By Jocelyn Solis-Moreira Aug 26 2021 New research led by Devang K. Sanghavi of the Mayo Clinic in Florida, USA, suggests pre-intubation use of nitric oxide for patients with COVID-19–related hypoxemic respiratory may help reduce patients’ mortality. Their findings show that inhaling nitric oxide in this patient population could reduce the need for future intubation and other...
Human Genome at Super Resolution
A better understanding of the detailed structure, mechanism, and function of the human genome can illuminate biological mysteries about genetic function and yield important clues about the origins of genetic changes that give rise to dysfunction and disease. Such detailed understanding begins with the ability to see the entire genome in super-resolution at a maximum...
New Hope for Muscle-Related Diseases?
Investigators who previously developed a recipe for turning skin cells into primitive, muscle like cells that can be maintained indefinitely in the lab without losing the potential to become mature muscle have now uncovered how this recipe works and what molecular changes it triggers within cells. The research, led by Harvard Medical School scientists at Massachusetts...
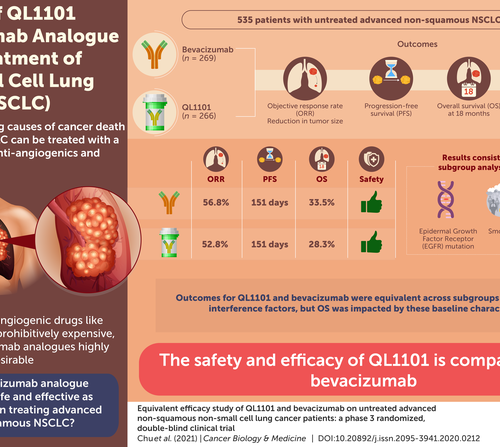
A cost-effective anti-angiogenic drug to treat lung cancer is finally here
New research shows that the QL1101, structurally similar to an existing cancer drug, is a safe and effective alternative for lung cancer treatment. In 2018, lung cancer caused 1.8 million cancer deaths worldwide. It is the most common type of cancer, with non-small cell lung cancers (NSCLCs) accounting for 85% of lung cancers. Most recent lung cancer research focuses...
Steerable Catheter to Navigate Tortuous Blood Vessels in Brain
AUGUST 25TH, 2021 CONN HASTINGS A team at University of California San Diego invented a way to make steerable catheters that can more precisely navigate the tortuous architecture of the brain vasculature. The device was bioinspired by delicate structures found in nature, including flagella and insect legs, and uses principles from soft robotics to create a...
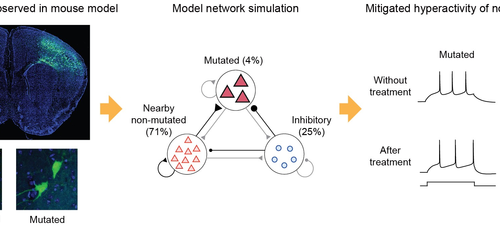
A mechanism underlying most common cause of epileptic seizures revealed
THE KOREA ADVANCED INSTITUTE OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY (KAIST) IMAGE: NEURONS CARRYING SOMATIC MUTATIONS IN MTOR LEAD TO FOCAL EPILEPTOGENESIS VIA NON-CELL AUTONOMOUS HYPEREXCITABILITY OF NEARBY NON-MUTATED NEURONS. (LEFT) NEURONS WITH MTOR MUTATION (GREEN) OBSERVED IN A MOUSE BRAIN SECTION IMAGE. (MIDDLE) NETWORK MODEL CONSISTING OF A SMALL PORTION OF MUTATED AND A LARGE PORTION...
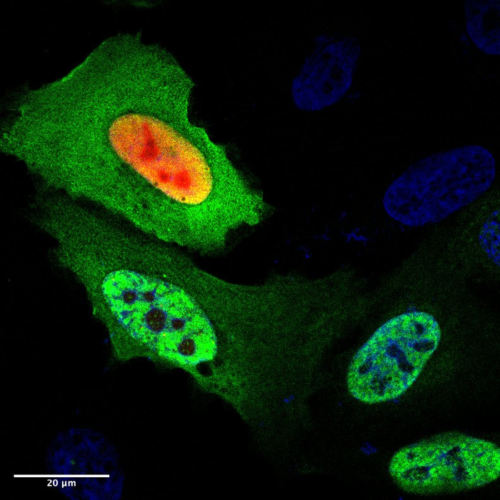
Restoring “chaperone” protein may prevent plaque build-up in Alzheimer’s
UNIVERSITY OF PENNSYLVANIA SCHOOL OF MEDICINE IMAGE: DAXX (RED COLOR AT TOP) PREVENTS THE AGGREGATION OF MUTANT P53 PROTEIN ASSOCIATED WITH CANCERS (DARK GREEN COLOR AT BOTTOM) IN CELLS. CREDIT: XIAOLU YANG, PHD PHILADELPHIA — For the first time, Penn Medicine researchers showed how restoring levels of the protein DAXX and a large group of...
A possible new treatment for osteoarthritis joint issues
by Tokyo Medical and Dental University Treatment of osteoarthritis by miRNA introduction. Credit: Department of Systems BioMedicine , TMDU Researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) identify a small RNA molecule with the potential to help slow cartilage deterioration in people living with osteoarthritis Osteoarthritis (OA) is a debilitating joint disease that affects millions of...
Why the dreaming phase matters
by University of Tsukuba Credit: Bilanol/Shutterstock Scientists have long wondered why almost all animals sleep, despite the disadvantages to survival of being unconscious. Now, researchers led by a team from the University of Tsukuba have found new evidence of brain refreshing that takes place during a specific phase of sleep: rapid eye movement (REM) sleep, which is when...
Team unveils widespread tumor suppression mechanism that stops cancer progression by interfering with cell metabolism
by The Wistar Institute Wistar’s Dr. Dario Altieri. Credit: The Wistar Institute According to a study by The Wistar Institute, the tumor suppressor Parkin, whose levels are reduced in different cancer types, causes acute metabolic and oxidative stress, suppresses mitochondrial trafficking, and blocks tumor cell movement, reducing primary and metastatic tumor growth. These findings, published today...