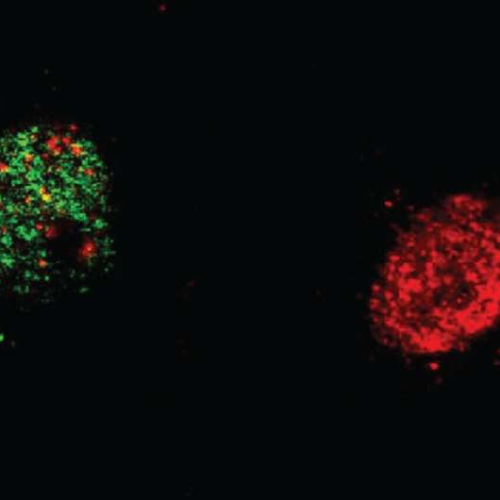
July 25, 2024 by Ecole Polytechnique Federale de Lausanne Neurons have variable levels of chromatin compaction, shown as different shades of red. The less compact a neuron, the more likely it is to be recruited into the memory trace (green). Credit: Giulia Santoni (EPFL)When we form a new memory, the brain undergoes physical and functional...
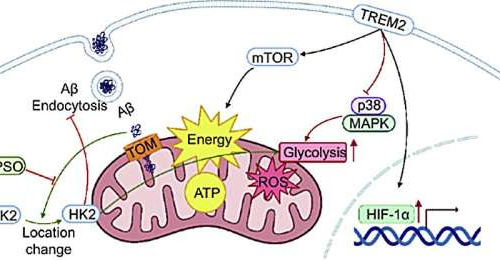
Exploring the interaction between microglial dysfunction and mitochondrial impairment in Alzheimer’s disease
July 25, 2024 by Tsinghua University Press Abnormal microglial energy metabolism in AD. Translocation of Aβ into microglial mitochondria by the outer membrane translocase (TOM) impairs mitochondrial function and inhibits phagocytosis. TREM2 promotes gene expression of the transcription factor HIF1α and mTOR signaling, but inhibits p38/MAPK signaling and glycolysis in microglia. TPSO inhibits the activation...
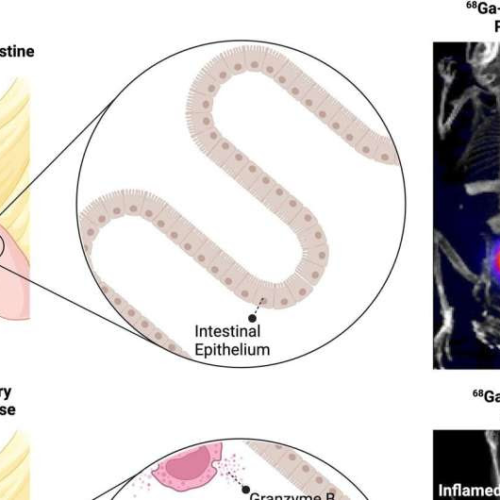
Novel PET imaging tool identifies early signs of inflammatory bowel disease and predicts response to treatment
July 25, 2024 by Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging Visual Abstract. Active bowel inflammation disrupts the bowel cell lining, which causes the inflammatory T cells to secrete Granzyme B into the extracellular space, progressively accentuating the inflammatory response through a feed-forward mechanism. In the normal or non-inflamed bowel, there is no extracellular Granzyme...
Researchers close in on new technology for objectively measuring pain
July 25, 2024 by Jesse Jenkins, New Jersey Institute of Technology Wunmi Sadik is the director of NJIT’s BioSensor Materials for Advanced Research and Technology (BioSMART) Center. Credit: NJITOn a scale of one to ten, how much pain do you feel? It’s a question many patients get from their doctor in the U.S. each day,...
CU Anschutz scientists identify key protein behind spread of shingles virus
NEWS RELEASE 25-JUL-2024 For the first time, researchers identify the mechanism that allows the varicella zoster virus to spread far from the infection site Peer-Reviewed PublicationUNIVERSITY OF COLORADO ANSCHUTZ MEDICAL CAMPUS VIDEO: THE VARICELLA ZOSTER VIRUS, WHICH RESIDES IN OVER 95% OF US, CAUSES CHICKEN POX AND THE MORE SERIOUS SHINGLES INFECTION. CUANSCHUTZ RESEARCHERS HAVE...
