As the number of people who have fought off SARS-CoV-2 climbs ever higher, a critical question has grown in importance: How long will their immunity to the novel coronavirus last? A new Rockefeller study offers an encouraging answer, suggesting that those who recover from COVID-19 are protected against the virus for at least six months,...
Year: <span>2021</span>
New research could lead to more treatment options for diabetes patients
For the first time, scientists have come up with a precise atomic-level explanation for why glulisine- a commonly used medication to treat diabetes- is faster acting than insulin. The findings, published in Scientific Reports, could have benefits for diabetes patients in ensuring that more improved insulin can be developed for future treatment. Image credit: Reversing Your...
An Example of High Dose Fisetin Exhibiting Senolytic Effects in Mice
Fisetin is perhaps the most intriguing of the first generation senolytic compounds, those capable of selectively destroying senescent cells in old tissues and thus producing rejuvenation to a meaningful degree. Senolytics have been demonstrated in animal studies to reverse many age-related conditions to a greater degree than any other approaches. Why is fisetin intriguing? Because in mice, it appears to be about...
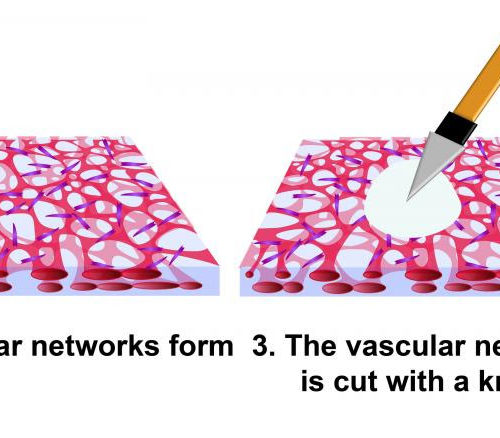
New insights into wound healing process
AMERICAN INSTITUTE OF PHYSICS IMAGE: Biomedical engineers have developed a technique to observe wound healing in real time, discovering a central role for cells known as fibroblasts. The work is the first demonstration of a wound closure model within human vascularized tissue in a petri dish. This image shows steps in wound healing in a...
New drug combination shows promise as powerful treatment for AML
SANFORD BURNHAM PREBYS MEDICAL DISCOVERY INSTITUTE IMAGE: PETER ADAMS, PH.D., PROFESSOR IN THE TUMOR INITIATION AND MAINTENANCE PROGRAM AT SANFORD BURNHAM PREBYS’ NCI-DESIGNATED CANCER CENTER. CREDIT: SANFORD BURNHAM PREBYS MEDICAL DISCOVERY INSTITUTE LA JOLLA, CALIF. – Jan 20, 2020 – Scientists have identified two drugs that are potent against acute myeloid leukemia (AML) when combined,...
Why You Still Need to Wear a Mask After Getting the COVID-19 Vaccine
by Mandy Armitage, MD, January 13,2021 Key takeaways: You should still wear your mask and keep your distance from others after you have been vaccinated. We don’t know yet how well the COVID-19 vaccines reduce the spread of the virus. Almost 9 million people in the U.S. have received at least one dose of a COVID-19 vaccination,...
Nicotine promotes breast cancer lung metastasis, finds study
Reviewed by Emily Henderson, B.Sc. Jan 21 2021 Breast cancer is the second most common cancer among women in the United States, and cigarette smoking is associated with a higher incidence of breast cancer spread, or metastasis, lowering the survival rate by 33% at diagnosis. While cigarette smoking’s link to cancer is well-known, the role...
Research establishes antibiotic potential for cannabis molecule
UNIVERSITY OF QUEENSLAND IMAGE: BACTERIA GROWING IN THE SHAPE OF THE SYNTHETIC CANNABIDIOL MOLECULE. CREDIT: INSTITUTE FOR MOLECULAR BIOSCIENCE, UNIVERSITY OF QUEENSLAND. Synthetic cannabidiol, better known as CBD, has been shown for the first time to kill the bacteria responsible for gonorrhoea, meningitis and legionnaires disease. The research collaboration between The University of Queensland and Botanix Pharmaceuticals Limited could lead to...
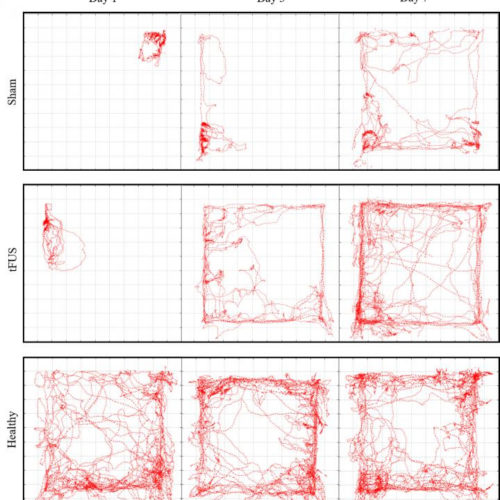
Nonsurgical treatment for cerebral infarction using wearable wireless ultrasound devices
NATIONAL RESEARCH COUNCIL OF SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY IMAGE: REPRESENTATIVE TRAJECTORIES FOR STROKE MODEL RATS TREATED WITH SHAM AND TFUS, COMPARED TO A HEALTHY RAT (BOTTOM ROW) CREDIT: KOREA INSTITUTE OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY(KIST) Cerebral infarction, commonly known as ischemic stroke, has a high mortality rate and causes severe damage to nervous cells in the brain owing to...
Ultra-small nanomedicines which stably deliver oligonucleotides to refractory cancers
INNOVATION CENTER OF NANOMEDICINE Summary Ultra-small nanomedicines of approximately 18 nm were fabricated by dynamic ion-pairing between Y-shaped block copolymers and nucleic acid drugs, such as siRNA and antisense drugs. Chemically modified and double-stranded oligonucleotides dramatically enhanced the stability of the ultra-small nanomedicines in the blood circulation. The ultra-small size allows for high permeability in...