POSTED BY SARALYN CRUICKSHANK-JOHNS HOPKINS COVID-19 vaccines have been the subject of speculation and anticipation for months—so why hasn’t the US made more progress on vaccination? It’s been three weeks since the COVID-19 vaccines began arriving at hospitals, clinics, and pharmacies. Operation Warp Speed—the US vaccination development, testing, and distribution effort—had made 20 million vaccine...
Year: <span>2021</span>
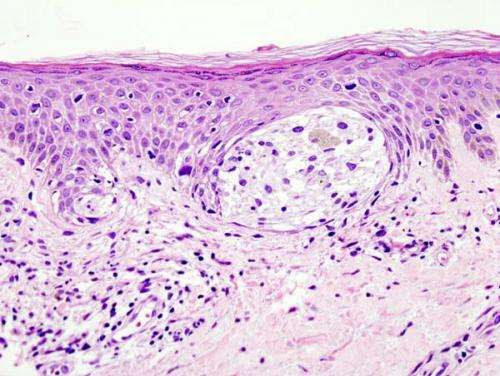
Research explores how melanoma grows and spreads
by Texas A&M University Melanoma in skin biopsy with H&E stain — this case may represent superficial spreading melanoma. Credit: Wikipedia/CC BY-SA 3.0 The first step in treating cancer is understanding how it starts, grows and spreads throughout the body. A relatively new cancer research approach is the study of metabolites, the products of different steps...
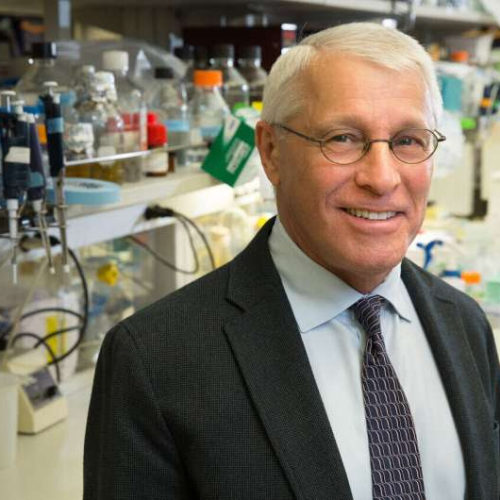
High doses of saccharin don’t lead to diabetes in healthy adults, study finds
by The Ohio State University Researchers at The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center conducted a study expecting to confirm how artificial sweeteners contribute to glucose intolerance, but surprisingly learned that the sweeteners have no adverse effects on healthy adults and do not change metabolic profiles or lead to diabetes. Credit: The Ohio State University Wexner Medical...
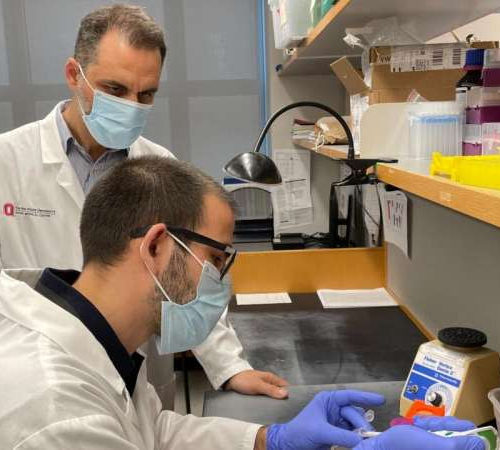
Scientists develop method to more efficiently isolate and identify rare T cells
by University of California, Los Angeles Dr. Owen Witte, MD. Credit: UCLA Broad Stem Cell Research Center Scientists from the Eli and Edythe Broad Center of Regenerative Medicine and Stem Cell Research at UCLA have developed a technique that will enable researchers to more efficiently isolate and identify rare T cells that are capable of targeting viruses, cancer and other diseases. The...
