by Denise Mann Healthday Reporter Nearly 1 in 5 people with hypertension may be unintentionally taking a drug for another condition that causes their blood pressure to climb even higher, a new study suggests. Left untreated or undertreated, high blood pressure will increase your risk for heart attack, stroke, kidney disease, and vision problems by...
Myelodysplasia, Clonal Hematopoiesis, and Aging
Asking whether an age-associated disease is a part of normal aging is an exercise in boundary drawing. The very definition of an age-related disease as something distinct from aging is the result of past boundary drawing. Many of these boundaries are quite arbitrary. Aging is a complex phenomenon, and people like to lay taxonomies on top...
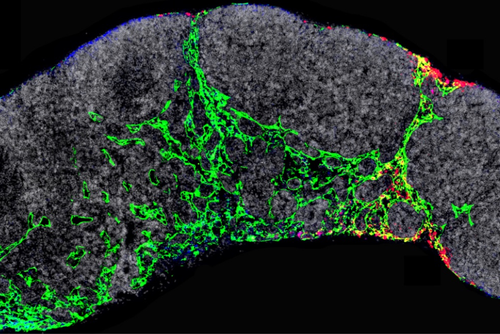
CNIO researchers discover a new mechanism involved in early melanoma metastasis
CENTRO NACIONAL DE INVESTIGACIONES ONCOLÓGICAS (CNIO) IMAGE: LYMPH NODE OF A MOUSE IN WHICH LYMPHATIC VESSELS (GREEN) AND TUMOR EXOSOMES (RED) THAT WILL DIRECT THE EARLY STAGES OF MELANOMA METASTASIS ARE VISUALIZED CREDIT: CNIO “We must not only look inside the tumour but also outside of it,” says Héctor Peinado, a researcher at the Spanish National...
International collaboration set to investigate new treatment strategy for lymphoma
QUEEN MARY UNIVERSITY OF LONDON An international collaboration involving researchers from Queen Mary University of London, Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center (MSK), New York, and Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Boston has secured a €1M research grant from Dutch blood cancer charity, Lymph&Co, to investigate a new treatment target for lymphoma. The aim of the project is...
Bench-to-bedside drug design could lead to new Alzheimer’s disease treatments
by University of Glasgow Credit: CC0 Public Domain An international team of scientists and pharmaceutical collaborators has made a breakthrough “bench to bedside” discovery, ten years in the making, which they hope will advance the future treatment of Alzheimer’s disease in patients. The research—conducted at the University of Glasgow and the biotechnology company Sosei-Heptares Ltd...
Hepatitis B virus can trigger genetic changes in liver cells years before cancer diagnosis
by The Francis Crick Institute Credit: CC0 Public Domain Researchers at the Francis Crick Institute and Universidade de Santiago de Compostela have identified how the hepatitis B virus (HBV) can support the survival and growth of liver cancer, with this process starting early in tumor development; in some instances up to 20 years before cancer...
How Roquin controls the activity of immune cells
by Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich Credit: Heissmeyer Group Ludwig Maximilians University Munich (LMU) immunologists have discovered how mutations in Roquin-1 trigger autoimmunity, but can also improve the body’s fight against cancer cells. With autoimmune diseases such as lupus erythematosus, severe inflammation occurs in different areas of the organism. The immune system mistakenly identifies the body’s own structures as...
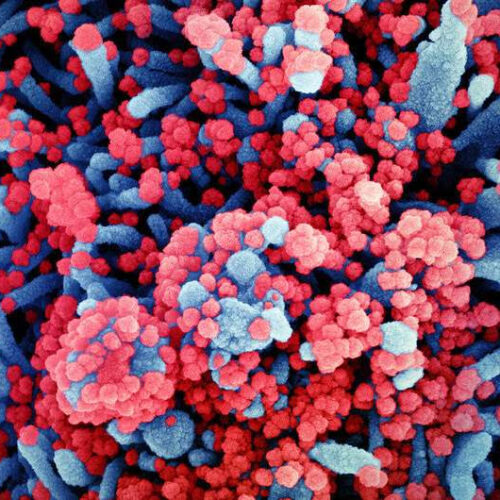
COVID-19 : Measuring viral RNA to predict which patients will die
by University of Montreal Colorized scanning electron micrograph of a cell (blue) heavily infected with SARS-CoV-2 virus particles (red), isolated from a patient sample. Image captured at the NIAID Integrated Research Facility (IRF) in Fort Detrick, Maryland. Credit: NIAID The amount of a SARS-CoV-2 genetic material—viral RNA—in the blood is a reliable indicator in detecting...
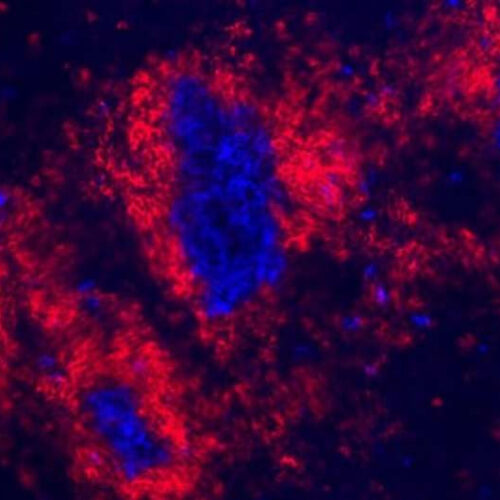
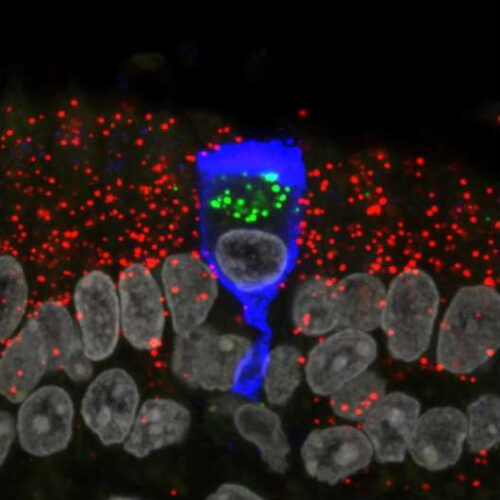
Researchers find that SARS-CoV-2 infects sustentacular cells in the olfactory epithelium of COVID-19 patients
by Max Planck Society A lone infected sustentacular cell is surrounded by non-infected cells in the olfactory mucosa of a COVID-19 patient who died four days after diagnosis of the infection. The infected cell has the characteristic shape of a wine glass. The blue color comes from staining with an antibody against the nucleocapsid protein...
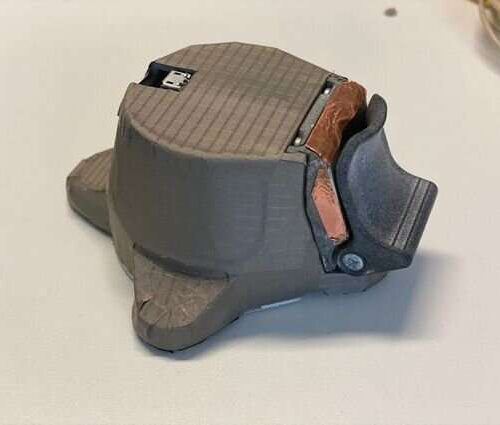
AI-assisted device could soon replace traditional stethoscopes
by Aalto University The device analyses bodily functions and offers the doctor probable diagnoses and suggestions for further examinations. Credit: Aalto University Stethoscopes are among doctors’ most important instruments, yet there have not been any essential improvements to the device since the 1960s. Now, researchers at Aalto University have developed a device that analyzes a...