by Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine Credit: Pixabay/CC0 Public Domain Johns Hopkins Medicine researchers say they have added to evidence that the compound farnesol, found naturally in herbs, and berries, and other fruits, prevents and reverses brain damage linked to Parkinson’s disease in mouse studies. The compound, used in flavorings and perfume-making, can prevent the...
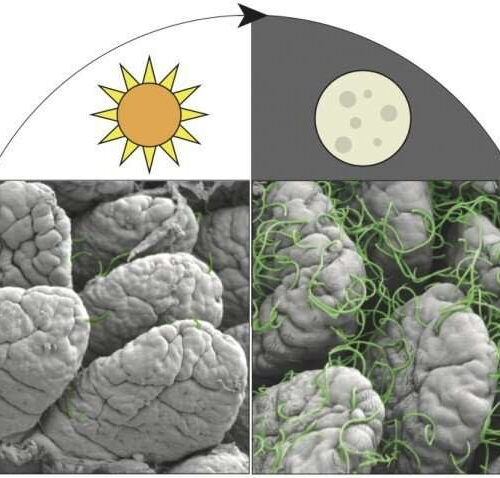
Fighting off food poisoning depends on the time of day
by UT Southwestern Medical Center Scanning electron micrograph shows segmented filamentous bacteria attaching to the intestinal surface of a mouse. More bacteria attach during the night than during the day. Credit: UT Southwestern Medical Center The body’s ability to prevent food poisoning by producing a natural antimicrobial compound increases during the day, when exposure to noxious...
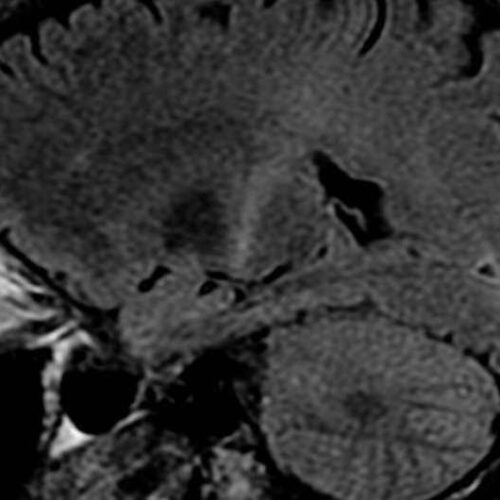
Researchers identify a cellular defect common to familial and sporadic forms of ALS
by National Institutes of Health An MRI with increased signal in the posterior part of the internal capsule can be tracked to the motor cortex consistent with the diagnosis of ALS. Credit: Frank Gaillard/Wikipedia Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) is a rapidly progressive and fatal degenerative disease affecting the nerve cells in the brain and spinal cord...
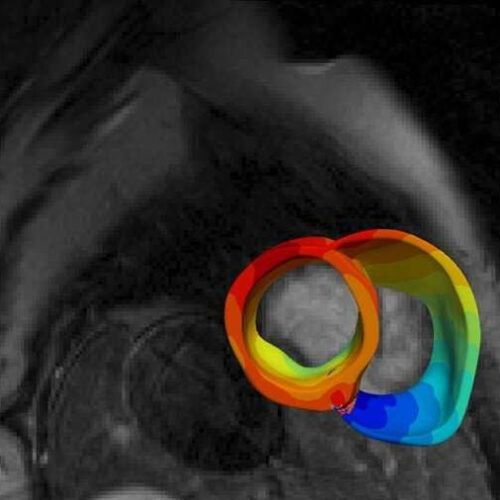
New tool predicts sudden death in inflammatory heart disease
by Johns Hopkins University A model of a patient’s heart is constructed from the MRI and PET scans. Color bands represent the electrical wave of the irregular heartbeat. Johns Hopkins scientists used data from the heart models to train their prediction algorithm. Credit: Johns Hopkins University Johns Hopkins University scientists have developed a new tool for...
The hunt for an antiviral pill to treat COVID-19 at home
By Rich Haridy July 27, 2021 Several novel antiviral pills to treat COVID-19 are currently being tested in humans photographee. EU/Depositphotos As the US Government invests billions of dollars into COVID-19 antiviral research, scientists are racing to develop a pill that people can take at home to treat the disease in its earliest stages. If last...
The overlooked superpower of mRNA vaccines
By Meredith Wadman Jul. 28, 2021, 10:45 AM Individuals facing the threat of COVID-19 may care most about a vaccine’s ability to forestall grave diseases that could lead to a hospital bed or worse. And a number of vaccines perform that vital task well, including those from Johnson & Johnson and AstraZeneca, which are based...
New composite material has potential for medical use
University of Georgia researchers have developed a new material with properties ideal for medical products such as masks and bandages. It’s also better for the environment than the materials in current use. Using nonwoven fabrics—fabrics produced by bonding fiber without weaving or knitting—the team led by Gajanan Bhat was able to make composite materials that are stretchable, breathable,...
Team creating insulin-producing implant for Type 1 diabetes
Rice University bioengineers are using 3D printing and smart biomaterials to create an insulin-producing implant for Type 1 diabetics. The three-year project is a partnership between the laboratories of Omid Veiseh and Jordan Miller that’s supported by a grant from JDRF, the leading global funder of diabetes research. Veiseh and Miller will use insulin-producing beta cells made from human stem cells...
Spinal Fluid Biomarkers Detect Neurodegeneration, Alzheimer’s Disease in Living Patients
Alzheimer’s disease and related diseases can still only be confirmed in deceased patients’ brains via autopsy. Even so, the development of biomarkers can give patients and their families answers during life: Alzheimer’s disease can be accurately detected via peptides and proteins in a patient’s cerebrospinal fluids (CSF), which can be collected through a lumbar puncture...
UC study: Researchers question prevailing Alzheimer’s theory with new discovery
Scientists at UC say restoring a brain protein, not removing amyloid plaques, should be the target Experts estimate more than 6 million Americans are living with Alzheimer’s dementia. But a recent study, led by the University of Cincinnati, sheds new light on the disease and a highly debated new drug therapy. Image credit: Pixabay (Free Pixabay...