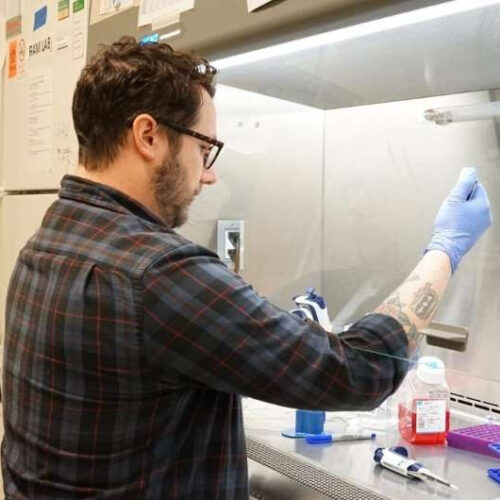
by Phil Ciciora, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Credit: Pixabay/CC0 Public Domain A new paper co-written by a University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign legal scholar argues that the state of California’s proposal to manufacture and distribute insulin at cost could be a game-changer for curbing out-of-control price increases on insulin and a boon to public health....
Study offers first glimpse of how many suffer from previously unknown VEXAS syndrome
by NYU Langone Health Credit: Unsplash/CC0 Public Domain About 13,200 men and another 2,300 women in the United States over age 50 are estimated to have VEXAS syndrome, according to a new study. Long considered a mystery illness until its genetic basis was identified in 2020, the latest findings, led by researchers at NYU Grossman...
How regulatory T cells halt aberrant, self-reactive T cells
by University of Washington School of Medicine Laboratory research in immunology at the Ram Savan Lab at the University of Washington School of Medicine in Seattle. Credit: Ram Savan lab New research findings show in detail how self-reactive T cells—white blood cells that mistakenly attack healthy instead of infected cells, thereby causing an autoimmune or...
Study suggests a way to re-energize tired T cells when treating cancer, viral infections
by Ohio State University Medical Center Scanning electron micrograph of a human T lymphocyte (also called a T cell) from the immune system of a healthy donor. Credit: NIAID A new study by researchers at The Ohio State University Comprehensive Cancer Center—Arthur G. James Cancer Hospital and Richard J. Solove Research Institute (OSUCCC—James) suggests a...
Could altering vaginal microbiome treat vaginal dryness and painful sex during menopause?
by The North American Menopause Society Credit: CC0 Public Domain As women age, they are more susceptible to vaginal dryness and pain during intercourse because of vulvovaginal atrophy (VVA). A new study suggests that ospemifene and systemic hormone therapy both result in improving VVA symptoms and likely improve the vaginal microbiome by reducing potentially harmful...
COVID toll realized: CVD deaths take big jump, especially among certain populations
by American Heart Association Credit: Pixabay/CC0 Public Domain The number of people dying from cardiovascular disease (CVD) in the U.S. escalated during the first year of the COVID-19 pandemic, from 874,613 CVD-related deaths recorded in 2019 to 928,741 in 2020. The rise in the number of CVD deaths in 2020 represents the largest single-year increase...
Parkinson’s Disease: Focus on Hallucinations
Marine Cygler January 23, 2023 PARIS ― Hallucinations affect more than half of patients with Parkinson’s disease. They are often hidden by those experiencing them, yet they are something neurologists must be made aware of in their patients, since they are associated with poor long-term outcomes and a reduced quality of life. Hallucinations also are a source of...
AHA Scientific Statement on Rapid Evaluation for Suspected TIA
Megan Brooks January 20, 2023 A new scientific statement from the American Heart Association (AHA) offers a standardized approach to rapidly evaluate patients with suspected transient ischemic attack (TIA), keeping in mind the challenges faced by rural centers with limited resources. TIAs are “warning shots” of a future stroke and require emergency evaluation, Hardik Amin, MD, chair of the writing committee...
Novel Tool Empowers Patients to Resolve Vertigo on Their Own
Megan Brooks January 19, 2023 A web-based system can help patients with benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV) diagnose and treat a recurrent bout of dizziness on their own, results of a randomized controlled trial show. “BPPV appears to be a vestibular disorder that is highly appropriate for telemedicine and digital therapeutics,” write investigators, led by Hyo-Jung Kim, PhD, and...
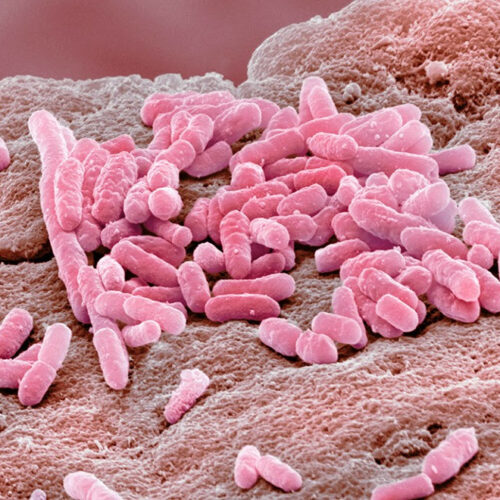
How antidepressants help bacteria resist antibiotics
Liam Drew In the presence of antidepressants, the Gram-negative bacteria, E. coli, can fend off antibiotics. Credit: Steve Gschmeissner/Science Photo Library The emergence of disease-causing bacteria that are resistant to antibiotics is often attributed to the overuse of antibiotics in people and livestock. But researchers have homed in on another potential driver of resistance: antidepressants....