Klüver-Bucy syndrome (KBS) is a very rare neurological condition associated with damage to the brain’s temporal lobes. It can cause a number of behavioral symptoms, such as hyperorality and hypersexuality. KBS may occur after a person experiences a traumatic brain injury. It may also occur secondary to a few other conditions, including: Alzheimer’s disease Parkinson’s...
Year: <span>2022</span>
Faster Response to IV vs Intranasal Ketamine in Depression
Nancy A. Melville May 26, 2022 NEW ORLEANS – New research reveals that patients with treatment-resistant depression who were treated with repeated intravenous ketamine show no significant differences in achieving response or remission, compared with those receiving the intranasal formulation of the drug, esketamine – although fewer treatments appear necessary with the intravenous formulation. Dr Balwinder Singh...
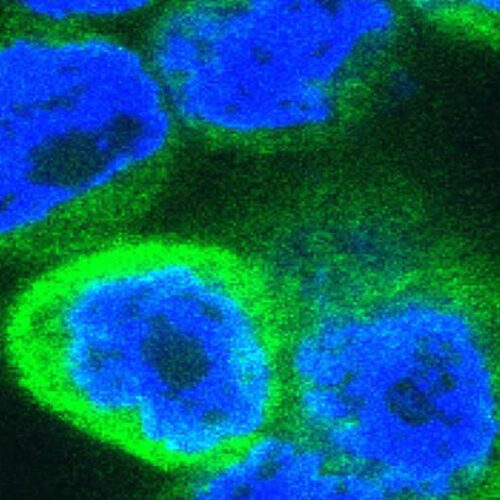
Immune surprise: Recently evolved alarm molecule drives inflammation
byTrinity College Dublin Human cells expressing inflammatory cytokines (stained green). Credit: Professor Martin Laboratory; Trinity College Dublin Scientists from Trinity College Dublin have made an important breakthrough in understanding how inflammation is regulated. They have just discovered that a key immune alarm protein previously believed to calm down the immune response actually does the opposite....
How the Brain Distinguishes Memories From Perceptions
The neural representations of a perceived image and the memory of it are almost the same. New work shows how and why they are different. Perception and memory use some of the same areas of the brain. Small but significant differences in the neural representations of memories and perceptions may enable us to distinguish which...
‘Sticky’ cholesterol and hypertension may increase heart attack, stroke risk
High levels of a specific form of cholesterol plus high blood pressure are tied to a doubled risk of cardiovascular events in a new study. Image credit: Stas Pylypets/Stocksy. Researchers investigated the effect of lipoprotein (a) cholesterol levels and hypertension on cardiovascular risk. They found that higher lipoprotein (a) levels increase cardiovascular risk in patients with hypertension. This relationship...
Cleveland Clinic study finds higher levels of common diet-associated microbe elevates heart failure risk
CLEVELAND CLINIC IMAGE: NEW CLEVELAND CLINIC RESEARCH FINDS HIGHER LEVELS OF COMMON DIET-ASSOCIATED MICROBE ELEVATES HEART FAILURE RISK. CREDIT: CLEVELAND CLINIC December 16, 2022, CLEVELAND – New research at Cleveland Clinic expands the link between what we eat and how the gut microbiome impacts our susceptibility to develop different diseases – in this case, how a specific gut...
Walnuts the new brain food for stressed university students
by University of South Australia Walnuts may counteract the effects of academic stress on the gut microbiota during periods of stress, especially in females. Credit: Open Verse Stressed university students might want to add walnuts to their daily diet in the weeks leading up to their next exam. A new clinical trial of undergraduate students...
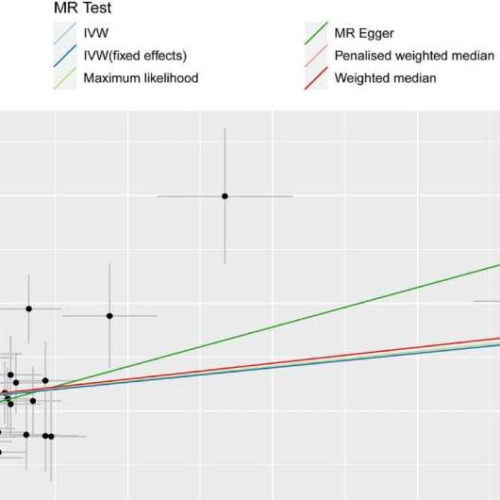
Study finds that insomnia could cause lower back pain and vice versa
by Ingrid Fadelli, Medical Xpress Individual estimates about the potential causal effect of insomnia and low back pain. The x-axis shows that the single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) effect on insomnia in (A) and the y-axis shows the SNP effect on low back pain; (B) shows the results of the reverse causal inference. Several methods of...
Using synthetic gene circuits to better control the timing of immunotherapy
Reviewed by Emily Henderson, B.Sc. Dec 16 2022 In two separate studies, researchers demonstrate how synthetic biology can be used to tackle a difficult issue in cancer immunotherapy: the way immunotherapy-related approaches focused on short-term killing of tumor cells may fail to eradicate tumors because growth of tumors happens on longer timescales. Here, two research...
Pandemic’s two-year global death toll may be close to 15 million
by Dennis Thompson Almost 15 million people likely died as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020 and 2021, nearly three times more than previously reported, a new World Health Organization study estimates. The researchers said the COVID-19 pandemic caused about 4.5 million more deaths than would have been expected in 2020, and 10.4...