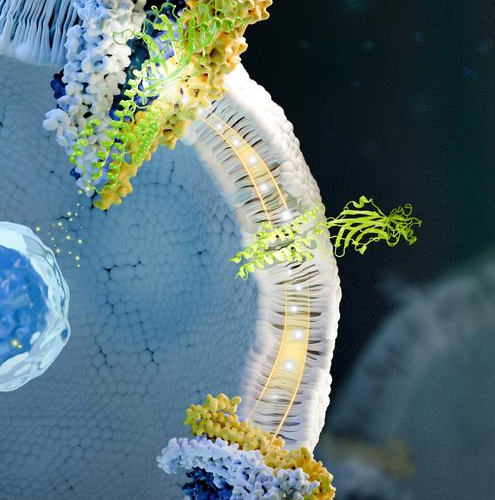
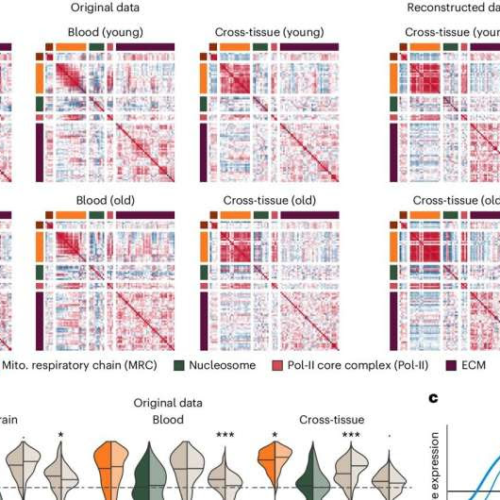
September 3, 2024 by Gabriele Meseg-Rutzen, University of Cologne Representative gene–gene relationship changes with age, captured by pairwise correlation and a GRN-based approach. Credit: Nature Aging (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s43587-024-00696-yGene regulation in our cells—the decision on which proteins are produced for the various processes of the cell—is strictly regulated. It has long been assumed that this...
Aspirin for CRC Prevention May Work Best in Adults With Unhealthy Lifestyles
Megan Brooks August 27, 2024 TOPLINE:Aspirin provides greater protection against colorectal cancer (CRC) in people with unhealthy lifestyles, particularly smokers with higher body weight, new data suggest. METHODOLOGY:Aspirin is an established agent for CRC prevention. Whether individuals with more lifestyle risk factors might derive greater benefit from aspirin remains unclear.Researchers analyzed regular aspirin use (defined...
A new drug target for psychiatric disorders
News Release 4-Sep-2024 Misha Kudryshev’s lab at the Max Delbrück Center has identified a potentially new drug target for serotonin, which is involved in depression and schizophrenia Peer-Reviewed PublicationMax Delbrück Center for Molecular Medicine in the Helmholtz Association image: Researchers have identified an intermediate form of the 5-HT3A serotonin receptor (blue). In its final form,...
Hormone therapy tied to less biological aging in postmenopausal women
September 4, 2024 by Lori Solomon Postmenopausal women who use hormone therapy (HT) are biologically younger than those not receiving HT, according to a study published online Aug. 29 in JAMA Network Open. Yufan Liu and Chenglong Li, Ph.D., from Peking University in Beijing, evaluated the association between HT use and discrepancies between chronological and...
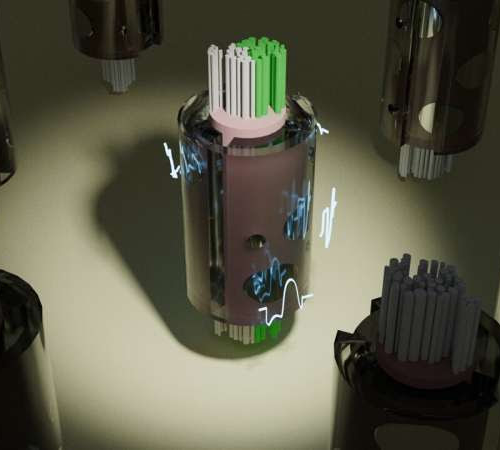
Optimizing electrical stimulation therapies with machine learning
September 4, 2024 by Michaela Martinez, Duke University A new tool to model peripheral nerve stimulation rapidly discovered optimal electrical waveforms (white traces) which, when delivered through the metal contacts of a cuff electrode placed on the vagus nerve, activates only therapeutic target fibers (in green) to avoid side effects. The optimization process involves testing...
