by University of California, San Francisco Credit: Pixabay/CC0 Public Domain The discovery of how to shift damaged brain cells from a diseased state into a healthy one presents a potential new path to treating Alzheimer’s and other forms of dementia, according to a new study from researchers at UC San Francisco. The research focuses on microglia, cells...
Alcohol use can alter gut microbes, but not in the way you might think
by University of California – San Diego Credit: CC0 Public Domain Chronic alcohol use is a major cause of liver damage and death: Approximately 30,000 persons in the United States die annually from alcoholic liver diseases, such as cirrhosis. Among the negative impacts of excessive alcohol use is its ability to adversely affect the gut microbiome,...
Powerful new antibody neutralizes all known SARS-CoV-2 variants
by Children’s Hospital Boston Credit: Unsplash/CC0 Public Domain As SARS-CoV-2 has evolved and mutated, therapeutic antibodies that worked early in the pandemic have become less effective, and newer variants, especially omicron, have developed ways to evade the antibodies we make in response to vaccines. A new, broadly neutralizing antibody developed at Boston Children’s Hospital could potentially...
How a cell remembers?
Researchers track protein binding, build synthetic proteins to study gene expression. How does a nose remember that it’s a nose? Or an eye remember that it’s an eye? As scientists probe the question of how cells remember what kind of cells they are supposed to be, or their genetic lineage, it’s important to understand how...
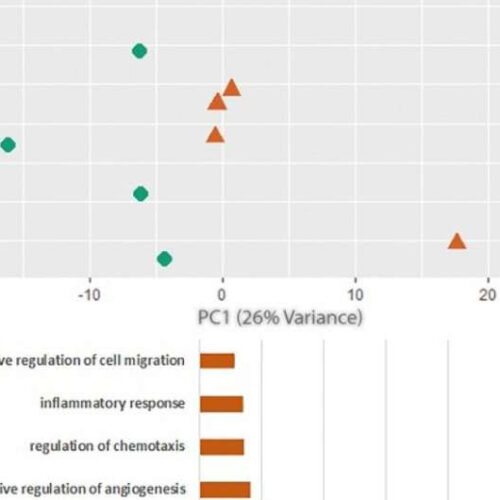
Study uncovers what happens inside artery plaque to trigger strokes
by Tulane University Principal component analysis (PCA) indicates plaque rupture is associated with alterations in the transcriptome. (A) PCA plot of the top 1750 most variable transcripts in asymptomatic and recently ruptured plaques. (B) Gene ontology of the transcripts associated with recently ruptured plaques. (C) Gene ontology of the transcripts associated with asymptomatic plaques. Scientific Reports (2022). DOI:...
DNA-Based Nanorobot Interacts with Live Cells
AUGUST 11TH, 2022 CONN HASTINGS GENETICS, NANOMEDICINE Researchers at INSERM (Institut national de la santé et de la recherche médicale) in France, and collaborators, have developed a DNA-based nanorobot called the Nano-winch. The tiny creation is made using DNA molecules and a “DNA Origami” approach. The tiny robot is so small that it can land on...
Researchers find medicine for asthma and eczema helps COVID patients
by Josh Barney, University of Virginia Credit: Emily Faith Morgan/University of Virginia A medication used to treat asthma and eczema can improve survival rates for patients with moderate to severe COVID-19, a clinical trial conducted at UVA Health suggests. UVA is the first to test this novel and promising approach to COVID-19 treatment. The study centered...
Light-Activated Hydrogel Disrupts Oral Biofilms, Whitens Teeth
AUGUST 15TH, 2022 CONN HASTINGS DENTISTRY, MATERIALS Researchers at Nanchang University in China developed a photodynamic hydrogel treatment for teeth that disrupts bacterial biofilms, helps to prevent cavities, and whitens teeth. The gel is applied to the teeth and is then activated using green light, which is less harsh on nearby skin than the high intensity...
Gene mutations from patients with debilitating seizure and movement disorder created in mice
UNIVERSITY OF MARYLAND SCHOOL OF MEDICINE IMAGE: MICE GENETICALLY ENGINEERED TO CARRY MUTATIONS THAT MAKE THE KCNMA1 ION CHANNEL MORE ACTIVE (LEFT) ARE HUNCHED AND IMMOBILIZED AFTER A STRESS TEST WHICH TRIGGERS INVOLUNTARY IMMOBILITY; NORMAL MICE (MIDDLE) SHOW TYPICAL MOUSE BEHAVIOR, AND THOSE WITH A MUTATION CAUSING REDUCED KCNMA1 ION CHANNEL ACTIVITY APPEAR RESTLESS. CREDIT:...
Researchers identify hormone from fat cells that restrains tumor growth in mice
UNIVERSITY OF MICHIGAN The findings offer a proof-of-concept for developing therapies against hepatocellular carcinoma, the most common form of liver cancer. Jiandie Lin and his team use mice as a model to study how molecular and cellular changes are affected by nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, and how these changes consequently lead to the progression of this...