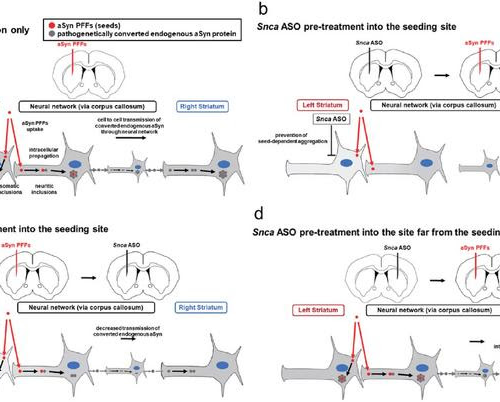
Antisense oligonucleotide treatment shows promise in treating Parkinson’s disease progression
NEWS RELEASE 25-JUL-2024 Peer-Reviewed PublicationTOKYO MEDICAL AND DENTAL UNIVERSITY IMAGE: RESEARCHERS FROM JAPAN INVESTIGATED HOW ASOS ADMINISTERED LOCALLY INTO THE BRAINS OF MICE MODELS FOR PARKINSON’S DISEASE CAN HELP PREVENT THE FORMATION AND SPREAD OF HARMFUL ASYN AGGREGATES THROUGH DIFFERENT REGIONS. THEIR FINDINGS SHOW ASOS COULD BE A PROMOTING THERAPEUTIC STRATEGY TO BOTH PREVENT AND...
UH engineer develops technique that enhances thermal imaging and infrared thermography for police, medical, military use
NEWS RELEASE 25-JUL-2024 Overcomes challenges faced by conventional thermal imaging, eliminates wavelength and temperature dependence Peer-Reviewed PublicationUNIVERSITY OF HOUSTON IMAGE: UNIVERSITY OF HOUSTON PROFESSOR OF ELECTRICAL AND COMPUTER ENGINEERING JIMING BAO IS SET TO IMPROVE THERMAL IMAGING AND INFRARED THERMOGRAPHY TECHNIQUES USED TO MEASURE AND VISUALIZE TEMPERATURE DISTRIBUTIONS WITHOUT DIRECT CONTACT WITH THE SUBJECT BEING...
Electrical currents may make body’s cancer-killing cells even better killers
NEWS RELEASE 25-JUL-2024 Peer-Reviewed PublicationTRINITY COLLEGE DUBLIN Scientists have discovered that electrical currents may make Natural Killer (NK) cells – our very own cancer-killing immune cells – even better killers, which could have significant implications for treating some cancers. The scientists found that Tumour Treating Fields (TTF) in the laboratory (which mimic exposure of brain...
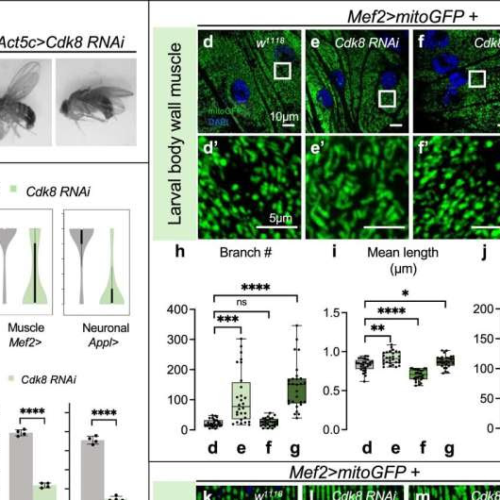
Fruit fly study identifies gene that may reverse Parkinson’s disease
JULY 24, 2024 by Simon Fraser University Cdk8 regulates mitochondrial morphology under physiological conditions. Credit: Nature Communications (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-47623-8Researchers at Simon Fraser University, in collaboration with a group from Baylor College of Medicine in Texas, have identified a gene that appears to reverse Parkinson’s disease symptoms in fruit flies. SFU’s Verheyen lab discovered that...
Mild COVID-19 can cause long-term cognitive losses, finds study
JULY 24, 2024 by Maria Fernanda Ziegler, FAPESP Credit: Unsplash/CC0 Public DomainMemory loss and attention deficit are frequent complaints of people who have survived severe COVID-19, but these and other cognitive impairments have also been observed in mild cases more than 18 months after the start of the infection, according to a study by researchers...