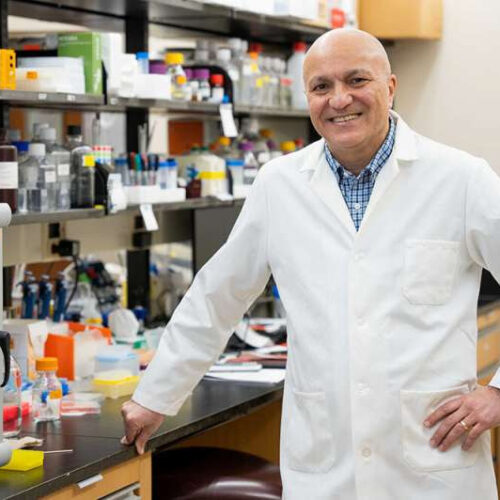
by Caroline Wallace, Medical University of South Carolina Dr. Besim Ogretmen’s team discovered that blocking certain ceramide molecules improves the anti-tumor function of aging T-cells. Credit: Marquel Coaxum MUSC Hollings Cancer Center researchers are finding solutions to the aging-related changes that reduce anti-cancer immunity. Besim Ogretmen, Ph.D., and colleagues found a novel link between aging, metabolism and anti-cancer...
Study on heavy drinking in young adults and the psychological impacts of COVID-19 yields unexpected findings
by McMaster University Credit: CC0 Public Domain A novel longitudinal study on heavy drinking in young adults and the psychological impacts of COVID-19 has revealed some unexpected findings that challenge preconceived notions regarding pandemic-related alcohol use. In a sample of nearly 500 young adults ranging in age from 18 to 25, researchers saw a reduction in problematic drinking and alcohol...
Gene therapy more cost effective than current treatments for hemophilia B
by St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital Credit: CC0 Public Domain A St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital analysis found a major gap between the cost to manufacture and distribute hemophilia B gene therapy and the $2 million-plus price reportedly under consideration for hemophilia gene therapy now in development. The study appeared online in the journal Blood. It is the first to report gene...
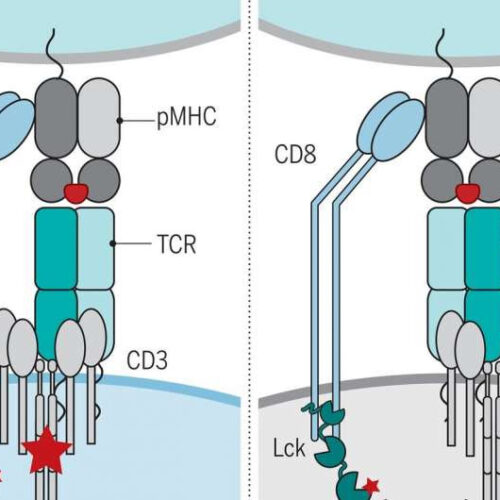
Fundamental advance in understanding T cell immunity
by Monash University The canonical polarity of TCR–pMHC docking is essential for colocalization of CD3 and coreceptor-associated Lck and for productive TCR signaling. Schematic shows how canonical TCR–pMHC recognition colocalizes Lck and CD3, driving TCR-mediated signaling. By contrast, a reversed TCR–pMHC recognition polarity mislocalizes Lck and CD3, impeding signaling. Credit: Science (2021). Monash University researchers have provided a...
The dream team: Scientists find drug duo that may cure COVID-19 together
by Tokyo University of Science Researchers screened a panel of drugs that are already approved for clinical use and identified two drugs that provided effective SARS-CoV-2 suppression: cepharanthine and nelfinavir. Credit: Louis Reed on Unsplash COVID-19 continues to claim lives around the world and is infecting millions more. Although several vaccines have recently become available, making significant...
Extensive study identifies over a dozen existing drugs as potential COVID-19 therapies
by The Scripps Research Institute A researcher at Calibr, the drug discovery division of Scripps Research, working in the high-throughput screening facility used to identify potential COVID-19 therapies. Credit: Scripps Research Mining the world’s most comprehensive drug repurposing collection for COVID-19 therapies, scientists have identified 90 existing drugs or drug candidates with antiviral activity against the coronavirus that’s driving the...
Researchers identify potential new antiviral drug for COVID-19
by NIH/Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development Transmission electron micrograph of SARS-CoV-2 virus particles, isolated from a patient. Image captured and color-enhanced at the NIAID Integrated Research Facility (IRF) in Fort Detrick, Maryland. Credit: NIAID The experimental drug TEMPOL may be a promising oral antiviral treatment for COVID-19, suggests a study of cell...
‘Next big wave’: Radiation drugs track and kill cancer cells
by Carla K. Johnson This 1974 microscope image made available by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention shows changes in cells indicative of adenocarcinoma of the prostate. In results released Thursday, June 3, 2021 by the American Society of Clinical Oncology, doctors are reporting improved survival in men with advanced prostate cancer from an...
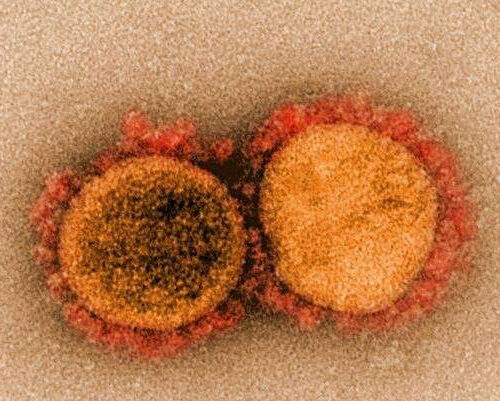
Prior COVID-19 infection reduces infection risk for up to 10 months
by University College London A colorized scanning electron micrograph of the SARS-CoV-2 virus. Credit: NIAID The risk of being infected with SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, is substantially reduced for up to 10 months following a first infection, according to new findings from the Vivaldi study led by UCL researchers. For the study, published in Lancet...
Machine learning is booming in medicine. It’s also facing a credibility crisis
By Casey Ross June 2, 2021 Reprints MIKE REDDY FOR STAT The mad dash accelerated as quickly as the pandemic. Researchers sprinted to see whether artificial intelligence could unravel Covid-19’s many secrets — and for good reason. There was a shortage of tests and treatments for a skyrocketing number of patients. Maybe AI could detect the...