by Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia Credit: Unsplash/CC0 Public Domain While most cases of type 1 diabetes are classified as autoimmune diseases, a minor proportion of these patients have non-immune-mediated type 1 diabetes, sometimes referred to as type 1 B diabetes. Researchers from Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP) have identified 41 previously unreported genetic markers for this less common...
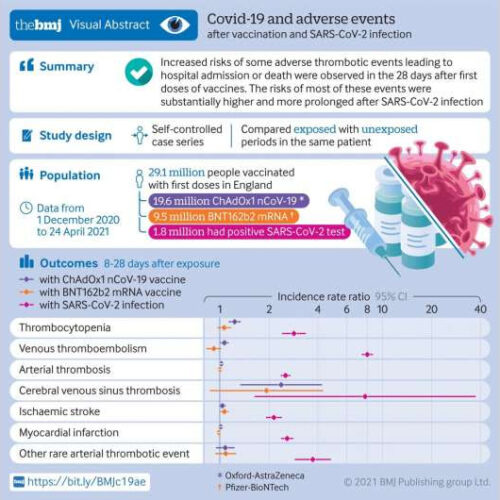
COVID-19, not vaccination, presents biggest blood clot risks: study
by University of Oxford Graphical abstract. Credit: DOI: 10.1136/bmj.n1931 Researchers from the University of Oxford have today announced the results of a study into thrombocytopenia (a condition with low platelet counts) and thromboembolic events (blood clots) following vaccination for COVID-19, some of the same events which have led to restricted use of the Oxford-AstraZeneca vaccine in...
Headed away to school? Here’s what students with health issues need to know
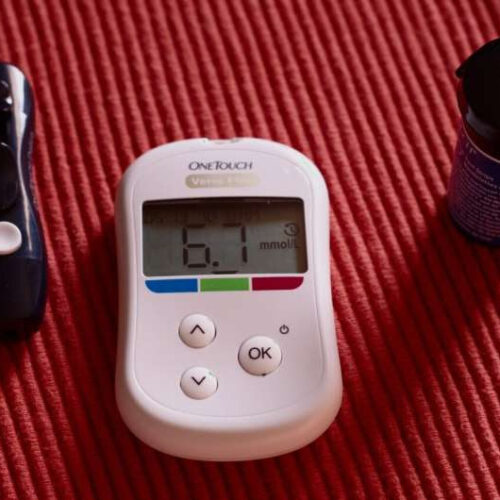
by Sandy West, Kaiser Health News Credit: CC0 Public Domain College is a time of transition, but for those managing chronic medical conditions, it may also be the first time they will be wholly responsible for their own health: Setting appointments, securing supplies and pharmaceuticals, and monitoring symptoms. For those heading to schools far from...
New cell phone and smart watch models can interfere with pacemakers and defibrillators
by Elsevier New research findings verify FDA recommendation for patients with implanted medical devices to keep their smart phones and watches at least six inches away to avoid interference with implanted medical devices. Credit: US Food and Drug Administration After reports of smart phone and watch interference with implanted medical devices, investigators affiliated with the Center for Devices...
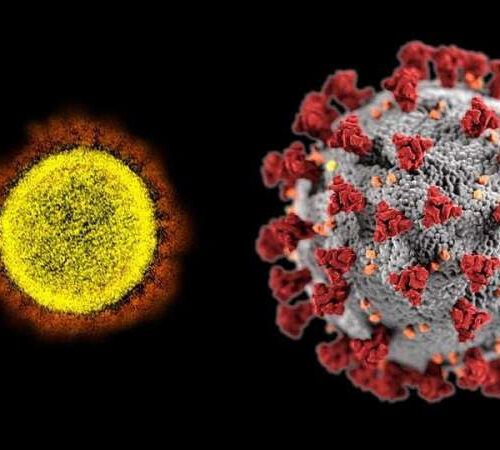
Vaccines effective even without post-shot symptoms or prior infection
by Johns Hopkins University Transmission electron micrograph of a SARS-CoV-2 particle (left) alongside a model of the virus (right). Johns Hopkins Medicine researchers have shown that mRNA vaccines against SARS-CoV-2 are effective even if a person does not experience post-shot symptoms or had a prior COVID-19 infection. Credit: National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, National...
