by University of York Credit: Pixabay/CC0 Public Domain Scientists have identified unique “indicators” in the blood of patients with severe and fatal COVID, paving the way for simple diagnostic tests to help doctors identify who will go on to become critically ill. In a study led by researchers at the Hull York Medical School and...
Insight into COVID-19 brain complications
Interview conducted by Emily Henderson, B.Sc. Dec 21, 2021 Thought LeadersProfessor Scott H. FaroProfessor of Radiology and NeurologyThomas Jefferson University In this interview, we speak to Professor Scott H. Faro about his latest research that looked into COVID-19 and its complications within the central nervous system. Please could you introduce yourself, tell us about your...
New Alzheimer’s prevention trial in young people
Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis is launching an international clinical trial aimed at preventing Alzheimer’s disease in people genetically destined to develop the illness at a young age. Unlike most other Alzheimer’s prevention trials, this one will enroll people before the disease has taken hold — up to 25 years before the...
Old protein – new function: tBID can directly trigger cell death
UNIVERSITY OF COLOGNE The protein tBID can trigger programmed cell death (apoptosis) by inducing damage in the energy suppliers of the cells, the mitochondria. Apoptosis is essential for maintaining tissue balance. In addition, apoptosis plays a critical role as a defence mechanism and in the elimination of damaged or redundant cells in our bodies. Impaired...
Scientists are just starting to tease out the microbiome’s role in CAR-T outcomes among cancer patients
By Angus Chen Dec. 20, 2021 Reprints ADOBE As cancer-killing CAR-T cells course through the body, they make occasional pit stops at the gut. What they do there — and which gut microbes they meet up with — could potentially change the prospects of these engineered immune cells. Scientists are just beginning to tease apart the...
Anxiety in children and adolescents could lead to young adult psychosis
UNIVERSITY OF BIRMINGHAM Children and adolescents who show persistent high levels of anxiety are more likely to become psychotic in their early 20s, according to a new study. But treating early anxiety by targeting stress hormones and non-resolving inflammation during childhood and teenage years could help to reduce the risk of young adults going on...
Slowness of gait can predict risk of frailty in older people
Researchers at the Federal University of São Carlos (UFSCar) in the state of São Paulo, Brazil, in partnership with colleagues at University College London in the UK have discovered an efficient, simple and inexpensive method of predicting the risk of functional disability in older people. They analyzed data from more than 3,000 over-sixties living in...
Prescribe fewer antidepressants, and for shorter periods, doctors advised
by British Medical Journal Credit: Unsplash/CC0 Public Domain Doctors should prescribe fewer antidepressants and for shorter periods of time, because of the ongoing uncertainties about their effectiveness and the potential severity and durability of the withdrawal symptoms associated with them, suggests a review of the evidence on antidepressant use, published online in the Drug and Therapeutics Bulletin....
Can a dangerous microbe offer a new way to silence pain?
by Harvard Medical School Spores of the anthrax bacteria (Bacillus anthracis). Credit: CDC Anthrax has a scary reputation. Widely known to cause serious lung infections in humans and unsightly, albeit painless, skin lesions in livestock and people, the anthrax bacterium has even been used as a weapon of terror. Now the findings of a new study...
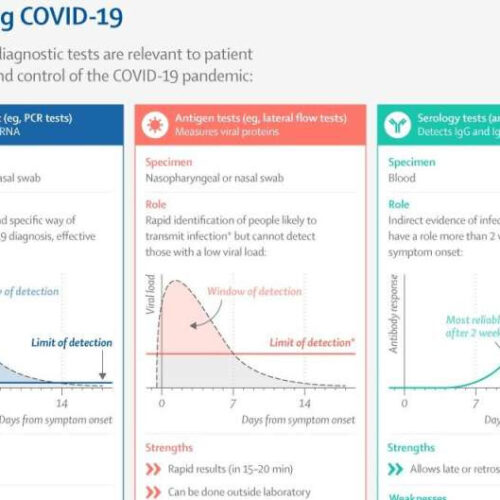
Infographic: COVID-19 diagnostic tests reviewed
by Lancet Credit: The Lancet Diagnostics have proven to be crucial to the COVID-19 pandemic response. A review in The Lancet evaluates the three major methods for the detection of SARS-CoV-2 infection and their role in managing the pandemic. This infographic provides a visual overview of the strengths and weaknesses of molecular (PCR), antigen (lateral flow), and serology...