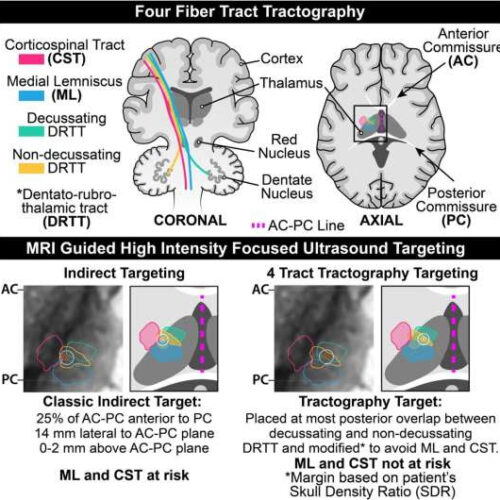
by UT Southwestern Medical Center Graphical abstract. Credit: Brain Communications (2022). DOI: 10.1093/braincomms/fcac273 UT Southwestern physicians have developed an improved targeting method, four-tract tractography, to personalize MRI-guided, high-intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU) used at UTSW to treat medication refractory tremor in essential tremor and tremor-dominant Parkinson’s disease. Results of the clinical cases utilizing this approach, published in Brain Communications,...
Year: <span>2023</span>
Product of Gut Microbiome Implicated in Heart Failure Risk
Sue Hughes December 22, 2022 Further evidence that the gut microbiome affects the development of cardiovascular disease, heart failure in particular, has emerged in a new report. The study directly linked elevated levels of phenylacetylglutamine (PAG), a byproduct created when microbes in the gut break down dietary protein, to increased heart failure risk and severity. It follows previous studies...
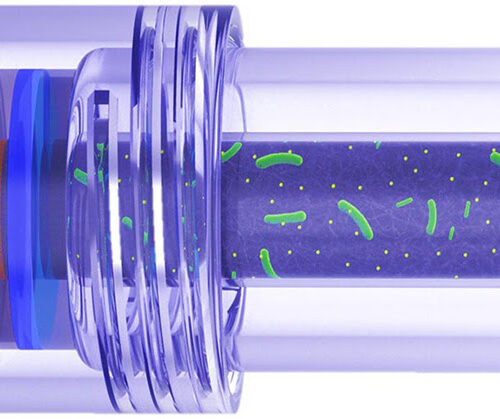
Microbial Fuel Cell Powers Ingestible Devices
DECEMBER 27TH, 2022 CONN HASTINGS GI Researchers at Binghamton University have developed a microbial fuel cell that can power ingestible devices, such as cameras, that can detect health issues in the gastrointestinal tract, and specifically within the small intestine. The fuel cell contains dormant Bacillus subtilis endospores that only germinate and become active when they encounter nutrient-rich intestinal fluid....
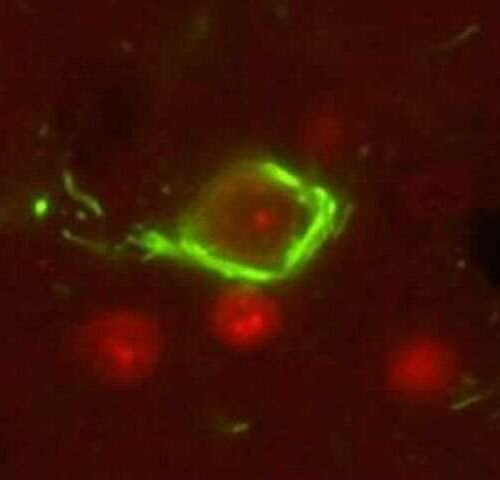
Targeting tau, the other protein behind Alzheimer’s disease
by Leila Gray, University of Washington School of Medicine Defective tau proteins form insoluble neurofibrillary tangles (green) that cause neurons to die. Credit: Kraemer Lab In November, researchers reported the drug lecanemab slowed the progression of Alzheimer’s disease. The effect was modest, but it has generated tremendous excitement because it was the first time a drug had...
Investigators develop new therapy for autism subtype
by Melissa Rohman, Northwestern University Credit: Pixabay/CC0 Public Domain A team of Northwestern investigators led by Peter Penzes, Ph.D., the Ruth and Evelyn Dunbar Professor of Psychiatry and Behavioral Sciences and director of the Center for Autism and Neurodevelopment, has developed a new therapy that could treat Phelan-McDermid syndrome, a subtype of autism spectrum disorder...
Making pig livers humanlike in quest to ease organ shortage
by Lauran Neergaard A pig kidney that has been “decelled” is held by a technician in a Micromatrix laboratory on Tuesday, Dec. 8, 2022, in Eden Prairie, Minn. This is a pig kidney that’s gradually being transformed to look and act like a human one, part of scientists’ long quest to ease the nation’s transplant...
