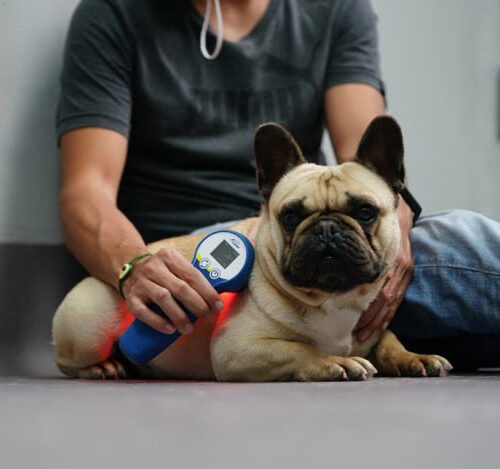
Experimentation helped demystify, legitimize, and simplify medical uses for long-known but little-understood light therapy. Can light help a wound heal faster? Alleviate pain? Prevent loss of eyesight? Multi Radiance Medical’s line of light-therapy devices, combining LED and super-pulsed laser light, includes products specially designed for use on animals. Credit: Iker Asteinza Castro/Animal Home Veterinary Hospital Although...
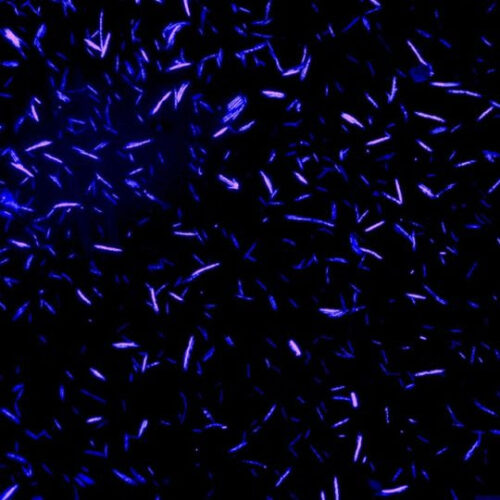
Study identifies gut bacteria that regulate cholesterol
Certain species of bacteria in the gut interact with and help balance levels of dietary cholesterol by using it to create a molecule that plays important roles in human health, according to a study published in Nature Microbiology. This microscope image shows gut microbes that use dietary cholesterol for their own metabolism (red) vs. non-interacting microbes (blue)....
Microneedling beats chemical peels for acne scar treatment
RUTGERS UNIVERSITY Chemical peels are a common treatment for acne scars, but a Rutgers study finds that microneedling is significantly more effective for patients with dark skin. Babar Rao, a professor of dermatology and pathology at Robert Wood Johnson Medical School, and fellow researchers randomly assigned 60 patients with acne scars and dark skin — Fitzpatrick Skin...
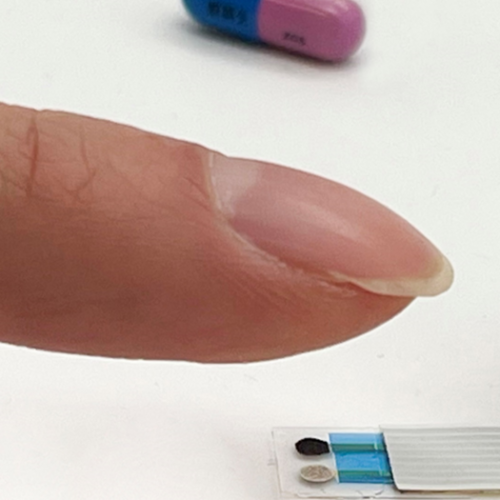
Sensor could help patients stay on top of their meds
AMERICAN CHEMICAL SOCIETY IMAGE: A TINY, TOUCH-BASED SENSOR USES SWEAT TO DETECT THE LEVEL OF LITHIUM IN THE BODY. CREDIT: JIALUN ZHU AND SHUYU LIN CHICAGO, Aug. 21, 2022 — Lithium can alleviate the symptoms of bipolar disorder and depression — if taken in just the right amount. Too little won’t work, while too much...
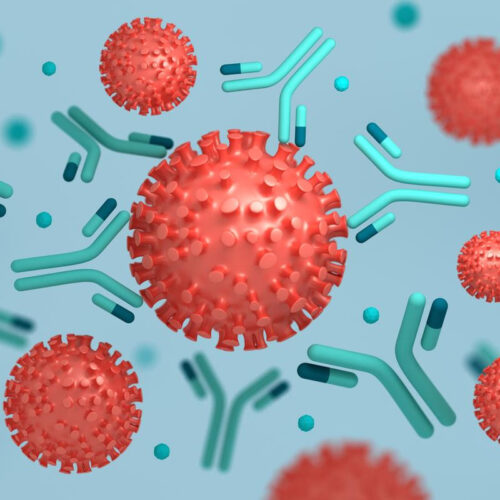
Antibody “master key” discovery could neutralize all COVID variants
By Rich Haridy August 21, 2022 A new study describes a part of the coronavirus spike protein shared across all variants that makes it vulnerable to novel antibodies targeting that region Depositphotos A new study published in Nature Communications has homed in on a part of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein that seems to be shared across all...
Severe COVID-19 increases risk of life-threatening blood clots
by Alex Gardner, University of Pennsylvania Credit: Pixabay/CC0 Public Domain Individuals hospitalized with COVID-19 are more likely to develop venous thromboembolism—a potentially life-threatening condition—than those hospitalized with influenza, according to a new study from the Perelman School of Medicine. The study, published in the Journal of the American Medical Association, evaluates the absolute risk of hospitalized deep...
Study identifies new dementia risk genes through novel testing approach
by University of California, Los Angeles Credit: Unsplash/CC0 Public Domain A new UCLA-led study has identified multiple new risk genes for Alzheimer’s disease and a rare, related brain disorder called progressive supranuclear palsy (PSP) by using a combination of new testing methods allowing for mass screening of genetic variants in a single experiment. The study, published...
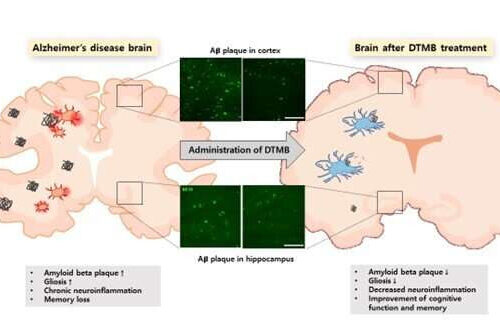
Can the protein that defeats metabolic diseases conquer dementia?
by Pohang University of Science & Technology (POSTECH) Changes in the amount of amyloid-β aggregates in brain tissue following the administration of DTMB drug. Credit: POSTECH Alzheimer’s disease is a representative neurodegenerative disease showing up at an increasing rate in an aging society. Sufferers of this disease are not only portrayed in media, but can...
Real-world data links rosuvastatin to adverse effects on kidneys
Rosuvastatin is associated with increased risks for hematuria, proteinuria, and kidney failure with replacement therapy (KFRT) compared with atorvastatin use, according to a study published online July 19 in the Journal of the American Society of Nephrology. Jung-Im Shin, M.D., from the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health in Baltimore, and colleagues used deidentified electronic...
Researchers identify the target of immune attacks on liver cells in metabolic disorders
by Weill Cornell Medical College Illustration of human liver anatomy. Credit: Shutterstock When fat accumulates in the liver, the immune system may assault the organ. A new study from Weill Cornell Medicine researchers identifies the molecule that trips these defenses, a discovery that helps to explain the dynamics underlying liver damage that can accompany type...