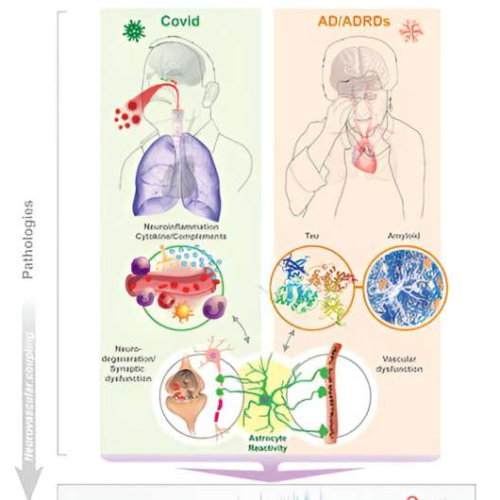
September 2, 2024 by Hillary Smith, University of Kentucky UK researchers find Alzheimer’s-like brain changes in long COVID patientsResearch illustration by Tom Dolan. Credit: University of KentuckyNew research from the University of Kentucky’s Sanders-Brown Center on Aging shows compelling evidence that the cognitive impairments observed in long COVID patients share striking similarities with those seen...
Long noncoding RNAs emerge as promising biomarkers for mood disorders
September 2, 2024 by Genomic Press The network plot illustrates the interconnectedness of three distinct mood disorders (major depressive disorder: MDD, bipolar disorder: BD, and suicidal behavior: SB) based on shared lncRNA profiles detected in the peripheral circulation. Credit: Genomic Psychiatry (2024) DOI: 10.61373/gp024i.0046In a review article, researchers have uncovered compelling evidence that long noncoding...
Two-in-one treatment could hold promise for incurable brain cancer, mouse study shows
September 2, 2024 by Walter and Eliza Hall Institute of Medical Research Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cells, genetically engineered leukocytes (white blood cells), in their fight against glioblastoma, a deadly type of glioma. Credit: Journal for ImmunoTherapy of Cancer (2024). DOI: 10.1136/jitc-2024-009486Researchers at WEHI have identified a promising new two-in-one treatment that not only...
Longevity Breakthrough: New Treatment Reverses Multiple Hallmarks of Aging
By University of Texas M. D. Anderson Cancer Center September 2, 2024 Researchers have shown that restoring youthful levels of a telomerase subunit can significantly alleviate aging signs in models, potentially impacting age-related diseases like Alzheimer’s and cancer. Their study identified a compound that maintains the telomerase reverse transcriptase (TERT) levels, reducing cellular aging, inflammation,...
Scientists uncover the role of dopamine in mediating short-term and long-term memory dynamics
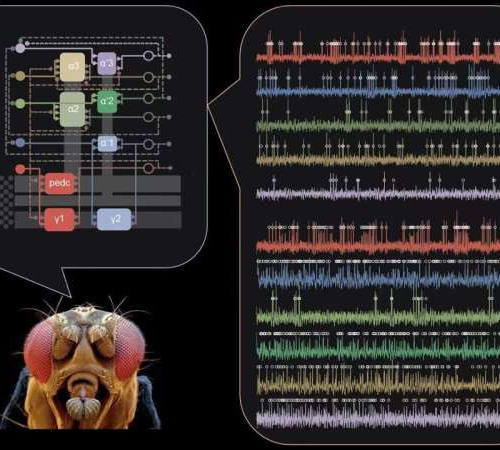
August 26, 2024 by Tejasri Gururaj , Medical Xpress Neural activity gives information about how fruit flies respond to various sensory stimuli, revealing insights into how they process and encode these experiences into short-term and long-term memories. Credit: Cheng Huang. Fly image credit: https://prints.sciencesource.com/featured/6-fruit-fly-drosophila-melanogaster-oliver-meckes-eye-of-science.html.In a recent study published in Nature, researchers from Stanford University and...
Kidney disease medication found to reduce risk of cardiovascular death in certain heart failure patients in new study
By Jacqueline Howard, CNNPublished 6:00 AM EDT, Sun September 1, 2024 Few treatments are available for a type of heart failure that includes mildly reduced or preserved ejection fraction. simonkr/E+/Getty Images/File A medication that is currently used for chronic kidney disease in patients with type 2 diabetes has been found to reduce the risk of...
