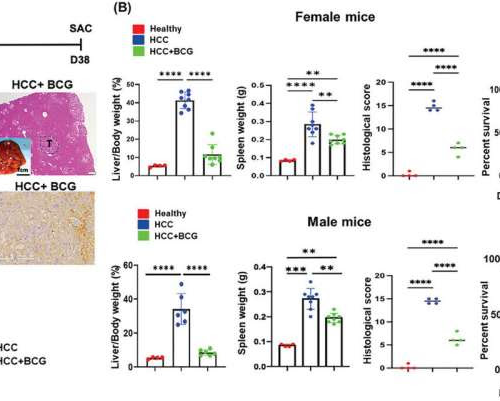
by Nadine A Yehya, UC Davis BCG treats HCC and extends the survival time of HCC mice. A) The diagram of the experimental procedure for BCG treatment. Plasmids myr-AKT1 and NRasV12 (AKT and RAS) were transfected into the livers on day 0 (D0) using hydrodynamic injection. BCG (or PBS) was subcutaneously injected on day 10 (D10)....
Higher exercise volume after concussion tied to lower symptom burden in multicenter study
by Elana Gotkine For children with concussion, higher cumulative moderate-to-vigorous physical activity (cMVPA) during the first and second weeks post-injury is associated with lower symptom burden, according to a study published online Feb. 16 in JAMA Network Open. Andrée-Anne Ledoux, Ph.D., from the Children’s Hospital of Eastern Ontario Research Institute in Ottawa, Canada, and colleagues...
Guideline now recommends fecal microbiota transplant for the majority of recurrent C. diff patients
by American Gastroenterological Association A medical illustration of Clostridioides difficile bacteria, formerly known as Clostridium difficile, presented in the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) publication entitled, Antibiotic Resistance Threats in the United States, 2019. Credit: CDCIn the first comprehensive evidence-based guideline on the use of fecal microbiota-based therapies for gastrointestinal disease, the American Gastroenterological...
Chronic inflammation and inactivity may affect age-related changes in gene and protein expression in skeletal muscle
by Wiley Credit: CC0 Public DomainNew research indicates that some age-related changes in gene and protein expression in the skeletal muscles of older individuals may be affected more by physical inactivity and chronic inflammation than primary aging, or intrinsic maturational processes. Physical inactivity and chronic inflammation are the most important drivers of secondary aging, or changes...
Red light can reduce blood glucose levels, says study
by City University London Credit: Pixabay from PexelsIn a new study appearing in the Journal of Biophotonics, researchers have found that 670 nanometers (nm) of red light stimulated energy production within mitochondria, leading to increased consumption of glucose. In particular, it led to a 27.7% reduction in blood glucose levels following glucose intake, and it reduced...
J-shaped curve apparent between dietary thiamine and worsening mental acuity
by British Medical Journal Credit: Pixabay/CC0 Public DomainThere seems to be a J-shaped curve between dietary thiamine (vitamin B1) and worsening mental acuity among cognitively healthy older people, suggests research published in the open-access journal General Psychiatry. The sweet spot seems to be a daily intake of 0.68 mg, below which there is relatively little impact....
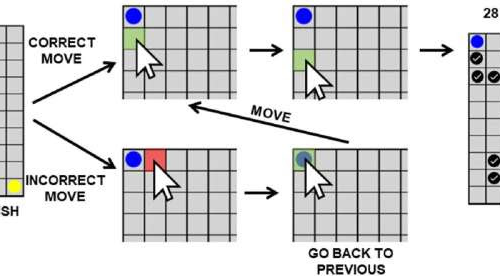
Playing video games may improve attention and memory, research finds
by Lero Depiction of two example sequences containing two correct moves (top) and an incorrect move and correction (bottom) for the Groton Maze Task. Each time a correct move is made, the corresponding tile flashes green. When an incorrect move is made, the corresponding tile flashes red. The right-most image highlights the 28 moves and...
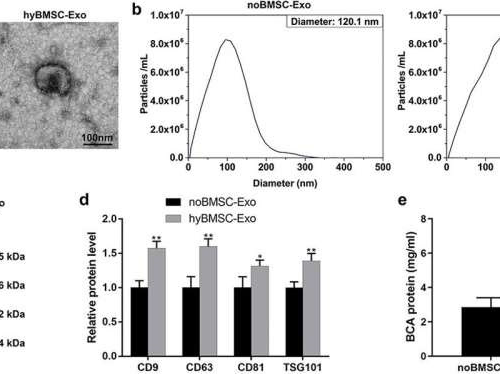
Researchers pioneer novel stem cell therapy for diabetic wound healing
by TranSpread Hypoxia facilitates exosome production and release from BMSCs. (a) Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) revealed the morphology of noBMSC-Exos and hyBMSC-Exos (scale bar: 100 nm). (b) The size distribution of noBMSC-Exos and hyBMSC-Exos was examined using nanoparticle tracking analysis (NTA). (c and d) Western blotting analysis for exosome surface marker proteins, including CD9, CD63,...
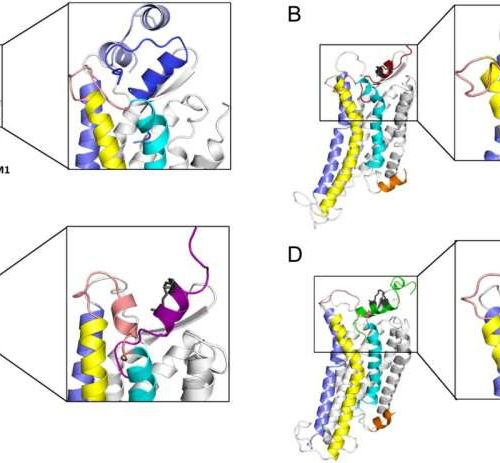
Modifying brain molecule relaxin-3 can potentially reduce side effects in treating anxiety, depression and more
by National University of Singapore An illustration of computer-modeled structures of complexes formed between RXFP3 and relaxin-3 or relaxin-3 B-chain stapled peptides. Credit: NUS Yong Loo Lin School of Medicine and University of Colombo, Sri LankaDrugs that treat conditions like depression and anxiety often come with varying side effects, as they regulate various functions within the...
Blocking key protein may halt progression of Alzheimer’s disease
by CU Anschutz Medical Campus Credit: CC0 Public DomainResearchers at the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus have found that inhibiting a key protein can stop the destruction of synapses and dendritic spines commonly seen in Alzheimer’s disease. The study, whose first author is Tyler Martinez, a student in the Pharmacology and Molecular Medicine Ph.D. program...