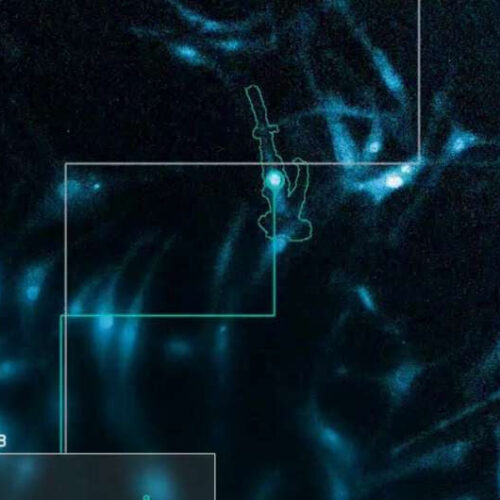
Study reveals how immune cells can be trained to fight infections
by Stuart Wolpert and Todd Schindler, University of California, Los Angeles In this image from a microscopy video, scientists track the activity of NFκB inside the cell as it responds to a stimulus. Credit: Brooks Taylor/UCLA The body’s immune cells naturally fight off viral and bacterial microbes and other invaders, but they can also be reprogrammed...