Blood test of three factors predicts 30-year risk of heart attack, stroke and cardiovascular death in American women
News Release 31-Aug-2024 A study led by Brigham researchers finds that measuring three modifiable factors together provided greater information on risk compared to any marker used alone; inflammation shown to be at least as important as cholesterol, yet rarely measured Peer-Reviewed PublicationBrigham and Women’s Hospital KEY TAKEAWAYS Brigham researchers assessed data from more than 27,000...
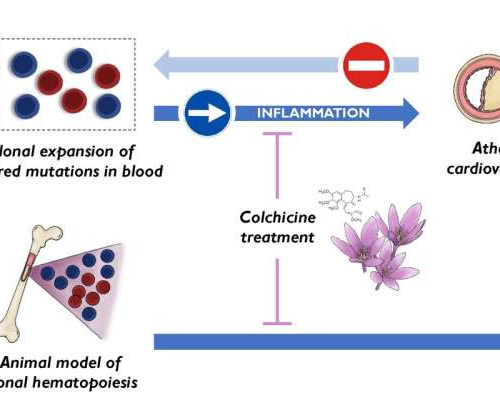
Scientists discover a new cardiovascular risk factor and identify a drug able to reduce its effects
August 30, 2024 by Centro Nacional de Investigaciones Cardiovasculares Carlos III (F.S.P.) Summary of main findings by CNIC researchers. Clonal hematopoiesis and the expansion of blood cells carrying certain acquired mutations represent a new cause of atherosclerosis and cardiovascular disease, not a consequence of it. The effects of some of these mutations can be attenuated...
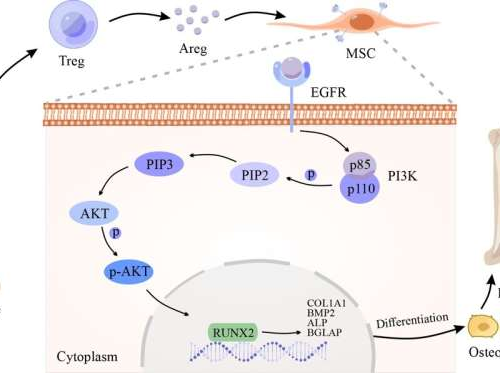
A distinct ‘repair’ role of regulatory T cells in fracture healing
August 30, 2024by Higher Education Press Credit: Tingting Wu, Lulu Wang, Chen Jian, Zhenhe Zhang, Ruiyin Zeng, Bobin Mi, Guohui Liu, Yu Zhang, Chen ShiA study in Frontiers of Medicine uncovers a unique reparative function of regulatory T cells (Tregs) in the process of fracture healing, a discovery that adds a new dimension to our...
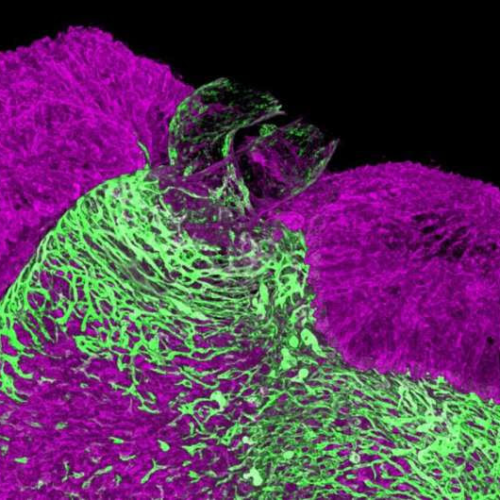
New clues on how the heart makes arteries
August 30, 2024 by Max Delbrück Center for Molecular Medicine A 3D image of an embryonic mouse heart. Endothelial cells vascularize the heart muscle walls (shown in green). This process establishes the coronary vasculature that nourishes the heart muscle. Credit: Max Delbrück CenterA team led by Dr. Elena Cano in the Integrative Vascular Biology Lab...