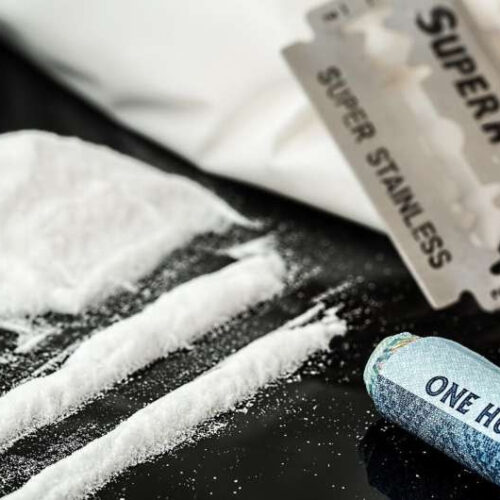
by Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine Credit: CC0 Public Domain Scientists have long known that cocaine works by latching on to molecular connectors on the surface of brain cells, allowing dopamine, a chemical that promotes feelings of pleasure and reward, to accumulate in the space between brain cells. Now, Johns Hopkins Medicine scientists say...
Flower nectar offers new weapon against Leishmaniasis
by Sanjeet Bagcchi, SciDev.Net Thyme is another plant that has floral nectars that contain bioactive flavonoids at concentrations that inhibit growth of diverse Leishmania in vitro. Credit: Jörg Keller (Pixabay) The nectar of common plants such as sunflower contain bioactive agents that can inhibit the growth of Leishmania and could be used to help fight the potentially...
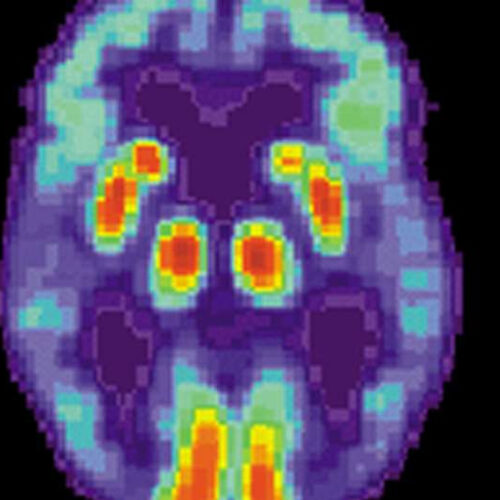
Experimental drug reverses synaptic loss in mouse models of Alzheimer’s
by Bill Hathaway, Yale University PET scan of a human brain with Alzheimer’s disease. Credit: public domain An experimental drug restored brain synapses in two mouse models of Alzheimer’s disease, raising hopes that it could help revive cognitive function in human dementia patients, Yale University researchers report June 1 in the journal Science Translational Medicine. While...
Promising compound kills range of hard-to-treat cancers by targeting a previously undiscovered vulnerability
by University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio Credit: Unsplash/CC0 Public Domain A compound, developed by a team including scientists from The University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio, kills a range of hard-to-treat cancer types in petri dishes and animal models by targeting a previously unexploited vulnerability, a new study...
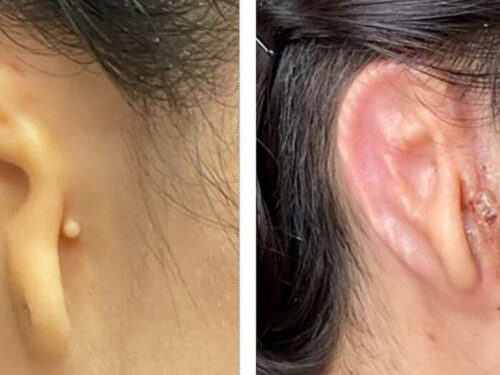
Doctors Transplant 3-D Printed Ear Made of Human Cells
June 2, 2022 in News A 20-year-old woman who was born with a small and misshapen right ear has received a 3-D printed ear implant made from her own cells, the manufacturer announced on Thursday. Independent experts said that the transplant, part of the first clinical trial of a successful medical application of this technology,...
