Carrying a child to term is a miracle of motherhood. A lot of women struggle to get pregnant and carry their babies to term. And now scientists at the University of Queensland found that women with a history of miscarriage and stillbirth have a higher risk of stroke in later life. There are women who...
New structure found in cells
Every cell contains millions of protein molecules. Some of them have the ability to phase-separate to form non-membrane-bound compartments, called biomolecular condensates, inside a cell. It has long been assumed that there was no further structure underlying these condensates, only solution-soluble proteins. A research group led by Rohit Pappu, the Gene K. Beare Distinguished Professor of biomedical...
Physical therapy noninferior to arthroscopic surgery for meniscal tear
Exercise-based physical therapy is noninferior to arthroscopic partial meniscectomy for patient-reported knee function at five years among patients with a degenerative meniscal tear, according to a study published online July 8 in JAMA Network Open. Julia C.A. Noorduyn, from OLVG Amsterdam, and colleagues compared the five-year effectiveness of arthroscopic partial meniscectomy and exercise-based physical therapy in 321...
Unexpected link between most common cancer drivers may yield more effective drugs
Two of the most common genetic changes that cause cells to become cancerous, which were previously thought to be separate and regulated by different cellular signals, are working in concert, according to new research from the University of Wisconsin–Madison. To date, researchers have focused on finding drugs that block one or the other to treat cancer. Understanding...
Cancer May Increase Risk of Type 2 Diabetes
Alicia Ault June 27, 2022 A large Danish study has found that cancer increases the risk of new-onset type 2 diabetes, especially certain types of cancer, most notably pancreatic malignancies. “Our study demonstrates that there is an elevated risk of developing diabetes if a person is affected by lung, pancreatic, breast, brain, urinary tract, or uterine...
Changes in Alzheimer biomarkers tied to withdrawal of positive airway pressure for obstructive sleep apnea
For patients with severe obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), withdrawal of positive airway pressure (PAP) is associated with changes in plasma Alzheimer disease biomarkers, according to a study published online June 13 in the American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine. Korey Kam, Ph.D., from the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York...
In Colitis Patients, Skin Conditions May Originate in the Gut
A new study by UC San Francisco researchers reveals how gut inflammation can disrupt not only the digestive system, but also the skin. It’s a tale in which the main players are specialized immune cells and the bacterial communities – called microbiomes – that dwell within the gut and skin. Scientists have become increasingly aware that disturbances to the...
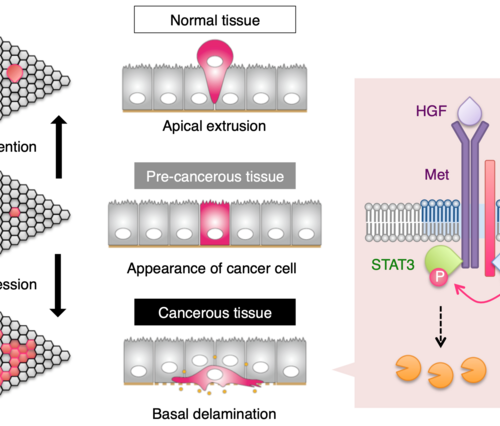
Breakthrough in study of how epithelial cells become cancerous
OSAKA UNIVERSITY IMAGE: MOLECULAR MECHANISM OF ESCAPE FROM APICAL EXTRUSION DURING CELL COMPETITION. CREDIT: 2022 KAJIWARA ET AL., SRC ACTIVATION IN LIPID RAFTS CONFERS EPITHELIAL CELLS WITH INVASIVE POTENTIAL TO ESCAPE FROM APICAL EXTRUSION DURING CELL COMPETITION , CURRENT BIOLOGY Osaka, Japan – Epithelial cells, which line the surfaces and organs of the body, can...
Adults with blood cancers respond to booster, not initial dose of COVID-19 vaccine
WILEY People with hematologic malignancies—or blood cancers including leukemia, lymphoma, and multiple myeloma—have an impaired immune system due to their disease and its treatment, putting them at risk of severe COVID-19 infection and experiencing a reduced response to COVID-19 vaccination. In a recent study published by Wiley online in CANCER, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Cancer Society,...
Drinking alone foreshadows future alcohol problems
CARNEGIE MELLON UNIVERSITY A new study from Carnegie Mellon University found that drinking alone during adolescence and young adulthood strongly increases risk for alcohol use disorder (AUD) later in life. This risk is especially high for women. The results are available in the July issue of the journal Drug and Alcohol Dependence. “Most young people who...