UNIVERSITY OF PLYMOUTH Real-world tests have shown that gait authentication could be a viable means of protecting smartphones and other mobiles devices from cyber crime, according to new research. A study led by the University of Plymouth asked smartphone users to go about their daily activities while motion sensors within their mobile devices captured data...
Researchers find early developmental gene can cause deadly aneurysms
by Yale University Credit: CC0 Public Domain Mutations of a gene that regulates formation of blood vessels in the brain of vertebrates can lead to potentially deadly aneurysms in adults, Yale School of Medicine researchers report in the December issue of Nature Medicine. Saccular brain aneurysms affect nearly 3% of the human population. If they rupture,...
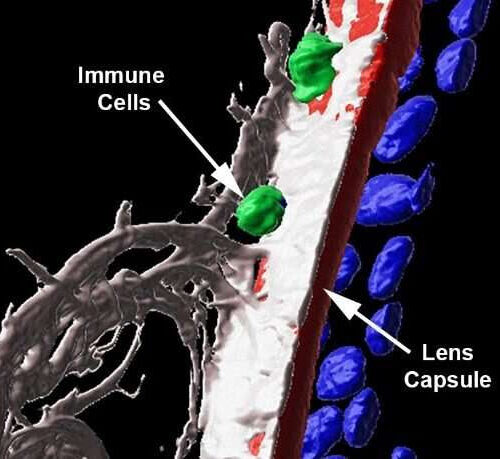
Immune cells could be doing much more than we think in protecting our eyes
by Karuna Meda, Thomas Jefferson University Credit: Thomas Jefferson University There’s a lot that our eyes have to protect themselves from—dust and debris; viruses and bacteria; chemicals from things we use every day like soaps and lotions; ultraviolet radiation from the sun; and hours of looking at computer screens or devices. Given all these potential...
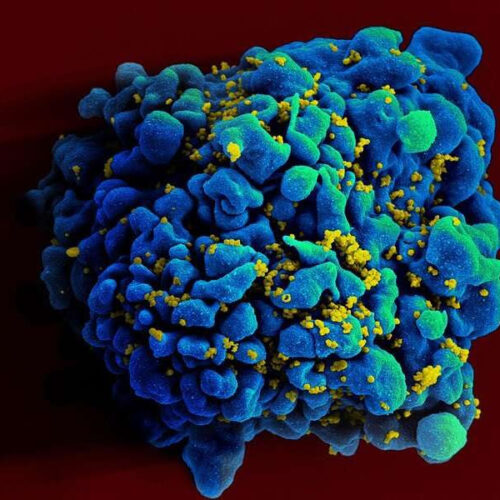
Experimental mRNA HIV vaccine safe, shows promise in animals
by NIH/National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases Scanning electromicrograph of an HIV-infected H9 T cell. Credit: NIAID An experimental HIV vaccine based on mRNA—the same platform technology used in two highly effective COVID-19 vaccines—shows promise in mice and non-human primates, according to scientists at the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), part...
Machine-learning system flags remedies that might do more harm than good
by Adam Zewe, Massachusetts Institute of Technology A new machine-learning system could give physicians risk scores for different treatments. Credit: Christine Daniloff, MIT Sepsis claims the lives of nearly 270,000 people in the U.S. each year. The unpredictable medical condition can progress rapidly, leading to a swift drop in blood pressure, tissue damage, multiple organ...
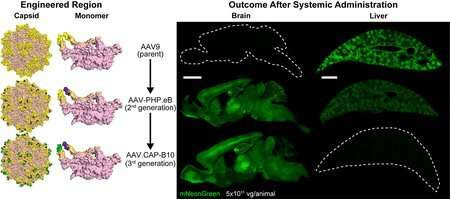
New technology is one step closer to targeted gene therapy
by Lori Dajose, California Institute of Technology Multiple sites of the AAV capsid are engineered to acquire brain specificity while being targeted away from the liver in mice after in vivo selection. On the left, the engineering sites on the AAV capsid and monomer are depicted in purple and green, while on the right transgene...
New biomarkers could predict rheumatoid arthritis susceptibility
by Washington State University Credit: Unsplash/CC0 Public Domain Cells from a cheek swab revealed biomarkers for rheumatoid arthritis that could lead to a way to diagnose and begin treatment before the disease develops, according to a study published in Scientific Reports. In the study, researchers from Washington State University and Arthritis Northwest in Spokane, Washington identified...
New FDA-approved eye drops could replace reading glasses for millions: “It’s definitely a life changer”
DECEMBER 9, 2021 / 10:14 AM / CBS NEWS A newly approved eye drop hitting the market on Thursday could change the lives of millions of Americans with age-related blurred near vision, a condition affecting mostly people 40 and older. Vuity, which was approved by the Food and Drug Administration in October, would potentially replace reading...
Elevated heart rate linked to increased risk of dementia
by Karolinska Institutet Yume Imahori, postdoc researcher at the Department of Neurobiology, Care Sciences, and Society, Karolinska Institutet. Credit: Stefan Zimmerman Having an elevated resting heart rate in old age may be an independent risk factor of dementia, according to a study at Karolinska Institutet in Sweden, published in the journal Alzheimer’s & Dementia: The Journal...
An illuminated 3D tour of lower back pain
Back pain affects many people at some point in their lives, and a common cause is damage to the squishy discs or flexible, rubbery tissues of the spine. However, observing this damage at an early stage is difficult with current imaging methods. Now, researchers reporting in ACS Nano can see microscopic soft tissue destruction in...