Mutant gene stops at-risk people from getting Alzheimer’s: Could it lead to treatment?
by Dennis Thompson The APOE4 gene is the most powerful genetic factor driving a person’s risk for developing late-onset Alzheimer’s disease. “It probably increases your risk two or threefold if you have one APOE4 copy, and if you have two APOE4 copies, it probably increases your risk about tenfold,” said Dr. Michael Greicius, a professor of...
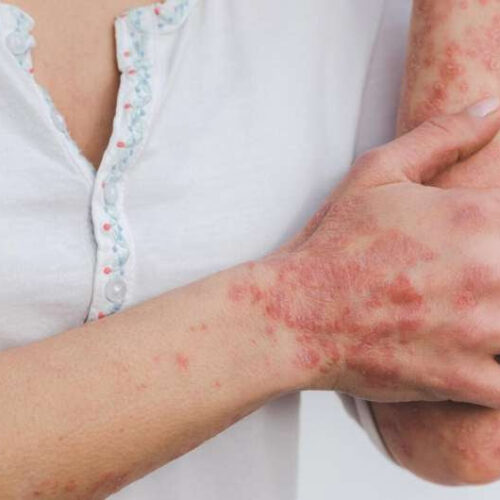
Psoriasis tied to higher risk for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
Credit: Estzer Miller on Pixabay Psoriasis is associated with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) in a U.S. outpatient population, according to a study published May 25 in JAMA Dermatology. Zhijie Ruan, M.Med., from the First Affiliated Hospital of Shantou University Medical College in China, and colleagues used data from 5,672 U.S. adults (aged 20 to 59...
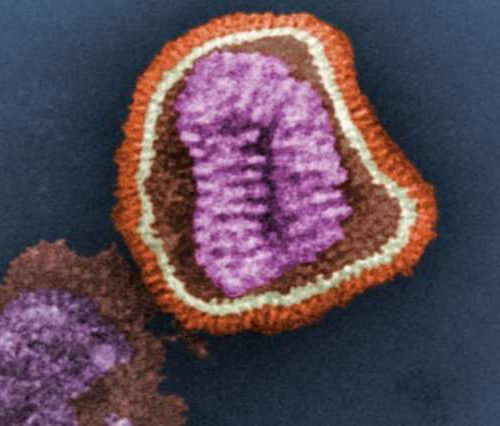
No more flu for you? Discovery blocks influenza virus’ replication in cells
by Holly Ober, University of California – Riverside This digitally-colorized transmission electron microscopic image depicts the ultrastructural details of an influenza virus particle. Credit: CDC, Frederick Murphy It happens every year, especially in winter. A virus saunters into your wide-open respiratory tract, worms its way into lung cells, and, next thing you know, you’re lying...
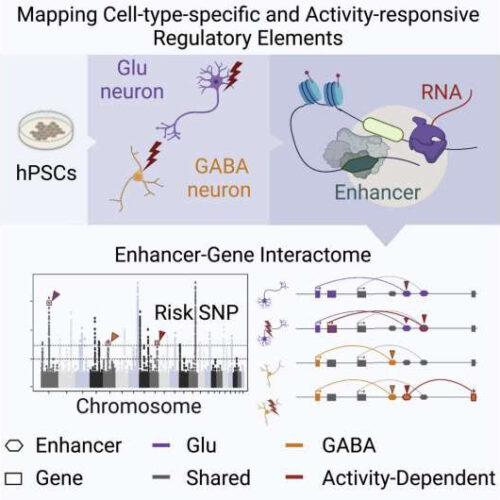
A stem cell model could help unravel the complex biology behind some psychiatric disorders
by The Mount Sinai Hospital Graphical abstract. Credit: Cell Reports (2022). DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2022.110877 Researchers from the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai have applied a novel stem cell model to map disease risk variants in human neurons, which could help provide insights into the biological mechanisms that underlie neuropsychiatric disorders such as autism and schizophrenia. The...
A surprising way to tamper with ugly ‘Dark Triad’ personality traits
by Southern Methodist University Credit: CC0 Public Domain Want to be less selfish, manipulative or impulsive? A new study has found that tasks designed to make someone more agreeable also effectively reduce a trio of negative personality traits known as the “Dark Triad”—Machiavellianism, narcissism, and psychopathy. SMU psychology professor Nathan Hudson’s study showed that practicing activities like “donating...