by Medical University of Vienna Skin microbiome identified as factor in stem cell transplants. Credit: Kateryna Kon/Shutterstock Organ damage occurs in up to 70% of patients in the first few months following stem cell transplant. The precise reasons for this potentially life-threatening reaction have long been the subject of scientific research. Researchers led by Georg...
Myocarditis seven times more likely with COVID-19 than vaccines
by Tracy Cox, Pennsylvania State University Credit: Pixabay/CC0 Public Domain The risk of developing myocarditis—or inflammation of the heart muscle—is seven times higher with a COVID-19 infection than with the COVID-19 vaccine, according to a recent study by Penn State College of Medicine scientists, now published in Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicine. Patients with myocarditis can experience...
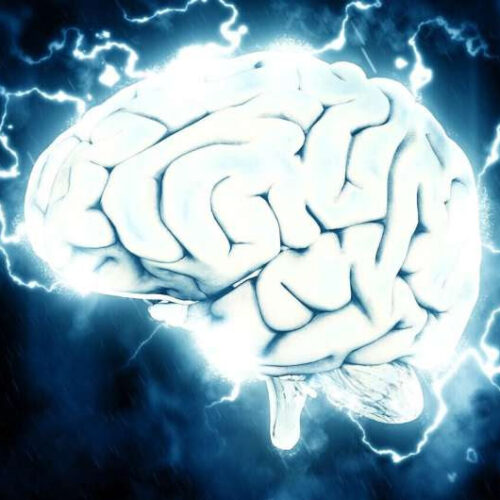
New study finds distinct brain networks associated with risk and resilience in depression
by Jennifer Brown, University of Iowa Credit: Pixabay/CC0 Public Domain A new study that links the location of brain injury to levels of depression in patients following the injury has identified two distinct brain networks; one associated with increased depression symptoms and one associated with decreased depression symptoms. The large-scale study led by researchers with...
Genetic testing helps detect children likely to have heart failure and require a transplant
by Centenary Institute Credit: Unsplash/CC0 Public Domain Genetic testing can diagnose cardiomyopathy—a disease of the heart muscle—in children and help detect who will have heart failure and require a transplant, a new study has found. Researchers at the Centenary Institute and the Murdoch Children’s Research Institute (MCRI) have shown that genetic testing for cardiomyopathy in children and their first...
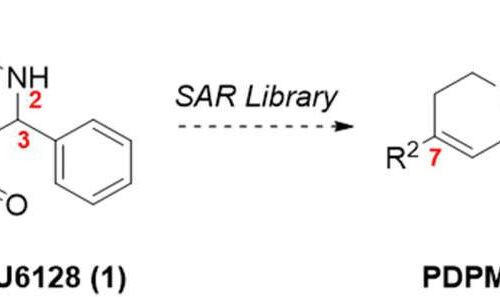
Researchers identify compounds that inhibit monkeypox virus replication
by Boston University School of Medicine Chemical structure of CMLDBU6128 (1) and overview of exploratory PDPM analog libraries based on variation at C3 (R1), C7 (R2), and N2 (R3). The red numbers represent sites of potential modifications described in this study. Credit: Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy (2022). DOI: 10.1128/aac.00841-22 Monkeypox is a viral zoonosis (a virus transmitted to humans from...
Allergy meds in street opioids make overdoses more deadly
A new study is sounding the alarm about the addition of antihistamines to street forms of opioids—and how they might make a fatal overdose more likely. The prime drug in question is diphenhydramine, found commonly in over-the-counter allergy meds such as Benadryl. Because opioid use can spur itchy skin in people who misuse the drugs, diphenhydramine is often mixed...
Aspirin as effective as standard blood thinner to prevent life-threatening blood clots and death after fracture surgery
by University of Maryland School of Medicine Credit: Unsplash/CC0 Public Domain Patients who have surgery to repair bone fractures typically receive a type of injectable blood thinner, low-molecular-weight heparin, to prevent life-threatening blood clots, but a new clinical trial found that over-the-counter aspirin is just as effective. The findings, presented today at the Orthopedic Trauma...
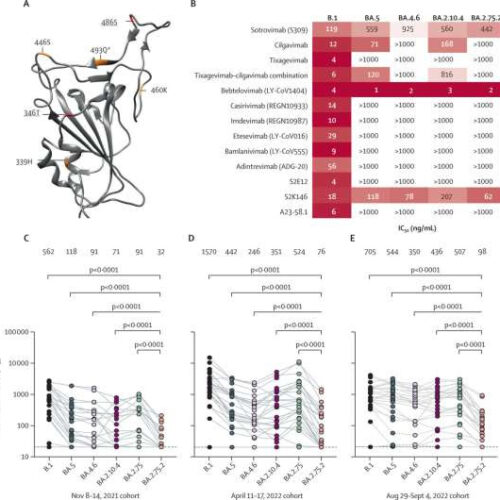
New omicron subvariant largely evades neutralizing antibodies
by Karolinska Institutet BA.2.75.2 escapes neutralizing antibodies. (A) Differences from BA.2 in BA.2.75 (orange), and BA.2.75.2 (red, underlined), depicted upon the SARS-CoV-2 BA.2 receptor binding domain (pdb:7UB0). Sensitivity of SARS-CoV-2 omicron sublineages and ancestral B.1 (D614G) to neutralization by monoclonal antibodies (B), and randomly sampled sera from blood donated in Stockholm, Sweden, between Nov 8–14,...
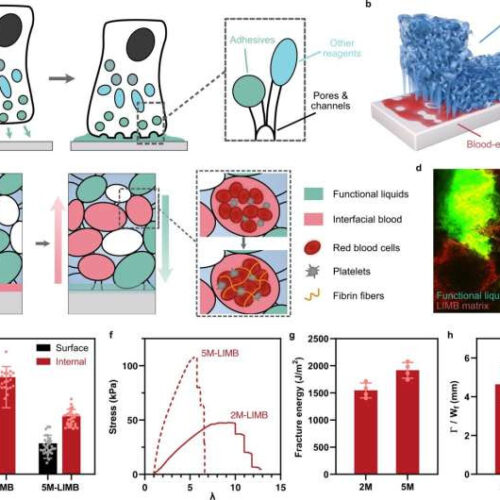
Flatworm-inspired medical adhesives stop blood loss
by McGill University Design of LIMB. a) Schematic illustration of marine organisms that contain interconnected micropores for adhesiveness and transport of liquid reagents. b) Schematic of LIMB adhering on blood-exposed substrates. c) Schematics showing that LIMB can uptake interfacial fluid, secrete functional liquids, and coagulate blood, thereby providing adhesion, hemostatic, and sealing function. d) Confocal...
Experimental cancer drug could be effective in treating idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
by National Jewish Health Credit: Pixabay/CC0 Public Domain Researchers have shown that the medication saracatinib shows promise as a treatment for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF). Saracatinib worked as well or better than two approved drugs at reducing tissue scarring in preclinical models of IPF according to the study published in the American Journal of Respiratory and...