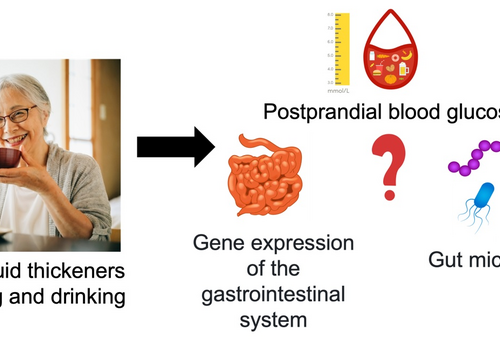
Xanthan gum-based fluid thickener can help decrease blood glucose levels
TOKYO MEDICAL AND DENTAL UNIVERSITY IMAGE: FIG.1: LONG-TERM CONSUMPTION OF THE XANTHAN GUM-BASED FLUID THICKENER. CREDIT: DEPARTMENT OF DYSPHAGIA REHABILITATION, TMDU Researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) showed that xanthan gum-based fluid thickener can decrease blood glucose levels after eating Tokyo, Japan -Type 2 diabetes mellitus is a common lifestyle disease that is prevalent worldwide....
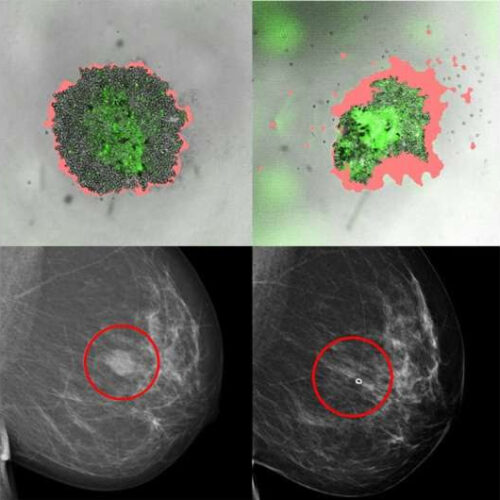
New method predicts the right treatment for breast cancer patients
by Karolinska Institutet The researchers developed and tested whole-tumor cell culture models derived from breast cancer patients that can predict how the tumors will respond to different treatments. Credit: Xinsong Chen et al, PNAS 2022 Researchers at Karolinska Institutet have developed a method that should be able to predict whether a patient with breast cancer will benefit from a particular...
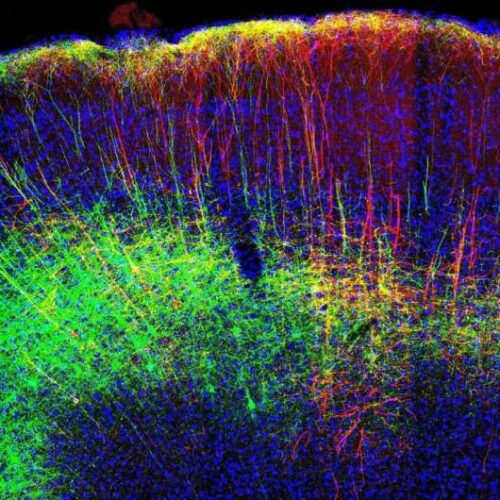
Researchers study pain-relieving neural mechanisms by activation of the motor cortex
by Universitätsklinikum Heidelberg Stained nerve tracts in the motor cortex of a mouse. Credit: Heidelberg University Hospital The motor cortex controls the voluntary movement of muscles. It remains largely unclear why its electrical or magnetic stimulation can alleviate therapy-resistant chronic pain—albeit unreliably. An interdisciplinary research group at the Medical Faculty of Heidelberg (MFHD) has now tracked down...
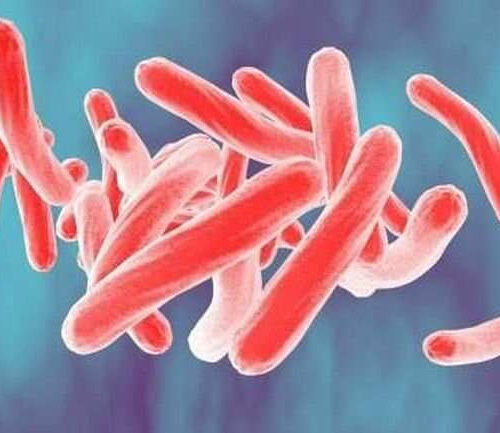
New blood test to identify infections could reduce global antibiotic overuse
by Nina Bai, Stanford University Medical Center Tuberculosis bacteria replicate inside human cells, as viruses do. A blood test developed at Stanford Medicine can distinguish between such bacteria and viruses with 90% accuracy. Credit: Kateryna Kon/Shutterstock In developing countries, most antibiotic prescriptions are not only pointless—an estimated 70% to 80% of them are given for...