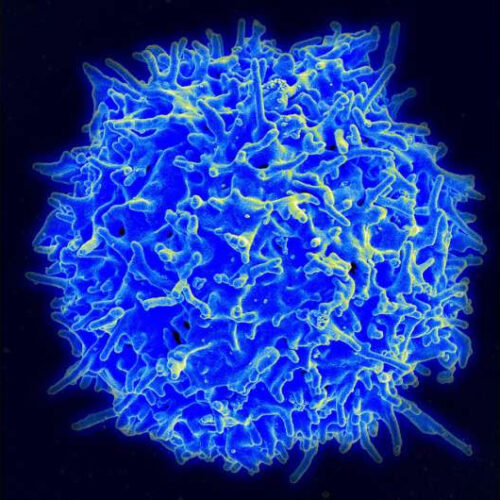
by Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center Scanning electron micrograph of a human T lymphocyte (also called a T cell) from the immune system of a healthy donor. Credit: NIAID In recent years, immune-based treatments for cancer have buoyed the hopes of doctors and patients alike. Drugs called immune checkpoint inhibitors have provided lifesaving benefits to a...
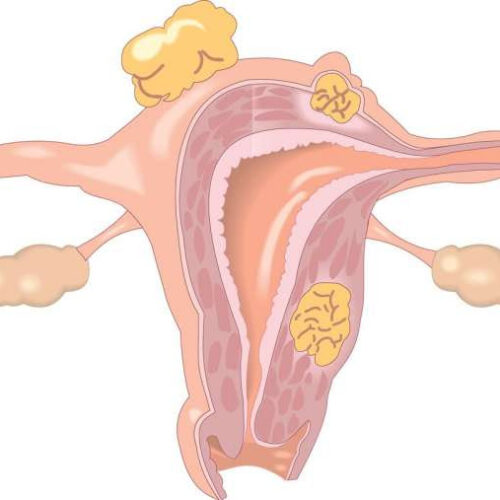
Researchers identify genetic cause of endometriosis and reveal potential drug target
by Baylor College of Medicine Credit: CC0 Public Domain Endometriosis is a painful, chronic condition in which tissue from the uterus inappropriately grows outside the uterus. Current treatments are limited and include surgery and hormone therapy, which can involve unwanted side effects. New research conducted by Baylor College of Medicine, the University of Oxford, the University of Wisconsin-Madison...
How migraines protect against diabetes
by American Chemical Society Credit: Sasha Wolff/Wikipedia People who get migraines are less likely to develop type 2 diabetes, while some people who develop diabetes become less prone to migraines. Today, scientists studying the link between these conditions report how the peptides that cause migraine pain can influence production of insulin in mice, possibly by regulating...
Complement protein Ba levels indicate transplant-associated thrombotic microangiopathy
by Osaka City University Thrombotic microangiopathy is a disease that clots the blood vessels around very important organs like the kidney and brain. Credit: Vector8DIY from pixabay.com Researchers discover a link between an increase in protein Ba of the complement immune system and the eventual development of thrombotic microangiopathy in patients who have received an allogeneic hematopoietic...
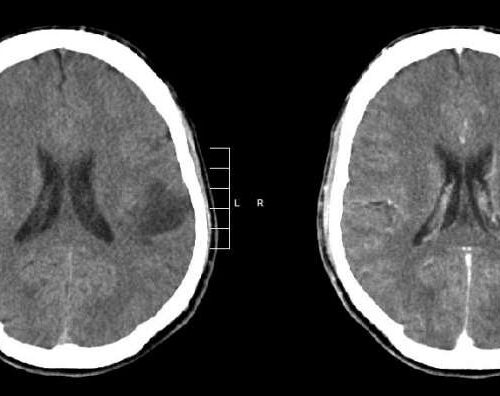
Uncovering epigenetic mechanisms regulating glioma growth
by Melissa Rohman, Northwestern University Glioma of the left parietal lobe. CT scan with contrast enhancement. Credit: Mikhail Kalinin/CC BY-SA 3.0 Northwestern Medicine investigators have discovered the epigenetic mechanisms involved in the regulation of multiple oncogenes in glioma cells, mechanisms that promote overall glioma tumor growth and resistance to therapy, according to a study published in...
Experimental chronic wound dressing made from human protein
The dressing could be applied to complex wounds such as venous ulcers, leg ulcers or foot ulcersFraunhofer IMWSVIEW 2 IMAGES If you’re trying to make a wound dressing that will be well-tolerated by the human body, you may be best off using human-derived materials. That’s the approach that German researchers have taken, creating a tropoelastin-based bandage. Tropoelastin...
The Immune System Should be a High Priority Target in the Development of Rejuvenation Therapies
The immune system has many roles. It doesn’t just destroy invading pathogens, but also hunts and kills potentially harmful cells, such as those that have become senescent or potentially cancerous. Further, immune cells are intricately involved in the processes of tissue maintenance. Regeneration from injury is a complicated dance of signals and changed states carried out between stem cells, immune cells,...
Research aims to improve health outcomes for pancreatic cancer patients
A Swinburne-led research team is exploring the use of a tiny implant that delivers chemotherapy directly into the tumour of a patient with pancreatic cancer. This device could hold the key to improving surgical outcomes for patients by shrinking the tumour so it can be safely removed. The proposed implant is part of a world-first project being...
New diabetes medication may reduce the chance of heart attacks and strokes
You need to take care of yourself in order to live a long and healthy life. But sometimes you needs some medicine to lower your risk of death. Scientists from the University of Glasgow have found that a new class of diabetes medications, called GLP-1 receptor agonists, can reduce the chance of heart attacks, strokes...
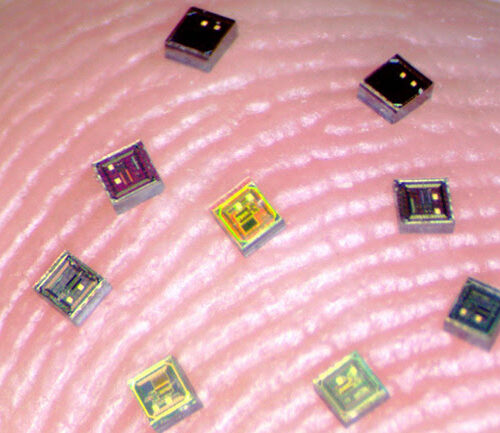
Tiny Neural Sensors for Brain Computer Interfaces
CONN HASTINGS NEUROLOGY, NEUROSURGERY Researchers at Brown University have developed wireless micro-implants that can function as a network of neural sensors and stimulators in the brain. The research team has dubbed their creation “neurograins,” which are intended to be implanted in the brain in large numbers. When inside, they can transmit data to an external communication hub, in the form...