by Heather Simonsen, Huntsman Cancer Institute Benjamin Myers, PhD in lab. Credit: Huntsman Cancer Institute Scientists have solved a long-standing mystery surrounding a cancer-promoting protein and how it causes tumor growth. The findings are an important step in the quest to make cancer drugs more effective since aggressive tumors often become adept at resisting drugs...
Therapeutic games and brain stimulation mitigates cognitive decline in older adults
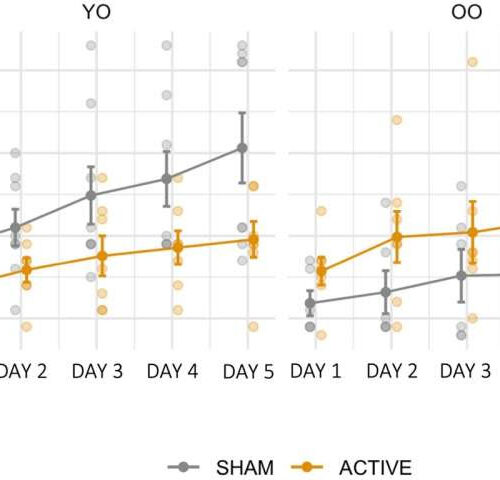
by University of Birmingham Training performance (n¯) for each training day, for the SHAM and ACTIVE groups, within each AGE level. Error bars represent the standard error of the mean. Credit: Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience (2022). DOI: 10.3389/fnagi.2022.1009262 Older people may be able to boost their working memory with a new approach that couples online therapeutic games...
Small-molecule drug reverses neural effects of concussion
by University of California, San Francisco Credit: Unsplash/CC0 Public Domain A small molecule called ISRIB that was identified at UC San Francisco can reverse the neuronal and cognitive effects of concussion in mice weeks after an injury occurred, new research has found. ISRIB blocks the integrated stress response (ISR), a quality control process for protein...
A new treatment improves key symptoms in Williams-Beuren syndrome
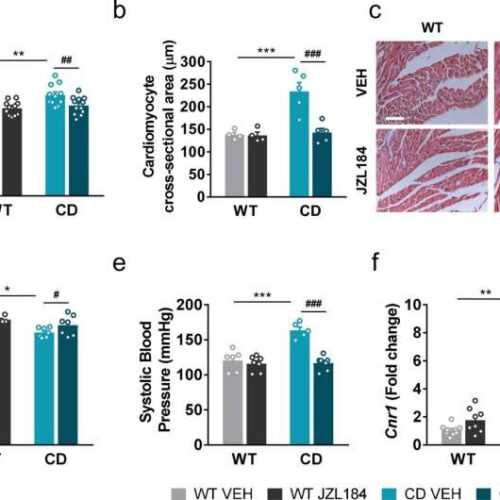
by Universitat Pompeu Fabra – Barcelona JZL184 administration regresses cardiac hypertrophy and the expression of cardiac Cnr1 alterations of complete deletion (CD) mice. Credit: eLife (2022). DOI: 10.7554/eLife.72560 Using an in vivo model that mimics the genetic alteration of Williams-Beuren syndrome, researchers from the UPF’s Neuropharmacology Laboratory—NeuroPhar, in collaboration with several other universities, found alterations in the...
Study of over five million people’s DNA reveals genetic links to height
by Queen Mary, University of London Credit: Unsplash/CC0 Public Domain The study, published today (12 October) in Nature, is the largest ever genome-wide association study, using the DNA of over 5 million people from 281 contributing studies. It plugs a sizeable gap in our understanding of how our genetic differences account for differences in height. Over...
Scientists discover mechanism of hearing
by Oregon Health & Science University Caenorhabditis elegans. Credit: Wikipedia Scientists at Oregon Health & Science University have revealed, for the first time and in near-atomic detail, the structure of the key part of the inner ear responsible for hearing. “This is the last sensory system in which that fundamental molecular machinery has remained unknown,”...
Old diabetes drugs slash the risk of dementia by more than a FIFTH, study finds
By MANSUR SHAHEEN DEPUTY HEALTH EDITOR FOR DAILYMAIL.COM PUBLISHED: 18:30 EDT, 11 October 2022 | UPDATED: 18:30 EDT, 11 October 2022 A class of diabetes drugs that have fallen out of fashion may help prevent Alzheimer’s, a major study suggests. Thiazolidinediones (TZDs) reduced the risk of developing the disease by more than a fifth in a study of more than half...
Could Vitamin C Help Reduce Gout?
Sara Novak October 06, 2022 Could taking vitamin C help reduce the chances of developing gout? A new study sheds light on this possibility. Gout is a form of inflammatory arthritis that has been on the rise in the US in recent decades. Considered a lifestyle disease, some research has shown that instances of the condition have more than doubled...
Discovery of a new antibiotic against resistant pathogens
UNIVERSITY OF BASEL For a long time, antibiotics were considered a silver bullet against bacterial infections. Over time, many pathogens have adapted to resist antibiotics, so the search for new drugs is becoming increasingly important. An international team of researchers including scientists at the University of Basel, has now discovered a new antibiotic by computational...
Blood levels of ‘free range’ DNA may signal early detection of dementia and frailty
JOHNS HOPKINS MEDICINE In a long-term prospective study of more than 600 older participants, Johns Hopkins Medicine researchers say they have evidence that higher levels of cell-free DNA circulating in the blood may signal increased risk of chronic inflammation associated with early signs of frailty and dementia. The findings, published Oct. 11 in the Journal of...