By Bronwyn Thompson August 09, 2023 Too much of a good thing: Current antibiotics have lost their power to fight constantly evolving microorganisms Depositphotos Decades of work has seemingly paid off with scientists developing a potent new synthetic molecule that swiftly knocked out 285 strains of bacteria it was tested on, setting it up as...
Synergistic effect of a traditional Chinese medicinal compound on existing diabetes drug found
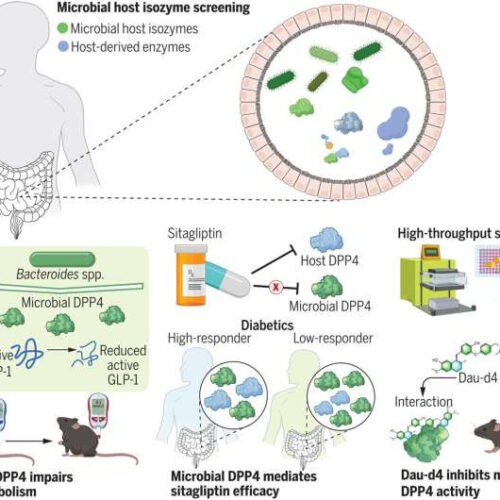
by Justin Jackson, Medical Xpress Discovery and inhibition of a gut microbial–host isozyme to regulate host metabolism. Differences in the gut microbiota may explain why some individuals respond to antidiabetic DPP4 inhibitors but others do not. An activity-based enzyme activity screening system identified gut microbial DPP4 isozymes that can decrease active GLP-1 but cannot be...
A novel theory of aging, independent of damage accumulation
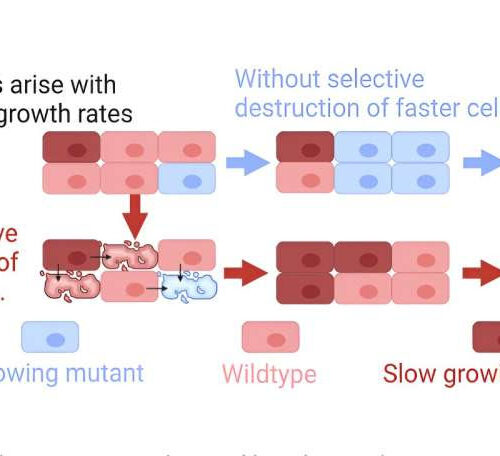
by Impact Journals LLC Outcomes of cell competition and control by selective destruction. Credit: Aging (2023). DOI: 10.18632/aging.204956 A new editorial paper titled “A novel theory of ageing independent of damage accumulation” has been published in Aging. The underlying cause or causes of aging are an enduring mystery, but in 1977, Kirkwood postulated that organisms might gain a...
Stem cell therapy rescues symptoms of Alzheimer’s disease
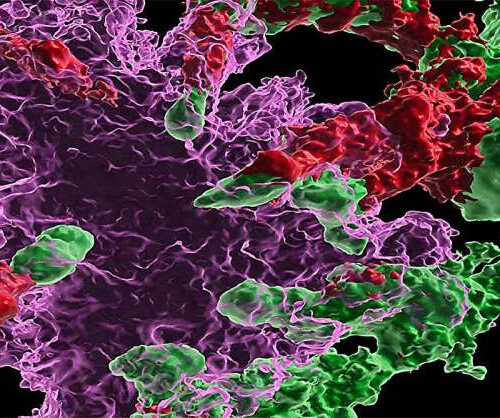
by University of California – San Diego Systemic transplantation of wild-type hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells (green) led to their differentiation into microglia-like cells (red), which reduced the amount of beta amyloid plaques (magenta) in the brain. Credit: Priyanka Mishra and Alexander Silva, UC San Diego Health Sciences In the ongoing search for a cure for...
Researchers unlock mystery of cartilage regeneration in lizards, insight into osteoarthritis-damaged cartilage
by Keck School of Medicine of USC A green anole lizard regenerating its tai. Credit: Ariel Vonk/Lozito Lab A team of researchers from the Keck School of Medicine of USC have published the first detailed description of the interplay between two cell types that allow lizards to regenerate their tails. This research, published on August 10 in Nature Communications, focused...
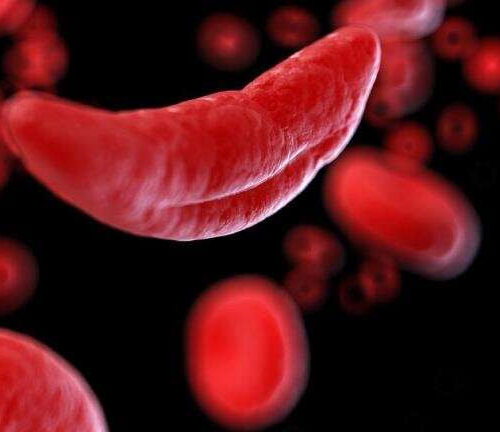
Research sheds new light on gene therapy for blood disorders
by University of Michigan Credit: National Institutes of Health Research from experts at Michigan Medicine, the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia and Penn Medicine is breaking ground on new ways of treating blood disorders, such as sickle cell anemia, through gene therapy. The study is published in the journal Science. To cure blood disorders, patients must undergo high dose chemotherapy...
