By Michael Irving January 04, 2023 A new type of treatment turns cancer cells into double agents that kill existing tumors Depositphotos Scientists at Brigham and Women’s Hospital (BWH) have found a way to fight cancer with cancer. The team genetically engineered cancer cells to release anti-cancer drugs at the site of established tumors, as...
Year: <span>2023</span>
Bacteria engineered to secrete rheumatoid arthritis drug in the body
By Rich Haridy January 04, 2023 Researchers genetically modified bacteria to secrete a peptide found to reduced inflammation associated with several autoimmune diseases Depositphotos Instead of injections or pills, why not engineer bacteria to secrete therapeutic molecules from within our gut? A new study is demonstrating this futuristic idea, showing how a genetically modified probiotic...
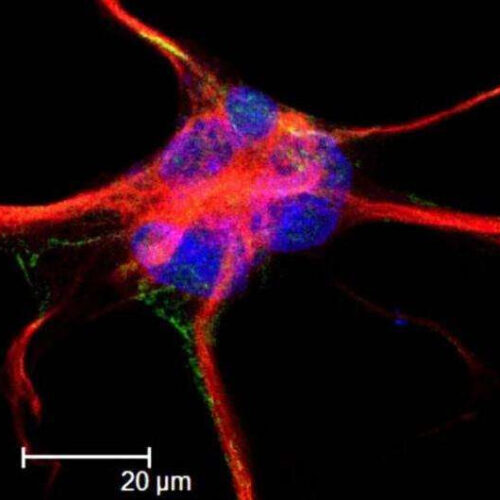
Lab-grown retinal eye cells make successful connections, open door for clinical trials to treat blindness
by Chris Barncard, University of Wisconsin-Madison Proof of synapses connecting pairs of retinal cells derived from human pluripotent stem cells comes from the red coloring of infection by a modified rabies virus passed from one cell with a yellow nucleus across the synapse to a cell that glows only red. Credit: UW-Madison / Gamm Laboratory....
Blood pressure drug holds promise for treating PTSD
by Medical College of Georgia at Augusta University Dr. Qin Wang and research scientist Hasib Rehman. Credit: Michael Holahan, Augusta University There is new evidence that a 50-year-old blood pressure drug could find new purpose as a treatment to mitigate the often life-altering effects of increasingly prevalent PTSD, scientists say. Clonidine is commonly used as a high...
Drug can spur liver regeneration in Alagille syndrome
by Sanford Burnham Prebys Medical Discovery Institute Duc Dong, Ph.D. Credit: Sanford Burnham Prebys Research led by Associate Professor Duc Dong, Ph.D., has shown for the first time that the effects of Alagille syndrome, an incurable genetic disorder that affects the liver, could be reversed with a single drug. The study, published in the Proceedings of the...
Dawn-to-dusk dry fasting leads to health benefits in the study of immune cells
by Baylor College of Medicine Credit: Unsplash/CC0 Public Domain Researchers at Baylor College of Medicine have found more evidence that dry fasting (fasting without food or liquid intake) from dawn to dusk can play an important role in overall health. In a new study published in Metabolism Open, researchers found that fasting from dawn to dusk for four...
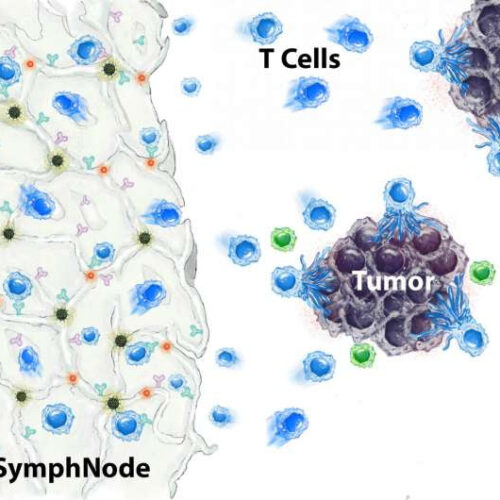
Tiny, implantable therapeutic sponge device helps kill cancer in mice
by Wayne Lewis, University of California, Los Angeles The SymphNode device (left), contains nanoparticles (red dots) that release a drug that blocks the activity of regulatory T cells (green), which suppress the body’s response to solid tumors. At the same time, the SymphNode’s microparticles (black dots) attract and beef up cancer-fighting T cells. Credit: Negin...
The molecules behind metastasis
by Greta Friar, Whitehead Institute for Biomedical Research Breast cancer stem cells (red) that have reached the lung begin to divide into clusters that could become metastatic tumors. Credit: Arthur Lambert Many cancer cells never leave their original tumors. Some cancer cells evolve the ability to migrate to other tissues, but once there cannot manage...
Biochemists describe structure and function of newly discovered CRISPR immune system
by Mary-Ann Muffoletto, Utah State University Credit: Utah State University Utah State University biochemists Thomson Hallmark and Ryan Jackson, along with collaborators, published two seminal papers this week. Their findings describe the structure and function of a newly discovered CRISPR immune system that—unlike better-known CRISPR systems that deactivate foreign genes to protect cells—shuts down infected cells...
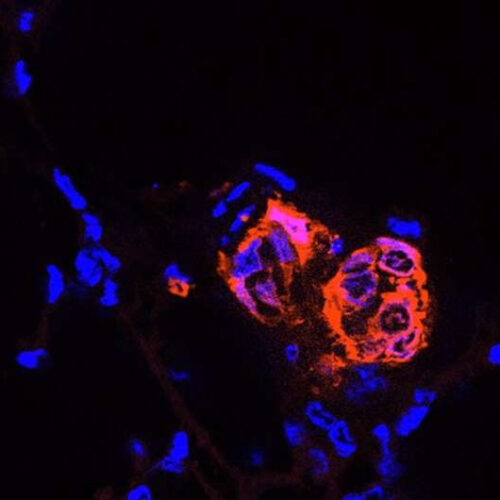
A tool to investigate rare, previously inaccessible cells that play a key role in multiple sclerosis
by Brigham and Women’s Hospital This is an astrocyte, labeled with GFAP (red), Focal Adhesion Kinase (FAK) green, and nuclear stain To-Pro (blue). Credit: Nathan S. Ivey at TNPRC. Via Wikipedia. Rare cell types can have an undue influence on human health. Previous research has suggested that a subset of astrocytes—star-shaped cells in the brain and spinal...