LOUISIANA STATE UNIVERSITY HEALTH SCIENCES CENTER New Orleans, LA – Research led by Drs. Yuhai Zhao and Walter J Lukiw at the LSU Health New Orleans Neuroscience Center and the Departments of Cell Biology and Anatomy, Neurology and Ophthalmology, reports for the first time a pathway that begins in the gut and ends with a potent...
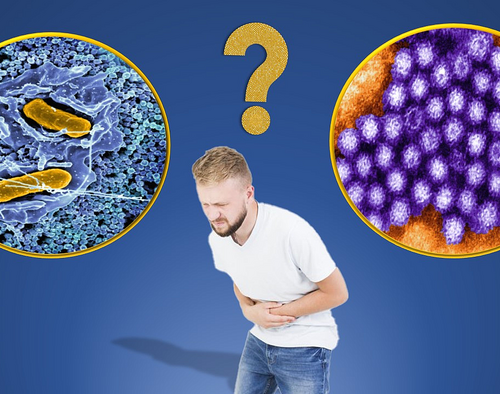
Study finds genetic method for identifying hundreds of disease agents ‘promising’
JOHNS HOPKINS MEDICINE IMAGE: DIAGNOSING THE SOURCE OF A PATIENT’S ILLNESS — IN THE PICTURED SCENARIO, A GASTROINTESTINAL DISORDER THAT MAY HAVE A BACTERIAL (SALMONELLA ON LEFT) OR VIRAL (NOROVIRUS ON RIGHT) CAUSE — MAY ONE DAY BE SIMPLER AND MORE ACCURATE USING NEXT-GENERATION SEQUENCING (NGS) THAN WITH CURRENT METHODS. A RECENT JOHNS HOPKINS MEDICINE...
Study identifies potential targets for treating venous ulcers
ELIFE The study, which includes the first resource detailing the role of microRNAs in the wound-repair process, shows that aberrant levels of a trio of microRNAs may impair healing in venous ulcers. The findings suggest that drugs targeting these microRNAs could help facilitate healing in patients. Venous ulcers commonly occur in the legs, caused by...
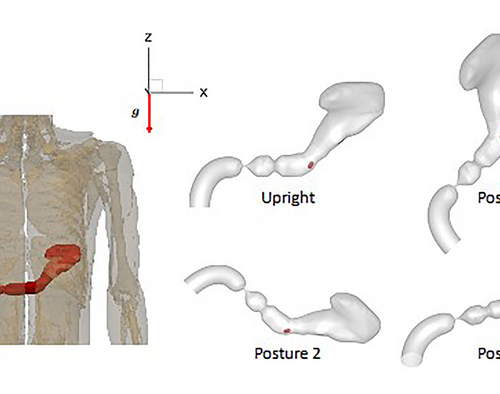
Body posture affects how oral drugs absorbed by stomach
AMERICAN INSTITUTE OF PHYSICS IMAGE: DIAGRAM SHOWING THE ORIGINAL POSITION OF THE STOMACH RELATIVE TO THE BODY AND DIFFERENT RELATIVE POSITIONS OF THE STOMACH WITH RESPECT TO THE DIRECTION OF GRAVITY CONSIDERED IN THIS STUDY. CREDIT: RAJAT MITTAL CREDIT: CREDIT: RAJAT MITTAL WASHINGTON, August 9, 2022 – A common, economic, and easy method of administering...
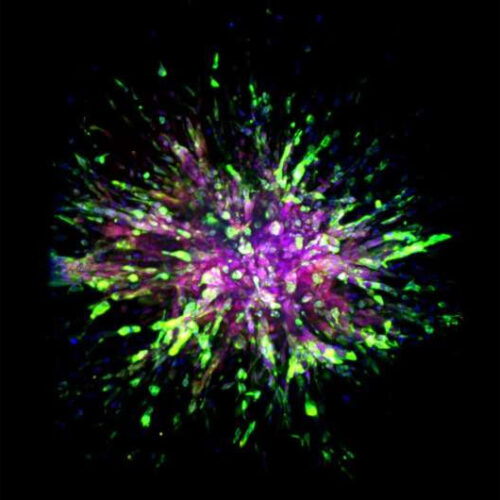
Scientists identify novel molecular biomarkers in cells that spread a deadly form of breast cancer
by Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine A triple-negative breast cancer organoid invades collagen tissue. Credit. Credit: Eloïse Grasset, Johns Hopkins Medicine Studying a deadly type of breast cancer called triple negative, Johns Hopkins Medicine scientists say they have identified key molecular differences between cancer cells that cling to an initial tumor and those that...