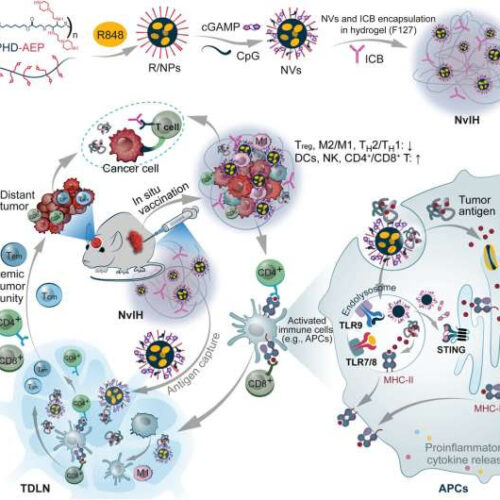
Single-dose injectable nanovaccine-in-hydrogel for robust cancer immunotherapy
by Thamarasee Jeewandara , Medical Xpress In situ vaccination with single-dose NvIH reduced TME immunosuppression, enhanced TME antitumor immune milieu, and elicited systemic antitumor immunity, resulting in robust immunotherapy of large poorly immunogenic tumors with abscopal effect. NvIH is composed of injectable (NVs + ICBs)-in-hydrogel that was loaded with triple immunostimulants (TLR7/8/9 and STING agonists...
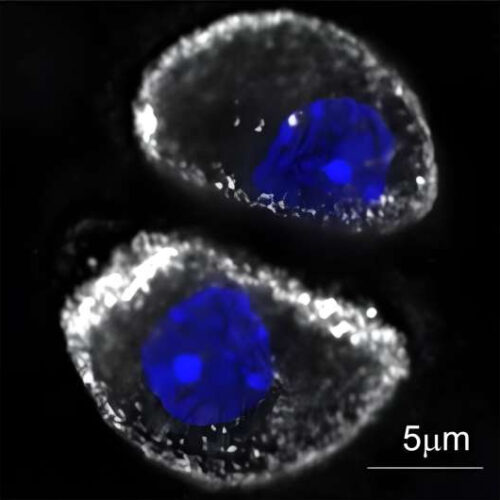
Research identifies protein that protects healthy joints from osteoarthritis
by University of Delaware The blue area is the cell nucleus, the white area is F-actin, the structural scaffolding of the cells. Researchers discovered adseverin regulates the amount of F-actin in the cells. In osteoarthritis loss of F-actin can eventually lead to cell death. Credit: University of Delaware A previously unstudied protein in the framework of...
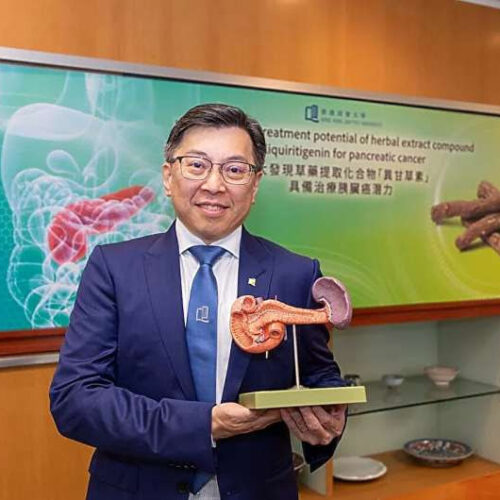
Treatment potential of herbal extract compound isoliquiritigenin for pancreatic cancer
by Hong Kong Baptist University A research team led by Dr Joshua Ko Ka-shun, Associate Professor, Teaching and Research Division of the School of Chinese Medicine at HKBU, found that isoliquiritigenin, a herbal extract compound of the Chinese herbal medicine licorice, can inhibit pancreatic cancer progression. Credit: Hong Kong Baptist University Research led by scientists of...
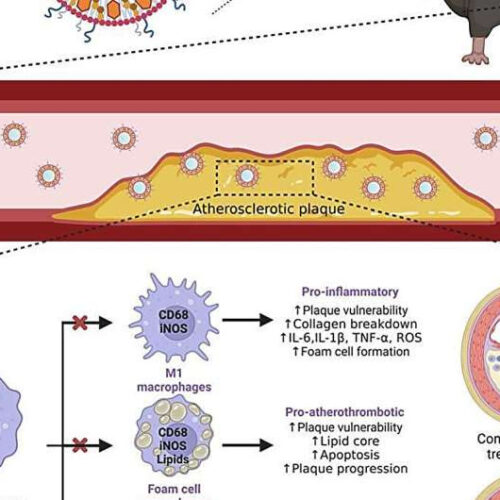
New treatment method reduces size and increases stability of atherosclerotic plaque on arterial walls
by National University of Singapore Graphical abstract. Credit: Journal of Controlled Release (2023). DOI: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2023.06.035 Atherosclerosis is a disease in which fat, cholesterol, and other substances build up inside artery walls. This can lead to plaque formation, which can block arteries and cause heart attacks and strokes. Atherosclerosis is the leading cause of coronary heart disease, and is...