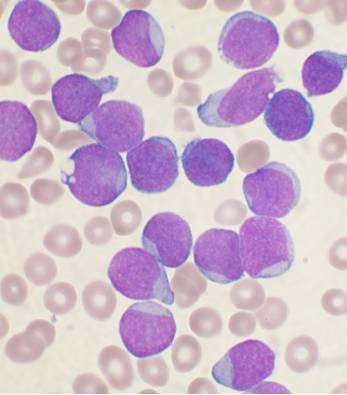
by Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia A Wright’s stained bone marrow aspirate smear of patient with precursor B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Credit: VashiDonsk/Wikimedia/CC BY-SA 3.0 Aberrant splicing of messenger RNAs encoding surface antigen CD22 leads to downregulation of this protein in pediatric B-lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL), rendering malignant cells resistant to the effects of CD22-directed immunotherapies, according...
Year: <span>2022</span>
Researchers find one autoimmune disease could lead to another
by CU Anschutz Medical Campus Credit: CC0 Public Domain Researchers at the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus have discovered that having one kind of autoimmune disease can lead to another. The scientists serendipitously found that mice with antibody-induced rheumatoid arthritis in their joints went on to develop spinal lesions similar to those in axial spondyloarthritis (AxSpA)...
With a ‘biological computer,’ scientists look to target cancer while sparing healthy cells
By Angus Chen Dec. 22, 2021 ADOBE The holy grail of cancer drug targets is akin to a unicorn horn: a marker that only cancer cells have, clearly distinguishing them from healthy cells. In reality, nearly all cancer drug targets are also found on many healthy cells, leading to serious off-tumor toxicity that — in...
What is the Contribution of Demyelination to Cognitive Decline in Aging?
Myelin is an insulator that sheaths the axons forming nervous system connections. It is essential to the correct electrochemical function of the nervous system. Severe conditions such as multiple sclerosis result when myelin is lost, degrading nervous system function to the point of disability and death. In normal aging, myelin is also lost, though to...
Gene helps dietary fat find its way in the body
After you finish a milkshake or a bowl of guacamole, those dietary fats have a typical route through your body. New research from the laboratory of Dr. Natasza Kurpios, associate professor in the Department of Molecular Medicine in the Cornell College of Veterinary Medicine, has now revealed a key molecular mechanism that can send those fats on the...
Psilocybin, in 10mg or 25mg doses, has no short- or long-term detrimental effects in healthy people
KING’S COLLEGE LONDON New research from the Institute of Psychiatry, Psychology, & Neuroscience (IoPPN) at King’s College London, in partnership with COMPASS Pathways, has established that psilocybin can be safely administered at doses of either 10mg or 25mg to up to six participants simultaneously. The research, published in The Journal of Psychopharmacology, is an essential...
COVID-19 and PTSD: Assessing the pandemic’s toll on mental health
by Yale University Credit: Pixabay/CC0 Public Domain Illness, grief, job loss, social isolation, uncertainty, and other pandemic-driven stressors have contributed to an increase in psychological distress on an unusually wide scale. As researchers and clinicians continue to grapple with the psychological fallout from COVID-19, a growing body of literature has examined the prevalence of post-traumatic...
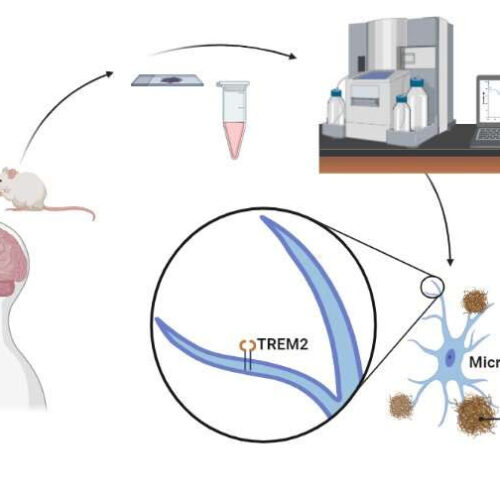
Research clears up how brain ‘cleaners’ fail in ALS
by Mayo Clinic Using samples donated to Mayo Clinic’s Brain Bank for Neurodegenerative Disorders, as well as mouse models, biochemistry, confocal microscopy, and computational simulations, researchers showed that a receptor on microglial cells, called TREM2, can clear a protein that builds up in the brains of patients with ALS. Image created with BioRender. Credit: Mayo...
Early data for multivariant COVID-19 vaccine booster shows promise
by Mike Addelman, University of Manchester Credit: Unsplash/CC0 Public Domain The first results of an early trial of a multivariant COVID-19 vaccine booster, launched in Manchester in September 2021, has shown it is driving a comprehensive immune response. U.S.-based biotechnology company Gritstone bio, Inc. in collaboration with The University of Manchester and Manchester University NHS Foundation...
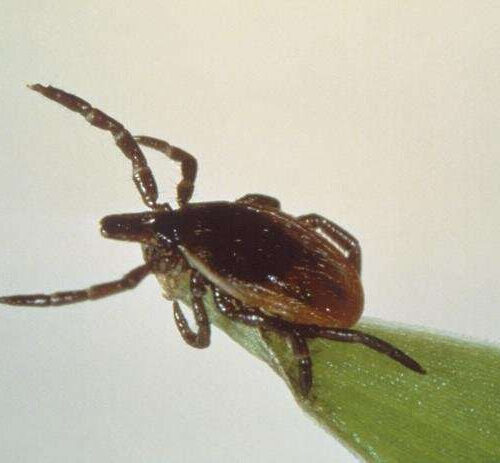
New tool emerging in fight against Lyme disease
by Carol Thompson Host-seeking blacklegged tick. Credit: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), CC0 As black-legged ticks crawl their way across Michigan, scientists hope a new vaccine in development could make their presence less menacing. The vaccine would rob the ticks of a trait that makes them exceptional vectors for Lyme disease: the ability to bite and...