By Rich Haridy June 23, 2021 New research has shown low-calorie diets increase levels of a bacterium called Clostridioides difficile, found in high levels in patients suffering from gut inflammationkaterynakon/Depositphotos A new study investigating how a low-calorie diet alters gut microbial populations is reporting unexpected results. The findings reveal a strange relationship between extreme caloric...
Common plant fiber gel doubled rate of tumor eradication
UNIVERSITY OF MICHIGAN Many people don’t realize that the trillions of bacteria, viruses, and fungi residing within the gastrointestinal tract–collectively called the gut microbiome– are connected to overall health, and specifically to cancer. Manipulating the gut microbiome to produce “beneficial” commensal microbes, which protect the host from pathogens and can boost immune responses, among other...
Study links brain energy deficits to migraine susceptibility
by Joan Perkins, University of Maine Credit: Unsplash/CC0 Public Domain Individuals who experience migraines are prone to a brain energy deficit between attacks, whether through increased demand or inadequate energy production according to a new analysis that finds that an energy impairment may cause brain oxidative stress, triggering a migraine as a protective response. This analysis...
Blood test to detect 50 types of cancer ‘accurate enough to be rolled out’
Nilima Marshall, PA Science Reporter Thu, 24 June 2021 A simple blood test that can detect more than 50 types of cancer before any clinical signs or symptoms of the disease is accurate enough to be rolled out as a multi-cancer screening test, according to scientists. The test, which is also being piloted by NHS...
Immunologists discover new trick used by MRSA superbug — may aid vaccine development
TRINITY COLLEGE DUBLIN New research has uncovered a novel trick employed by the bacterium Staphylococcus aureusto thwart the immune response, raising hopes that a vaccine that prevents deadly MRSA infections is a little closer on the horizon. Immunologists from Trinity College Dublin, working with scientists at GSK – one of the world’s largest vaccine manufacturers – discovered the...
Immunotherapy may be effective for subset of prostate cancer
BETH ISRAEL DEACONESS MEDICAL CENTER Boston – In recent years, cancer immunotherapy has been effective in treating patients with immunogenic, or so-called “hot” tumors with increased levels of inflammation and the presence of immune cells in and around the tumors. Prostate cancer, however, is considered a “cold” tumor, with few immune cells recognizing and infiltrating...
How neurons get past ‘no’
SALK INSTITUTE LA JOLLA–(June 24, 2021) When looking at a complex landscape, the eye needs to focus on important details without losing the big picture–a charging lion in a jungle, for example. Now, a new study by Salk scientists shows how inhibitory neurons play a critical role in this process. The study, published May 25,...
S. pneumoniae sticks to dying lung cells, worsening secondary infection following flu
by Jeff Hansen, University of Alabama at Birmingham This novel virulence trait, which increases the severity of S. pneumoniae superinfection, involves pneumococcal surface protein A, now identified as an adhesin. Credit: the University of Alabama at Birmingham A bout with the flu virus can be hard, but when Streptococcus pneumonia enters the mix, it can turn...
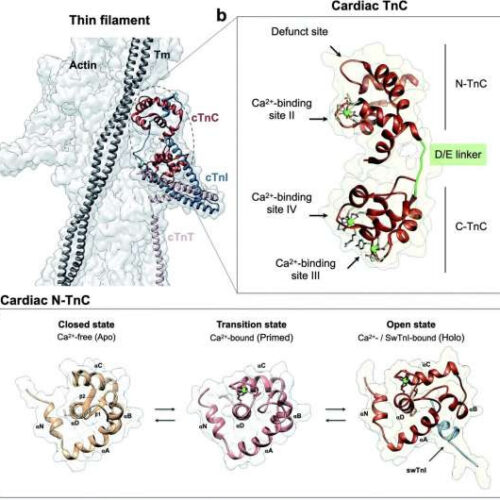
Researchers find small mutation disrupts protein network, causing heart disease
by Kathleen Haughney, Florida State University Fig. 1 Troponin C is the Ca2+ sensor of cardiac muscle. (a) Cardiac thin filament organization. Density maps are from PDB structure 6KN8. (b) Enlargement of the cardiac TnC subunit from the cardiac troponin (Tn) complex (PDB code 1J1E), shown as a ribbon structure. Regulatory and structural domains are N-TnC...
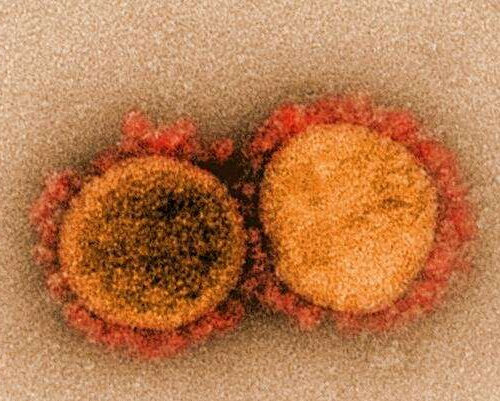
New class of compounds found to block coronavirus reproduction
by NYU Langone Health Transmission electron micrograph of SARS-CoV-2 virus particles, isolated from a patient. Image captured and color-enhanced at the NIAID Integrated Research Facility (IRF) in Fort Detrick, Maryland. Credit: NIAID A human genetic mechanism hijacked by SARS-CoV-2, the coronavirus behind the COVID-19 pandemic, to help it spread also makes it vulnerable to a new class of...