by Baylor College of Medicine Credit: CC0 Public Domain For chronic conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis, treatment often involves lifelong injections. Fear of needles, injection-associated infection and pain are responsible for patients skipping doses, which encourages the development of new delivery strategies that combine efficacy with limited side effects to treat patients adequately. Researchers at Baylor...
Year: <span>2023</span>
Study identifies four major subtypes of long COVID
by Jim Schnabel, Cornell University Credit: Unsplash/CC0 Public Domain The post-COVID syndrome known as long COVID has four major subtypes defined by different clusters of symptoms, according to a study led by researchers at Weill Cornell Medicine. The study, published Dec. 1 in Nature Medicine, was the largest of its kind to examine long COVID. The researchers, who represent...
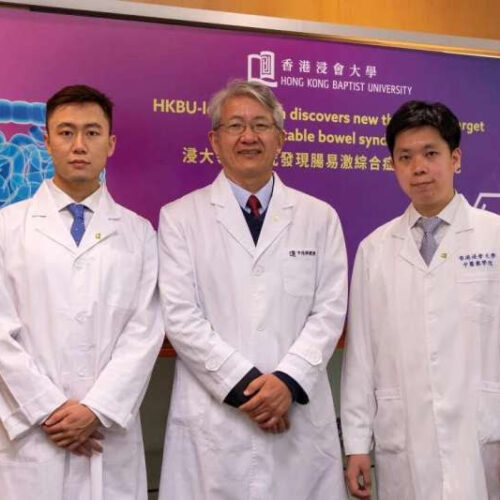
New therapeutic target for irritable bowel syndrome
by Hong Kong Baptist University The research team of Professor Bian Zhaoxiang, Director of the Clinical Division and Tsang Shiu Tim Endowed Professor in Chinese Medicine Clinical Studies (middle); Dr Xavier Wong Hoi-leong, Assistant Professor of the Teaching and Research Division (right); and Dr Zhai Lixiang, Post-Doctoral Research Fellow (left) of SCM at HKBU, has shown for the first time that...
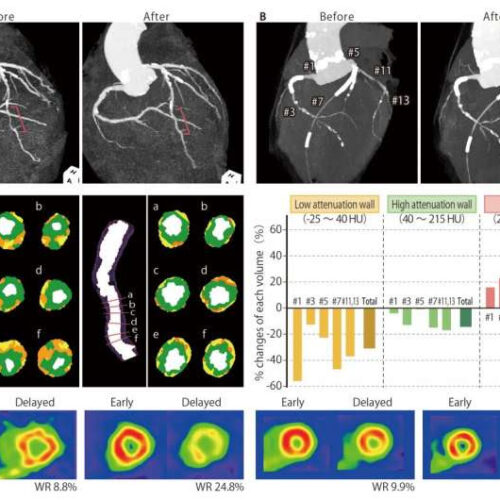
A dietary supplement leads to remarkable regression in atherosclerotic lesions
by Osaka University TGCV is an emerging cardiovascular disorder characterized by diffuse narrowing coronary atherosclerosis with triglyceride (TG) deposition caused by defective intracellular lipolysis. TGCV is an often-undiagnosed condition in patients who are resistant to standard therapies. Panels A and B concern two patients in their 60s with refractory angina pectoris and diabetes mellitus. After...
New cellular component with importance for the sense of smell discovered
by Ola Nilsson, Umea University Release of vesicles with transduction proteins in electron microscope magnification. Credit: Devendra Kumar Maurya Researchers at Umeå University have discovered a previously unknown cellular component, an organelle, inside neurons that we use to perceive smell. The discovery may have implications for further research on impaired sense of smell, which is a common symptom...
Metformin for Atrial Fibrillation?
BY JOSEPH GUSTAITIS | DECEMBER 30, 2022 Metformin, the most popular blood sugar-lowering medicine in the world, seems to be turning out to be the Swiss Army knife of medications. In recent years, there have been reports that metformin appears to improve mitochondrial function in people with diabetes, that it can help in chronic kidney disease (CKD), and...
Late-stage melanoma: Experimental drug combo puts 50% of patients into remission
Could a two-drug combination improve treatment response in late-stage melanoma? Glasshouse Images/Getty Images Researchers tested the efficacy of a drug combination for treating stage IV melanoma. They found that 71% of patients responded to the drug combination, and 50% had complete remission. The drug combination is now entering a larger trial with a more diverse cohort....
Researchers develop, validate tool to visualize 3D architectural properties of atherosclerosis plaques
BOSTON UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF MEDICINE (Boston)— Atherosclerosis is a long-term arterial vessel wall disease characterized by the build- up of lipid- rich and inflamed plaques. It often goes undetected, but highly inflamed plaques disrupt and form a blood clot attached to the vessel wall adjacent to the flowing blood. This acute event (atherothrombosis) can lead...
From Droplet to Discovery
Stem cells overflow with potential. Their ability to become other cell types is crucial to our bodies during development and throughout life. But this potential can be our downfall if it goes wrong, turning some of our most useful cells into malignant cancers. While investigating a pathway involved in stem cell differentiation, researchers at UC Santa Barbara found...
New COVID pill may be improvement over Paxlovid, Chinese trial suggests
by Cara Murez COVID-19 patients could soon have a new antiviral pill they can take to guard against severe disease. The treatment, called VV116, worked as well as Paxlovid in people who were at high risk of severe disease in a phase 3 trial in China. The trial was a “great success,” study co-author Ren Zhao, a...