A mechanism for metabolic disease is traced to a defective cellular scaffolding that holds together the brain’s hunger cells. By Max Kozlov Neurons (artist’s illustration) that affect hunger lose their ability to sense insulin when encased by a sticky scaffolding.Credit: KTSDesign/Science Photo Library A build-up of sticky goo that traps neurons in an appetite-control centre...
NANOPARTICLES DELIVER DRUGS TO KILL CANCER CELLS IN MICE
SEPTEMBER 17TH, 2024POSTED BY U. CHICAGO(Credit: Getty Images) TAGS : CANCER, NANOTECHNOLOGYUNIVERSITY : UNIVERSITY OF CHICAGO Researchers have developed a nanomedicine that increases the penetration and accumulation of chemotherapy drugs in tumor tissues and effectively kills cancer cells in mice. The study in Science Advances addresses a limitation of chemotherapy. Although chemotherapy is the primary...
DEADLY SNAIL VENOM COULD MAKE DIABETES MEDICINES BETTER
SEPTEMBER 17TH, 2024POSTED BY SOPHIA FRIESEN – UNIVERSITY OF UTAH(Credit: Getty Images) TAGS DRUG : DEVELOPMENT, MEDICATIONS, SNAILS, VENOMUNIVERSITY : UNIVERSITY OF UTAH Scientists are finding clues for how to treat diabetes and hormone disorders in an unexpected place: a toxin from one of the most venomous animals on the planet. Researchers have identified a...
When serotonin dims the light
News Release 18-Sep-2024 Neuroscience Peer-Reviewed PublicationRuhr-University Bochum image: Dirk Jancke (left) and Ruxandra Barzan from the Bochum research team Credit: RUB, Kramer In the jungle of serotonin receptors Receptors mediate the transmission of information between nerve cells. The release of serotonin alters nerve cell activities throughout the brain. At least 14 types of serotonergic receptors...
Could your phone detect hepatic encephalopathy by listening to you read?
News Release 18-Sep-2024 A novel model attempts to discern symptoms from recordings of a patient’s speech Peer-Reviewed PublicationMichigan Medicine – University of Michigan Research from the University of Michigan suggests that one day a phone app could be able to detect the development of hepatic encephalopathy in patients just by listening to them speak. The...
Neuralink Secures FDA Breakthrough Status for Vision-Restoring ‘Blindsight’ Implant
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY NEWS Elon Musk’s brain-chip venture, Neuralink, announced that it has earned the U.S. Food and Drug Administration’s (FDA) “breakthrough device” designation for its experimental vision-restoring implant, Blindsight. Image credit: Steve Jurvetson via Flickr, CC BY 2.0This significant milestone marks a key step forward for Neuralink as it continues to develop cutting-edge brain-chip...
Early treatment significantly reduces long-term disability in children with multiple sclerosis, new study finds
September 17, 2024 by European Committee for Treatment and Research in Multiple Sclerosis Credit: Unsplash/CC0 Public DomainNew research presented today at European Committee for Treatment and Research in Multiple Sclerosis 2024 reveals that initiating monoclonal antibody therapy during childhood, rather than delaying treatment until early adulthood, significantly reduces long-term disability in multiple sclerosis (MS) patients....
Abnormal electrolyte levels in people with eating disorders may increase risk of death, poor health outcomes
September 17, 2024 by ICES Infographic. Credit: ICESA study published in The Lancet Psychiatry found that 32% of individuals with an eating disorder had abnormal electrolyte levels, which were associated with a higher risk of death from any cause. The article is titled “Adverse outcomes and mortality in individuals with eating disorder-related electrolyte abnormalities: a...
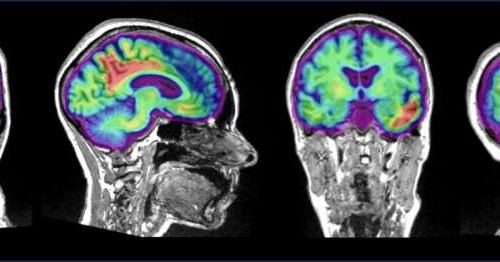
Understanding changes in pre-clinical Alzheimer’s disease: Study finds two proteins impact brain activity differently
September 18, 2024 by McGill University Credit: Jonathan Gallego RudolfAmyloid-beta and tau proteins have long been associated with Alzheimer’s disease. The pathological buildup of these proteins leads to cognitive decline in people with the disease. How it does that, though, remains poorly understood. A new study from the labs of Sylvain Baillet at The Neuro...
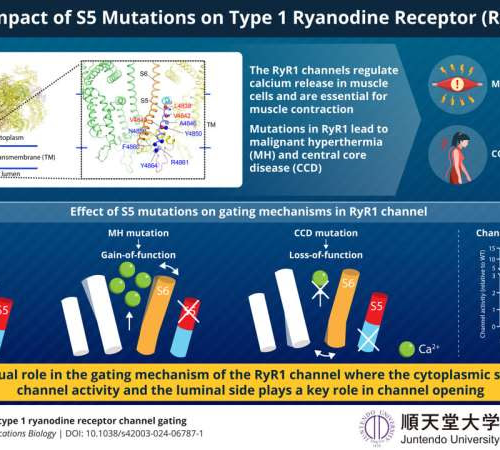
Scientists discover how mutations affect calcium release channel and impact muscle disorders
September 18, 2024 by Juntendo University Research Promotion Center S5 mutations disrupt RyR1 channel function, influencing both channel activity and gating mechanisms. This impacts the release of calcium and affects muscle contractions, leading to severe muscle diseases such as malignant hyperthermia and central core disease. Credit: Associate Professor Takashi Murayama from Juntendo University, Japan and...