UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA – RIVERSIDE IMAGE: UC RIVERSIDE SCIENTISTS ARE TRYING TO FIND THE MOLECULAR BASIS OF POPULAR DIETS SUCH AS KETO AND INTERMITTENT FASTING. CREDIT: PIXABAY Scientists from UC Riverside are studying how the popular keto and intermittent fasting diets work on a molecular level, and whether both sexes benefit from them equally. The...
Eating disorder symptoms and self-harm linked to higher levels of depression and anxiety during COVID-19 pandemic
UNIVERSITY OF BRISTOL The study, led by the University of Bristol and funded by Elizabeth Blackwell Institute, Medical Research Council, and Medical Research Foundation, has been published in the Journal of Eating Disorders. It looked at questionnaire information for 2,657 individuals from world-renowned health study Children of the 90s (also known as the Avon Longitudinal...
Trigger found for harmful inflammation in lupus, macular degeneration
UNIVERSITY OF VIRGINIA HEALTH SYSTEM IMAGE: JAYAKRISHNA AMBATI, MD, IS PART OF THE UNIVERSITY OF VIRGINIA SCHOOL OF MEDICINE’S DEPARTMENT OF OPHTHALMOLOGY AND THE FOUNDING DIRECTOR OF UVA’S CENTER FOR ADVANCED VISION SCIENCE. CREDIT: COURTESY AMBATI LAB Researchers at the University of Virginia School of Medicine have made a discovery linking lupus, a potentially debilitating...
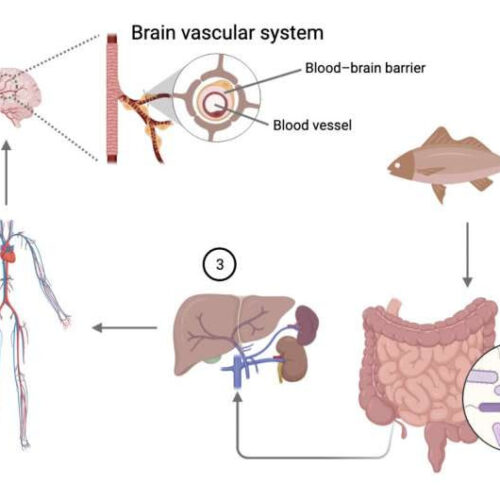
Molecule found in seafood plays role in protecting and improving cognitive function
by Nottingham Trent University The researchers have found that TMAO makes the blood-brain barrier less leaky. Credit: Nottingham Trent University Research at Nottingham Trent University and Queen Mary University of London investigated the role of trimethylamine N-oxide (TMAO) a molecule which is present in people’s diets and produced by the body during digestion of fish....
How the body uses fat to fight infection
by University of East Anglia Credit: Pixabay/CC0 Public Domain New research from the University of East Anglia and Quadram Institute reveals how our immune cells use the body’s fat stores to fight infection. The research, published today in the journal Nature Communications, could help develop new approaches to treating people with bacterial infections. The research team...
COVID-19 vaccine for kids ages five to 11: What families need to know
by Gillian Rutherford, University of Alberta Credit: Pixabay/CC0 Public Domain Ever since Canada approved the child-sized Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine against COVID-19 and started to distribute nearly three million doses, some parents have jumped at the chance to get their kids vaccinated, while others still have questions. “Even before it was approved, about 50 percent of parents...
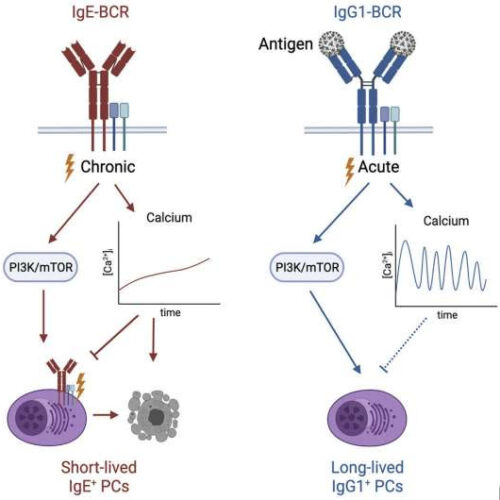
Scientists reveal how the body controls allergy-causing immune cells
by The Francis Crick Institute Graphical abstract. Credit: DOI: 10.1016/j.immuni.2021.11.006 Scientists at the Francis Crick Institute have uncovered biological processes key to regulating immune cells that can cause allergic reactions unless closely controlled. They hope this insight into an understudied aspect of our immune system could help expose what goes wrong when the body develops allergies or...
Buying a home? Research identifies 55 dangerous chemicals in building materials
by University of Michigan Credit: Pixabay/CC0 Public Domain The next time you purchase a new home, you might consider waiting a few weeks to move in. Many of the chemicals in a home’s building materials—in the scent of new carpet, the chalky smell of newly hung drywall, and of recently refinished floors—might not be great...
Pfizer/BioNTech says three doses ‘effective’ against Omicron
Credit: Pixabay/CC0 Public Domain Two doses of the BioNTech and Pfizer coronavirus vaccine may not be enough to protect against the Omicron variant, the companies warned Wednesday, but stressed it was “still effective” after a third jab. Omicron has caused global concern over signs that it can transmit faster than previous strains and fears that...
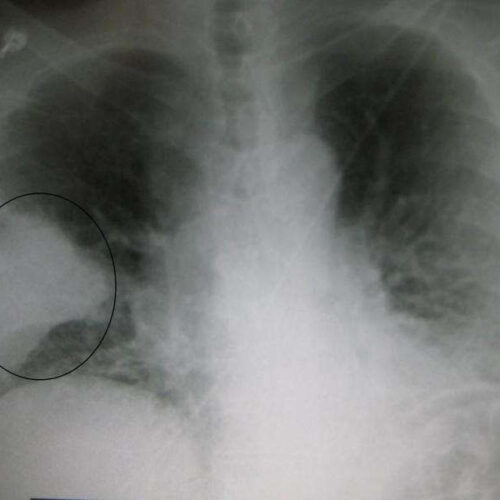
Study: Regular exercise reduces the risk of and death from pneumonia
by University of Bristol A black and white X-ray picture showing a triangular white area on the left side. A circle highlights the area. Credit: James Heilman, MD./Wikipedia People who exercise regularly can reduce their risk of developing and dying from pneumonia, new research has found. The study, led by the University of Bristol and...