September 16, 2024 by Lancet Credit: CC0 Public DomainMore than 39 million people around the world could die from antibiotic-resistant infections over the next 25 years, according to a study published in The Lancet. The new study by the Global Research on Antimicrobial Resistance (GRAM) Project is the first global analysis of antimicrobial resistance (AMR)...
Researchers discover new blood group system
September 16, 2024 by University of Bristol Credit: Unsplash/CC0 Public DomainThe discovery of a new blood group, MAL, has solved a 50-year-old mystery. Researchers from NHS Blood and Transplant (Bristol), NHSBT’s International Blood Group Reference Laboratory (IBGRL) and the University of Bristol identified the genetic background of the previously known but mysterious AnWj blood group...
Researchers find increased risk of autoimmune disease in stone bench-top industry, call for better screening
September 16, 2024 by Monash University Credit: Pixabay/CC0 Public DomainIn what could be a preview of an even greater disease burden for those workers in the artificial stone benchtop industry, Monash researchers have conducted a large study finding that those workers exposed to silica dust show a higher incidence of blood markers that are the...
These Creatures Occupy ‘Third State’ Beyond Life And Death, Scientists Say
16 September 2024ByPeter A Noble & Alex Pozhitkov, The Conversation Biobots could one day be engineered to deliver drugs and clear up arterial plaque. (Kriegman et al. 2020/PNAS, CC BY-SA)Life and death are traditionally viewed as opposites. But the emergence of new multicellular life-forms from the cells of a dead organism introduces a “third state”...
100x Improvement in Sight Seen After Gene Therapy Trial
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY NEWS The vision of people with a rare inherited condition that causes them to lose much of their sight early in childhood was 100 times better after they received gene therapy to address the genetic mutation causing it. Some patients even experienced a 10,000-fold improvement in their vision after receiving the highest...
Innovative technology may enable early diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease
News Release 16-Sep-2024 Breakthrough from Tel Aviv University: Peer-Reviewed PublicationTel-Aviv University image: Research team (Left to right) Prof. Uri Ashery and PhD candidate Ofir Sade. Credit: Tel Aviv University The researchers: “Our technology will enable the detection of initial signs of Parkinson’s at the cellular level up to 20 years before the first motor symptoms...
Monoclonal antibodies offer hope for tackling antimicrobial resistance
News Release 16-Sep-2024 Peer-Reviewed PublicationUniversity of Cambridge Monoclonal antibodies – treatments developed by cloning a cell that makes an antibody – could help provide an answer to the growing problem of antimicrobial resistance, say scientists. A team lead by researchers at the University of Cambridge has developed a monoclonal antibody drug, using a technique involving...
New model sheds light on the chemistry surrounding peptide helices
News Release 16-Sep-2024 Peer-Reviewed PublicationCenter for Research in Biological Chemistry and Molecular Materials (CiQUS) image: Dr. Julián Bergueiro at CiQUS: Credit: CiQUS – USC Helices are structures found naturally in many important molecules, such as proteins. These helices possess a twist that depends on the arrangement of their basic components. By understanding how a helix...
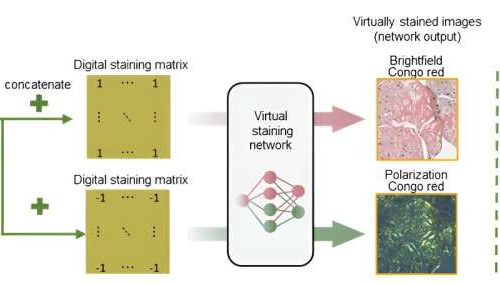
AI-based tissue staining can detect amyloid deposits without chemical stains or polarization microscopy
September 16, 2024 by UCLA Engineering Institute for Technology Advancement Virtual birefringence imaging and histological staining of amyloid deposits in label-free tissue. Virtual staining network and digital staining matrix framework generate two output images (brightfield and birefringence image channels), eliminating the need for polarization imaging and traditional chemical stains like Congo red used in clinical...
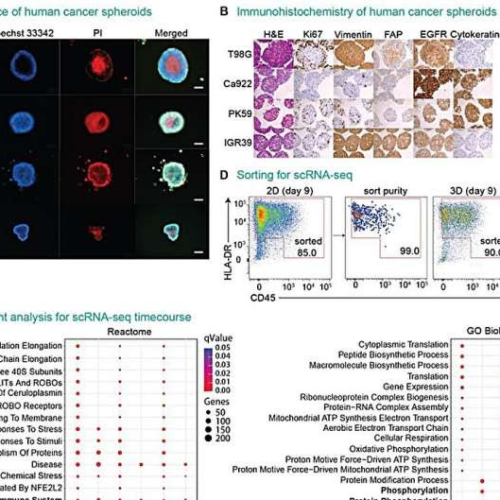
Reprogramming cancer cells to attack themselves
September 16, 2024 by Bob Yirka , Medical Xpress cDC1 reprogramming progresses in human cancer spheroids. Credit: Science (2024). DOI: 10.1126/science.adn9083A team of health and medical researchers affiliated with a host of institutions across Sweden has tested the possibility of reprogramming cancer cells into cDC1 cells as a means for destroying the protective shield around...