Sara Novak Brain fog is one of the most common, persistent complaints in patients with long COVID. It affects as many as 46% of patients who also deal with other cognitive concerns like memory loss and difficulty concentrating. Now, researchers believe they know why. A new study has found that these symptoms may be the...
Year: <span>2024</span>
Fibroblasts in the penis are more important for erectile function than previously thought
by Karolinska Institutet Credit: CC0 Public Domain Regular erections could be important for maintaining erectile function, according to a new study on mice published in Science by researchers at Karolinska Institutet. “We discovered that an increased frequency of erections leads to more fibroblasts that enable erection and vice versa, that a decreased frequency results in fewer...
Think Outside the Traditional Toolbox to Treat Itch
Damian McNamara ORLANDO — “Itch may not be as sexy as Mohs surgery or aesthetic procedures,” but treating it is important and meaningful to patients, particularly those who’ve found little relief previously, Shawn G. Kwatra, MD, said at the annual ODAC Dermatology, Aesthetic & Surgery Conference. Chronic itch is common, with presentations that range from...
How emotions affect word retrieval in people with aphasia
by Emily Caldwell, The Ohio State University Credit: Pixabay/CC0 Public DomainPeople with aphasia have more trouble coming up with words they want to use when they’re prompted by images and words that carry negative emotional meaning, new research suggests. The study involved individuals whose language limitations resulted from damage to the brain caused by a stroke—the...
Novel approach improves heart failure outcomes in animal model
by Ana María Rodríguez, Baylor College of Medicine Credit: Pixabay/CC0 Public DomainIn 2020, heart failure affected about 6.5 million people in the U.S. and 23 million around the world. Despite recent advances, the five-year survival rate remains approximately 50%, indicating an urgent need for a novel perspective for treating this condition. A new approach described in...
Oral interleukin-23-receptor antagonist peptide shows greater efficacy than placebo for plaque psoriasis
by Elana Gotkine For patients with moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis, the interleukin-23-receptor antagonist peptide JNJ-77242113 shows greater efficacy than placebo, according to a study published in the Feb. 8 issue of the New England Journal of Medicine. Robert Bissonnette, M.D., from Innovaderm Research in Montreal, and colleagues conducted a phase 2 dose-finding trial involving 255 patients...
Q&A: Should heart patients consider taking weight loss medications?
by Noah Fromson, University of Michigan Credit: Unsplash/CC0 Public DomainOver the last year, prescriptions for medications that can accelerate weight loss in people with diabetes or without it have skyrocketed. Known by brand names like Ozempic and Wegovy, the drugs have gotten a lot of attention for their cost, their potential impact on weight, and their...
New PET tracer detects inflammatory arthritis before symptoms appear
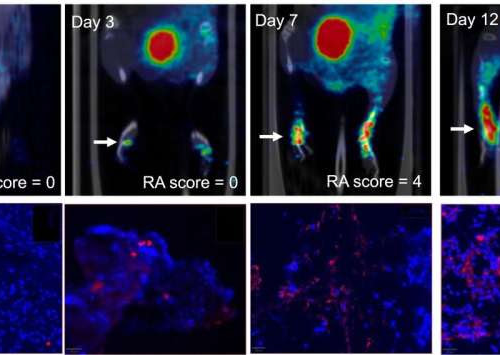
by Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging A) PET images of [68Ga]Ga-DOTA-ZCAM241 uptake at baseline and 3, 7, and 12 days after injection as inflammatory arthritis developed in single representative individual mouse. Images are normalized to SUV of 0.5 for direct comparison between time points. (B) CD69 immunofluorescence Sytox (Thermo Fisher Scientific) staining of...
Scientists gain new insights into how small intestine works
by Ernie Mundell It was the ancient Greeks who first divided the 20-foot length of the small intestine into three parts: The duodenum, the jejunum and the ileum. However, the organ may finally be ready for an update: U.S. researchers say the small intestine is actually comprised of five distinct segments, each being responsible for...
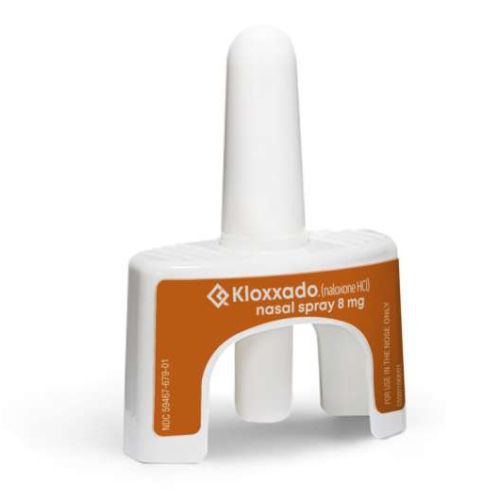
Higher-dose naloxone spray didn’t save more lives, researchers find
by Mike Stobbe This image provided by Hikma Pharmaceuticals shows the company’s nasal spray drug Kloxxado, containing 8 milligrams of naloxone. A study published Thursday, Feb. 8, 2024 finds that a new, higher-dose nasal spray for reversing opioid overdoses didn’t save more lives than the standard dose. However, it was tied to more vomiting and...