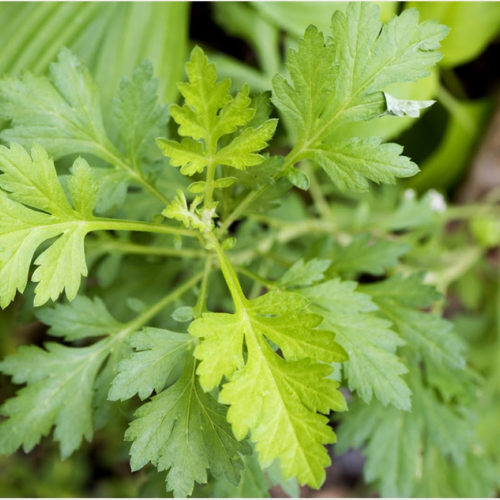
Extract of medicinal plant Artemisia annua interferes with replication of SARS-CoV-2 in vitro
By Sally Robertson, B.Sc. Jan 11 2021 Researchers in the United States have shown that extracts of an aromatic herb called Artemisia annua inhibit the replication of severe acute respiratory coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) – the agent responsible for the current coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic. Also known as “Sweet wormwood,” Artemisia annua (A. annua) is an herb from Asia that produces...
Nanomaterials for the Clearance of Senescent Cells
Senescent cell accumulation is a contributing cause of aging, and targeted destruction of senescent cells with senolytic therapies produces meaningful rejuvenation and reversal of age-related disease in animal models. First generation senolytics are largely repurposed small molecules. Second generation senolytics will include a range of more carefully designed strategies, including the nanoparticles allowing for selective...
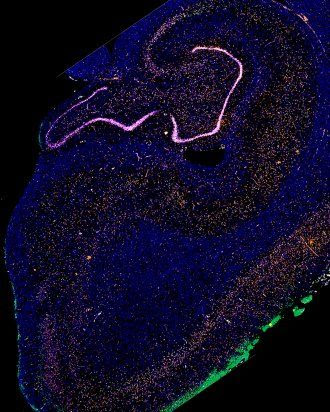
Brain Cells Most Vulnerable to Alzheimer’s Disease Identified by Scientists
A major mystery in Alzheimer’s disease research is why some brain cells succumb to the creeping pathology of the disease years before symptoms first appear, while others seem impervious to the degeneration surrounding them until the disease’s final stages. Now, in a study published in Nature Neuroscience, a team of molecular biologists and neuropathologists from the UCSF Weill Institute for...
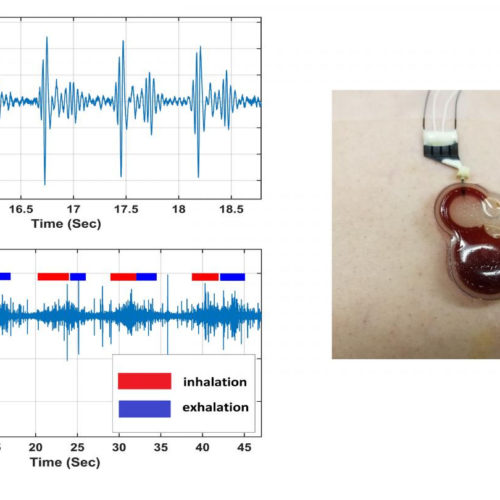
Wearable electronics for continuous cardiac, respiratory monitoring
AMERICAN INSTITUTE OF PHYSICS IMAGE: A small and inexpensive sensor, announced in Applied Physics Letters and based on an electrochemical system, could potentially be worn continuously by cardiac patients or others who require constant monitoring. Right: Wearable sensor attached to a patient’s chest. Left top: Heartbeat signal acquired from the sensor. Left bottom: Acquired breathing...
Tissue stiffness likely drives immune responses in many chronic diseases
BUCK INSTITUTE FOR RESEARCH ON AGING Stiffness in our tissues causes tension in our cells. Research from the Buck Institute, the University Health Network (University of Toronto), Stanford University, and the University of Alberta shows that stiffness impacts the innate immune system by upping its metabolism. The findings suggest the cellular tension likely sets off an inflammatory loop that...
New small antibodies show promising effects against COVID-19 infection
KAROLINSKA INSTITUTET Researchers at Karolinska Institutet in Sweden have developed, in collaboration with researchers in Germany and the U.S., new small antibodies, also known as nanobodies, which prevent the SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus from entering human cells. The research study, published in Science, shows that a combined nanobody had a particularly good effect – even if the virus mutated. According to the researchers, the...