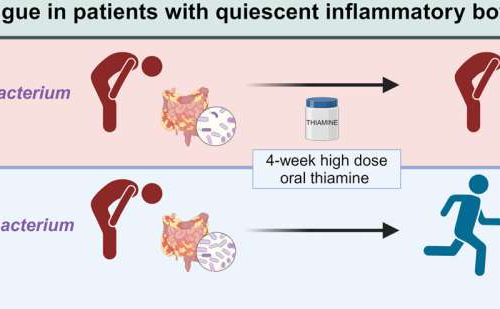
Vitamin B1 linked to reduced fatigue in some inflammatory bowel disease patients
September 3, 2024 by Aarhus University Graphical abstract. Credit: Gastro Hep Advances (2024). DOI: 10.1016/j.gastha.2024.08.012Fatigue is a common and often debilitating companion for people with inflammatory bowel conditions. Now, a new Danish study provides insight into why vitamin B1—also known as thiamine—helps some patients regain their energy, while others do not experience the same effect....
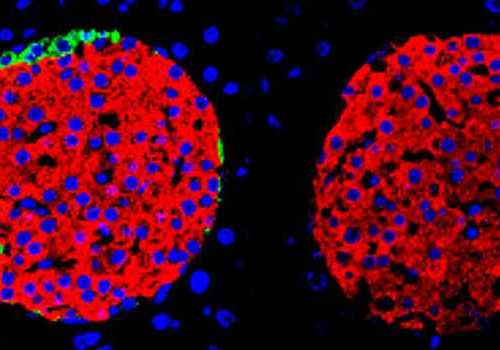
Beta cells alone can regulate blood sugar levels, study finds
September 3, 2024 by University of Geneva Pancreatic islets from adult mice. On the left, islet composed of different types of endocrine cells. Right: pancreatic islet composed solely of beta cells. Credit: Laboratoire Pedro Herrera – UNIGEOur glycemic balance is based on the ability of the pancreatic beta cells to detect glucose and secrete insulin...
Low-frequency rTMS improves urinary incontinence after stroke
September 3, 2024 by Lori Solomon Four weeks of low-frequency repeated transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS) positively impacts poststroke urinary incontinence, according to a study published online Aug. 8 in Scientific Reports. Jialu Chen, from the Second Affiliated Hospital of Chongqing Medical University in China, and colleagues investigated the therapeutic effect of low-frequency rTMS on the...
Breaking the link between obesity and atrial fibrillation with a new cellular target
News Release 4-Sep-2024 Peer-Reviewed PublicationUniversity of Illinois Chicago A cellular link between obesity and atrial fibrillation — a heart condition that afflicts over 33 million people worldwide — presents a promising target for new therapies, researchers from the University of Illinois Chicago report. Obesity is among the leading causes of atrial fibrillation, an irregular heart...
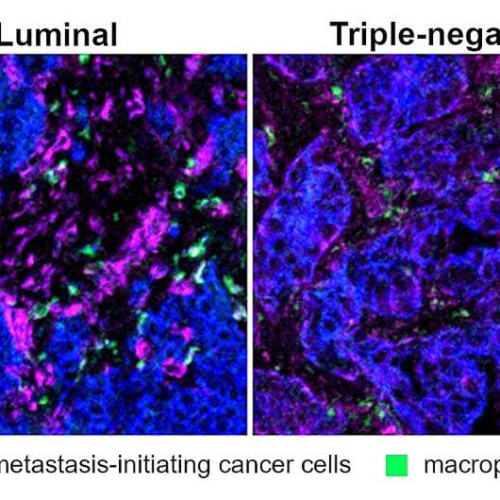
Scientists identify potential new immune system target to head off the spread of breast cancer cells
September 3, 2024 by Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine In a sea of cancer cells (blue), macrophages (green) are close neighbors to metastatic-initiating cancer cells (magenta). Credit: Won Jin Ho, Johns Hopkins Kimmel Cancer CenterIn a study using human breast cancer cells, scientists say they have potentially identified immune system white blood cells that...