Circadian clocks play a key role in fat cell growth
by Weill Cornell Medical College Circadian clock illustration. Credit: Shutterstock Disruption of the circadian clocks that keep the body and its cells entrained to the 24-hour day-night cycle plays a critical role in weight gain, according to a pair of studies by Weill Cornell Medicine investigators. One study, published June 27, in Cell Reports revealed...
New inhaled COVID-19 therapeutic blocks viral replication in the lungs
by Kara Manke, University of California – Berkeley UC Berkeley postdoctoral scholar Chi Zhu is part of a team of researchers who are developing a new COVID-19 therapeutic that can be administered as a nasal spray. The experimental treatment is effective against all SARS-CoV-2 “variants of concern” and could be readily modified to target other...
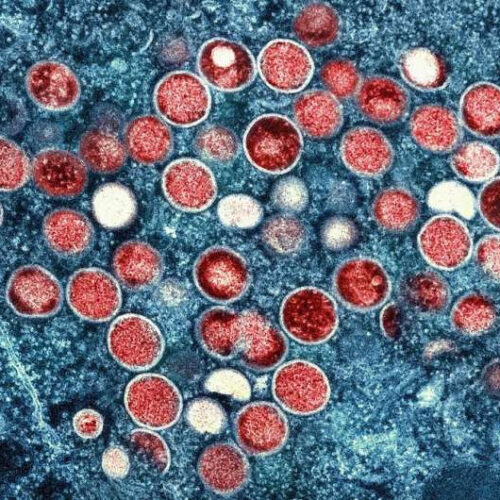
How does monkeypox spread? An expert explains why it isn’t an STI and what counts as close contact
by Rebecca S.B. Fischer, The Conversation This microscopy image shows monkeypox particles, colored red, within an infected cell, colored blue. Credit: NIAID Monkeypox is caused by a virus that, despite periodic outbreaks, is not thought to spread easily from person to person and historically has not spurred long chains of transmission within communities. Now, many researchers are left...
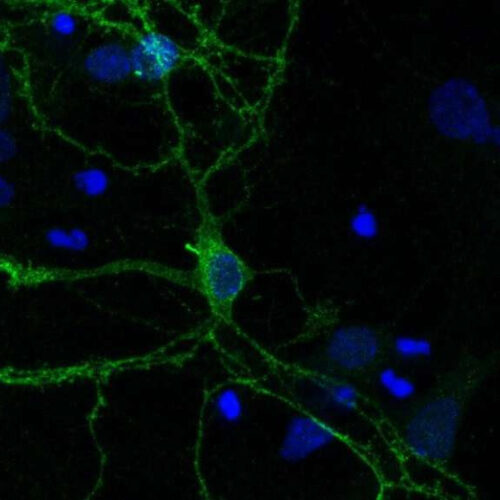
A role for cell ‘antennae’ in managing dopamine signals in the brain
by Emily Caldwell, The Ohio State University Microscope image of a cultured mouse neuron from the striatum region of the brain labeled with a green fluorescent antibody that detects dopamine receptor 1. The receptor localizes along the cell surface and is enriched in a primary cilium projecting from the cell body. Nuclei are indicated in...
Why am I so tired and when is it time to see the doctor about it? A GP explains
by Natasha Yates, The Conversation Credit: Shutterstock Everyone feels tired sometimes. But how do you know whether your tiredness is a problem worth seeing a doctor about? And with all the mental and emotional strain we have been under from the pandemic, isn’t it just normal to feel tired? Tiredness is subjective; what’s normal for...