By Bronwyn Thompson August 02, 2023 Sex-specific genetic therapy could make it easier for everybody to lose weight Depositphotos Obesity is a massive global crisis, with around 650 million adults and 124 million children and adolescents impacted. It’s also estimated that up to 70% of body size is directly linked to genetic factors. In addition...
Peptoids pop some viruses like the disease-causing balloons they are
By Michael Franco August 02, 2023 No matter how they’re shaped on the outside, targeting the lipid membrane beneath could lead to a new way of fighting many different viruses Depositphotos In the neverending human-vs-virus battle, scientists often focus on disrupting the protein coating on the bugs. New research shows a different way forward: using certain compounds...
First-of-its-kind cancer drug targets mechanism that causes metastasis
By Paul McClure August 03, 2023 Researchers have developed an monoclonal antibody drug that targets the process that causes cancer cells to spread in the body Depositphotos Metastatic cancer accounts for up to 90% of all cancer deaths in the US annually. But with researchers developing a first-of-its-kind drug that inhibits the process by which cancer cells...
Experimental insulin implant uses electricity to control genes
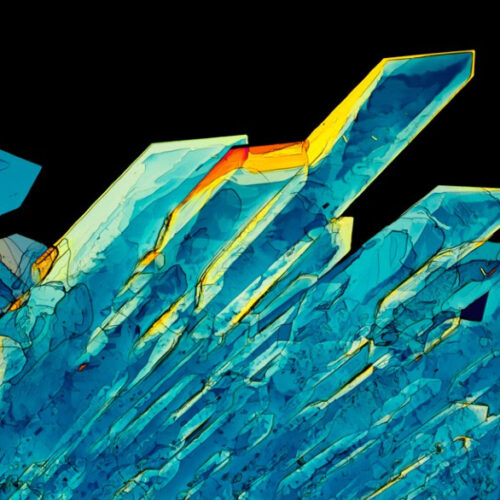
Lilly Tozer An insulin crystal viewed under a light microscope. People with type 1 diabetes do not make enough insulin, which helps to control blood sugar levels. Credit: Alfred Pasieka/Science Photo Library Genetically engineered human cells that produce insulin when stimulated by a small electric current could one day be used to develop better treatments...
Medicare may save $1.8B from four drugs in first year of price negotiations, research finds
Paul Schloesser Associate Editor A new paper published this week claims that in 2026, when Medicare negotiations for drug prices kick off, the minimum discount stipulated by the Inflation Reduction Act exceeds 2020 rebates for only four of the 10 drugs to be negotiated. On Sept. 1, CMS is expected to announce those 10 drugs...
Towards disease-oriented dosing of rapamycin for longevity
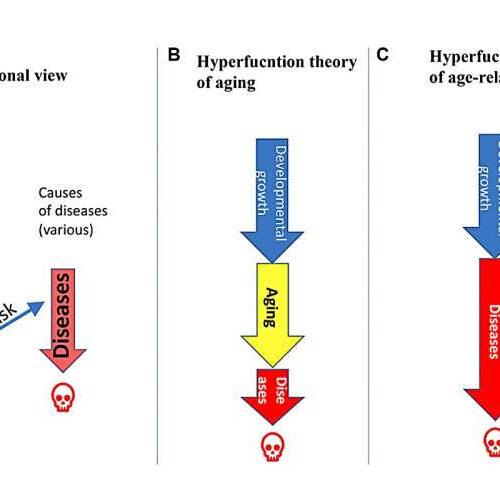
by Impact Journals LLC Relations between aging and age-related diseases (ARDs). Credit: Aging (2023). DOI: 10.18632/aging.204920 A new research perspective titled “Towards disease-oriented dosing of rapamycin for longevity: does aging exist or only age-related diseases?” has been published in Aging. In his new research perspective, Dr. Mikhail V. Blagosklonny from Roswell Park Comprehensive Cancer Center discusses aging and rapamycin (Sirolimus)—the only drug...
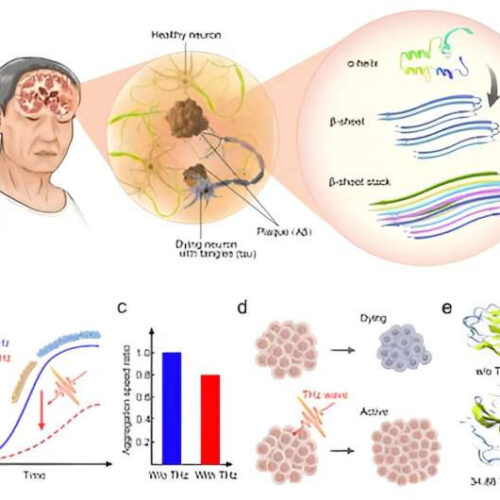
Potential Alzheimer’s treatment would use high-frequency terahertz radiation
by Chinese Academy of Sciences Schematic of the main content of this study. a The presence of extracellular β-amyloid deposition as neuritic plaques and the intracellular accumulation of hyperphosphorylated tau as neuro fibrillary tangles remain the primary neuropathologic features for AD diagnosis, and the amyloid deposition begins with the conversion of native monomers with more α-helices...
Cancer: A new drug prevents EMT, metastasis and resistance to anti-cancer therapy
UNIVERSITÉ LIBRE DE BRUXELLES Metastases and resistance to chemotherapy are the main causes of treatment failure and mortality in cancer patients. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), a process by which cancer cells detach from their neighboring cells and acquire invasive properties, plays a key role in the formation of metastases and the development of resistance to anti-cancer...
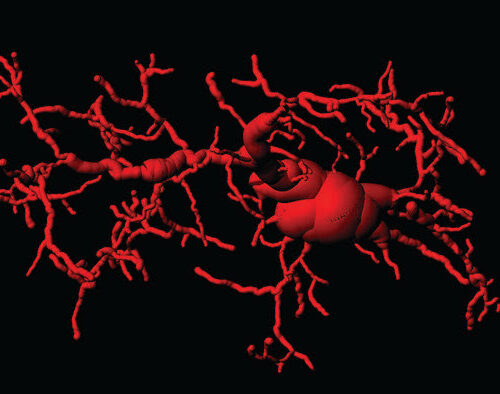
How immunity contributes to ageing and neurodegeneration
ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE FÉDÉRALE DE LAUSANNE IMAGE: AN ACTIVATED MICROGLIAL CELL IN THE BRAIN OF CGAS/STING ACTIVATED MICE. CREDIT: GULEN ET AL. NATURE 02 AUGUST 2023. DOI: 10.1038/S41586-023-06373-1 As we age, our bodies undergo various changes that can impact our overall health and make us more susceptible to diseases. One common factor in the ageing process...
Potential neuropathic pain treatment shows promise in preclinical tests
WEILL CORNELL MEDICINE A non-opioid designer molecule for treating chronic neuropathic pain by calming hyperactive pain-sensing neurons in the peripheral nervous system has had promising results in a preclinical study conducted by researchers at Weill Cornell Medicine and the Burke Neurological Institute. In the study, published Aug. 2 in the British Journal of Anaesthesia, the first-in-class drug conceptualized...