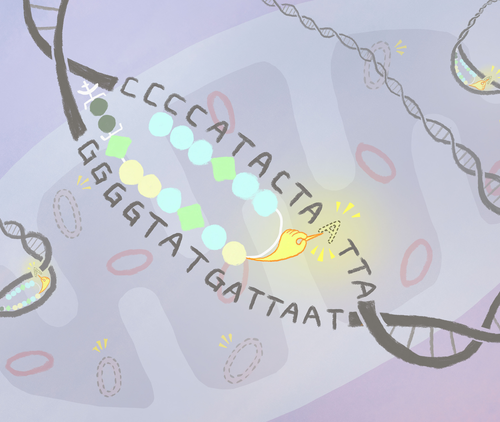
Deleting DNA to treat mitochondrial diseases
KYOTO UNIVERSITY IMAGE: HIS NEW COMPOUND CAN FIND AND HELP REMOVE MUTANT MITOCHONDRIA DNA FROM CELLS. CREDIT: MINDY TAKAMIYA/KYOTO UNIVERSITY ICEMS Mutant DNA sequences inside cellular mitochondria can be eliminated using a bespoke chemical compound. The approach, developed by scientists at Kyoto University’s Institute for Integrated Cell-Material Science (iCeMS) in Japan, could lead to better...
Pfizer jab side effects in 12-15 year olds at high risk of COVID-19 complications, mild to moderate
BMJ Pfizer jab side effects in 12-15 year olds at high risk of COVID-19 complications, mild to moderate Side effects clear up quickly in this group, findings show Study numbers small, but data representative of those most likely to benefit The side effects of the Pfizer-BioNTech jab against COVID-19 are likely to be mild to...
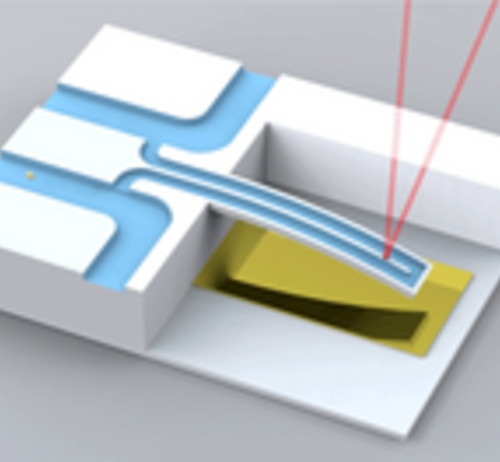
Breakthrough in sizing nanoparticles using fluid-filled tubes
UNIVERSITY OF MELBOURNE IMAGE: DISCOVERY IN NANOPARTICLES FINDINGS HAS IMPORTANT IMPLICATIONS FOR BIOTECHNOLOGY. CREDIT: MANALIS LAB, MIT The functionality of nanoparticles in a host of applications, including drug delivery and nano-optics, is often dictated by their mass and size. Measuring these properties simultaneously for the same nanoparticle has also been challenging. Now scientists from the...
Brain tissue inflammation is key to Alzheimer’s disease progression
UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH IMAGE: ASSISTANT PROFESSOR OF PSYCHIATRY AND NEUROLOGY, UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH SCHOOL OF MEDICINE. CREDIT: THARICK PASCOAL PITTSBURGH, Aug. 26, 2021 – Neuroinflammation is the key driver of the spread of pathologically misfolded proteins in the brain and causes cognitive impairment in patients with Alzheimer’s disease, researchers from the University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine reveal in a...
Malaria treatment shown to be 100% effective in Phase 2 trial
by Purdue University A repurposed cancer drug has been shown to be 100% effective in treating malaria in a Phase 2 clinical trial. Purdue University professor Philip Low led the international team that made the discovery. Credit: John Underwood A cancer drug repurposed to treat malaria has been shown to be nearly 100% effective in helping...