DECEMBER 27TH, 2021 KENAN RADDAWI CARDIOLOGY, DIAGNOSTICS, EXCLUSIVE, SPORTS MEDICINE We have all been living through a life-altering pandemic. As a result, words such as “oxygenation” and “pulse oximetry” have become mainstream and the general public has increased the use of pulse oximeters. This should come as no surprise since hypoxia (i.e., low blood oxygen level)...
Fiber, FODMAP, micronutrient intake lower in patients with active IBD
(HealthDay)—Compared with individuals without inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), those with active IBD have lower intakes of fiber; fermentable oligosaccharides, disaccharides, monosaccharides, and polyols (FODMAP); and micronutrients, according to a study published in the December issue of the Journal of Crohn’s and Colitis. Selina R. Cox, Ph.D., from King’s College London, and colleagues estimated nutrient, fiber, and...
Immune response to seasonal coronaviruses may offer protection against COVID-19
by RIKEN Credit: Pixabay/CC0 Public Domain A research group led by Shin-ichiro Fujii of the RIKEN Center for Integrative Medical Sciences have found that individuals with a certain HLA type may be able to mount a killer T cell response to COVID-19, thanks to the T cells responding to a portion of the virus’s spike...
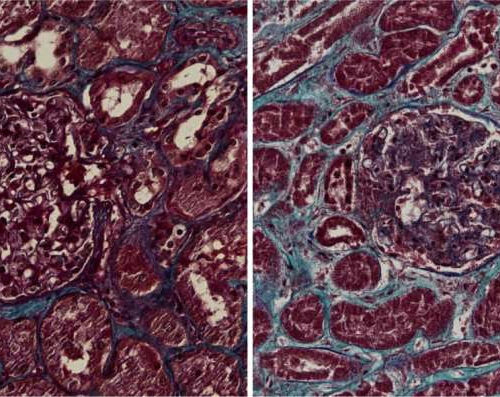
Kidney damage can result from coronavirus infection
by Radboud University Kidney sections from healthy control (left) and COVID-19 patient (right). Scar tissue is blue. Credit: Jitske Jansen and Bart Smeets, Radboudumc The coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 infects the kidneys and contributes to tissue scarring, as shown by researchers from the RWTH Uniklinik Aachen, Germany, and Radboudumc, The Netherlands. The developed scar tissue in the...
COVID-19 patients have severely increased levels of oxidative stress and oxidant damage, and glutathione deficiency
by Homa Shalchi, Baylor College of Medicine Credit: Pixabay/CC0 Public Domain Researchers at Baylor College of Medicine have investigated the effect of infection with COVID-19 on the levels of oxidative stress, oxidant damage, and glutathione, the most abundant physiological antioxidant. Compared to healthy age-matched individuals whose samples were taken before the pandemic started in 2019,...
A common risk factor for Alzheimer’s disease may predispose carriers to severe COVID-19
by University of Helsinki Credit: Pixabay/CC0 Public Domain A study conducted at the University of Helsinki and the Helsinki University Hospital (HUS) suggests that the APOE4 allele may also increase cerebral microhaemorrhages related to COVID-19 and associate with mental fatigue related to long COVID. Roughly one-third of Finns carry the APOE4 allele, a genetic variant that...
AAN issues guideline for treatment of painful diabetic neuropathy
by American Academy of Neurology Diabetic neuropathy refers to nerve damage due to diabetes and it may lead to pain and numbness, most often in the hands and feet. To help neurologists and other doctors determine the best treatment for people with diabetic neuropathy, the American Academy of Neurology (AAN) has issued a guideline on...
Flu is making a comeback in US after an unusual year off
by Carla K. Johnson Registered nurse Megan Chamberlain gives a flu shot to Anthony Devitt, of Marlboro, Vt., during a flu vaccine clinic on Route 9, in Brattleboro, Vt., that was hosted by Visiting Nurse and Hospice for Vermont and New Hampshire on Tuesday, Oct. 26, 2021. Credit: Kristopher Radder/The Brattleboro Reformer via AP, File...
BOOSTERS MAY BE VITAL FOR OMICRON PROTECTION
The Omicron variant is more prone to escape antibodies produced after vaccination or an infection than previous variants of SARS-CoV-2. As the world faces an impending wave of COVID cases due to Omicron, scientists are racing to assess vaccine efficacy against the new variant. In a new study, scientists report on their comprehensive analysis of...
Constant changes in COVID-19 safety guidelines cause distrust and suspicion
COVID-19 safety guidelines can only do their job if people trust them. If people find themselves pondering about the base of those guidelines, they are likely to distrust them and start thinking about withdrawing from collective efforts to stop the spread of COVID-19. Scientists in Canada and the United States found that frequent changes in...