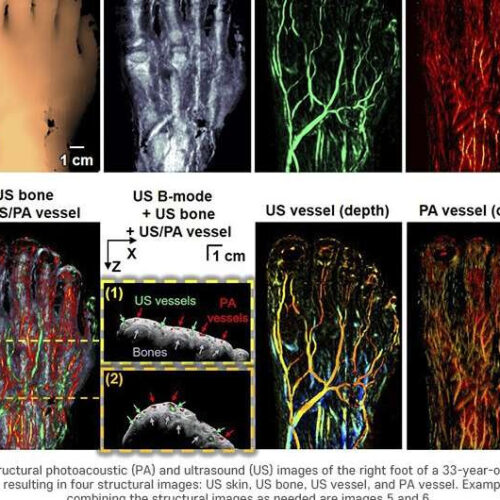
by Pohang University of Science and Technology Credit: Pohang University of Science and Technology The body is like a sophisticated network with a myriad of peripheral blood vessels connected from the heart to the extremities. If blood fails to pass through these peripheral blood vessels, a wound may not heal or even lead to necrosis....
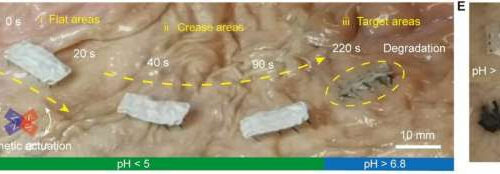
Nanofiber-based biodegradable millirobot that can release drugs in targeted positions in the intestines
by City University of Hong Kong Driven by magnetic force, Fibot moves in a pig’s stomach and is then degraded at the targeted position. Credit: Matter A nanofiber-based biodegradable millirobot called Fibot was successfully developed in research led by a scholar from City University of Hong Kong (CityU). Fibot can move in the intestines and degrade...
Sex matters in biomedical research: Many conditions affect men and women differently
by Monica de Paoli, The Conversation Until recently, most biomedical studies did not consider sex or gender. Credit: Pexels/Magda Ehlers Biomedical research—a broad term covering studies on subjects ranging from cells to experimental animal models—is the starting point for understanding how diseases develop and how we might prevent or treat them. Once such studies have...
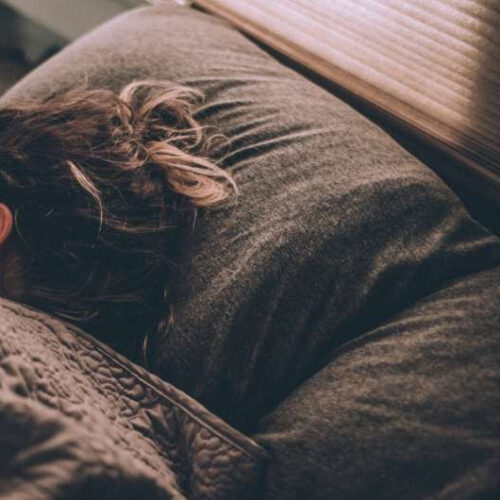
New sleep molecule discovered: ‘It shows just how complex the machinery of sleep is’
by University of Copenhagen Credit: Unsplash/CC0 Public Domain When brain scientist Birgitte Kornum from the Department of Neuroscience recently arrived in Rome for one of the largest sleep conferences in the world, she was completely taken aback. There were pharmaceutical companies everywhere—with stands, information material and campaigns. They all wanted to treat daytime sleepiness or to turn...
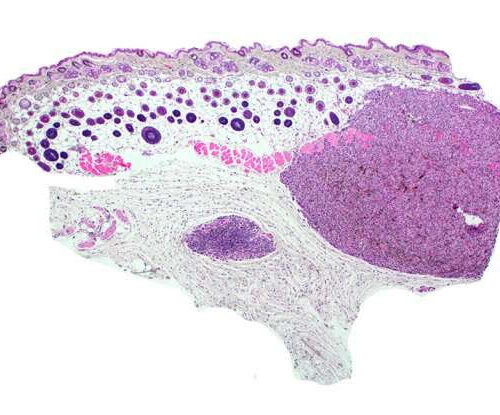
Researchers use CRISPR to build melanoma models from scratch using human cells
by Allessandra Dicorato, Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard A histology image of a melanoma model. Credit: Science (2022). DOI: 10.1126/science.abi8175 By introducing cancer-causing mutations into healthy skin cells step-by-step, Broad scientists have created models of skin cancer that can reveal the effects of mutations. Over the last two decades, researchers have discovered thousands of genetic mutations in cancer, but...
Osteoarthritis: Realigning bad knees may prompt the body to generate cartilage again
by Delthia Ricks, Medical Xpress Credit: CC0 Public Domain Osteoarthritis is a wear-and-tear disorder marked by bone thickening and cartilage degeneration, an excruciatingly painful disability and a major cause of impaired mobility as people age. But scientists have begun viewing this form of arthritis differently with a deeper understanding of the disorder’s causes and an...
Scientists prove diseased blood vessels communicate with the brain
An international team that includes University of Manchester scientists has demonstrated that nerve signals are exchanged between clogged-up arteries and the brain for the first time. The discovery of the previously unknown electrical circuit is a breakthrough in our understanding of atherosclerosis, a potentially deadly disease where plaques form on the innermost layer of arteries. The mice...
Why a Certain Plant Virus Is So Powerful at Fighting Cancer
A plant virus that infects legumes, called cowpea mosaic virus, has an extraordinary power that you may not have known about: when injected into a tumor, it triggers the immune system to treat cancer—even metastatic cancer prevents it from recurring. For the past seven years, researchers at the University of California San Diego and Dartmouth College...
Seven hours of sleep is optimal in middle and old age, say, researchers
Sleep plays an important role in enabling cognitive function and maintaining good psychological health. It also helps keep the brain healthy by removing waste products. As we get older, we often see alterations in our sleep patterns, including difficulty falling asleep and staying asleep and decreased quantity and quality of sleep. It is thought that these...
New drug shows promise slowing tumour growth in some hard-to-treat cancers
Scientists at Sinai Health and the University of Toronto say a new drug designed to block an enzyme essential for the survival of specific cancer cells shows promise in curbing tumor growth. The preclinical findings, published in the journal Nature, describe a new drug designed with CRISPR-Cas9 gene-editing technology in the lab of Daniel Durocher, a senior investigator...