The American Thyroid Association (ATA) is the foremost professional organization of doctors in the world committed to advancing thyroid patient care, educating the public about thyroid health, and doing research to help with the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of thyroid illnesses.
Thyroid illness affects almost 20 million Americans. But as many as 60% are unaware they are being affected or experiencing symptoms.
The thyroid is crucial for the excellent health and vitality of numerous body systems and activities. It covers everything from development and growth to normal metabolism. Even the excellent functioning of your kidneys and heart depend on your thyroid.
What is Thyroid?
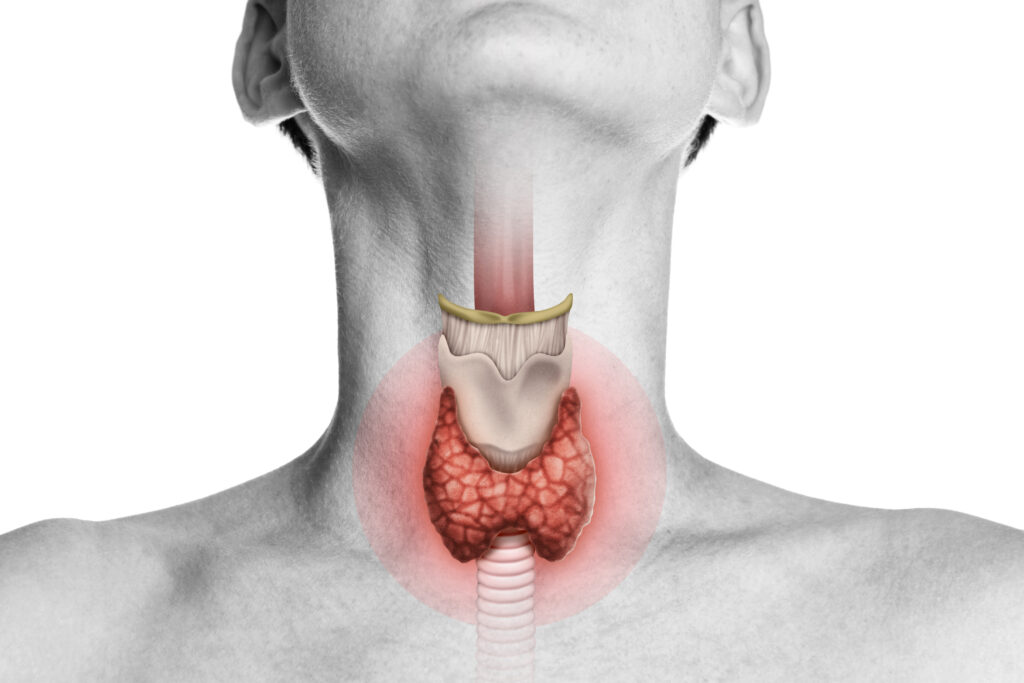
The thyroid is a gland that controls protein synthesis and metabolism. It controls the health of the heart, nervous system, and skin. It also controls calcium levels, menstrual cycles, and cholesterol levels.
Even though the thyroid is a little gland in the lower neck, it significantly impacts your health. The thyroid gland, which resembles a butterfly, produces thyroid hormones that aid in keeping your body warm and using energy. The heart, muscles, brain, and other organs usually function as a result of thyroid hormones.
Some of the most common thyroid problems include:
– Goiter – enlargement of the thyroid gland.
– Hyperthyroidism – when the thyroid gland makes more thyroid hormones than the body needs.
– Hypothyroidism – when the thyroid gland does not make enough thyroid hormones.
– Thyroid cancer
– Thyroid nodules – lumps in the thyroid gland.
– Thyroiditis – swelling of the thyroid.
What are the Symptoms of Thyroid?
– Unexplained weight gain or loss.
– Temperature-sensitive (either hot and sweaty or cold).
– Fatigue and sleep issues.
– Depression, anxiety, or other mood disorders.
– Swelling of the neck.
– Trouble swallowing or breathing.
– Changes in your hair, nails & skin.
– Persistent constipation, diarrhea, loose stools, or irritable bowel syndrome.
– Menstruation and fertility issues.
– Eye problems (dryness, blurred vision, swollen, puffy eyes, or proptosis).
– Muscular pains and joint discomfort.
Risk Factors of Thyroid Disorders
Although anyone can have hypothyroid, the following factors put you at higher risk:
– If you are a female.
– If you have a family history of thyroid disease.
– If you have type 1 diabetes or celiac disease.
– If you have received treatment for hyperthyroidism.
– If you have received radiation to your neck or upper chest.
– If you have had thyroid surgery.
How Thyroid disorders affect Men vs. Women
Men
Contrary to popular belief, men account for 20% of cases of thyroid disease, which typically is assumed only to affect women.
Many of the symptoms that women with thyroid illness experience affect men, although some are unique to men. These signs may frequently go unnoticed because thyroid disease is not necessarily a cause of them. These signs could consist of the following:
– Delayed ejaculation
– Erectile dysfunction
– Gynecomastia (male breast enlargement)
– Hair loss
– Low sex drive
– Low sperm count
– Loss of muscle mass
– Lowered testosterone levels
Women
An issue with the thyroid will eventually impact 1 in 8 women. About ten times as many women as men are at risk. Your menstrual cycle or fertility may be affected if you have a thyroid disease. This is due to the several ways in which the hormones your thyroid gland produces might impact your reproductive system.
– Girls with thyroid issues may experience a delayed or accelerated beginning of puberty.
– Your menstrual cycle may become lighter or heavier if your thyroid hormone levels are abnormal. Thyroid conditions occasionally cause periods to become irregular or even stop altogether.
– If thyroid conditions stop your ovaries from releasing mature eggs, this can affect your ability to get pregnant. If your thyroid is underactive, you may also be more likely to develop ovarian cysts.
– There is a chance that a thyroid condition could result in difficulties if you are pregnant. While hypothyroidism could increase your risk of early labor, miscarriage, and other significant issues, hyperthyroidism can increase the likelihood of severe morning sickness.
– Early menopause risk can be increased by thyroid conditions (in your early 40s or earlier).
Testing for Thyroid Problems
You can detect thyroid problems early with routine testing. Your doctor may prescribe tests to examine your thyroid as part of your yearly exam. They might start with a series of blood examinations like these:
– Thyroid blood tests.
– Ultrasound.
– Thyroid scan.
How to Manage your Thyroid
Consult an expert to assist you in tracking and managing your thyroid problems. Get regular thyroid examinations to determine whether you need to adjust your prescription dosage and take your prescriptions precisely as directed. To help manage thyroid disease and decrease its consequences, you should practice the following preventative measures:
– Avoid packaged foods.
– Practice good sleep hygiene.
– Get daily sunlight.
– Exercise regularly.
– Manage stress better.
– Quit smoking.
– Have vitamins, proteins, and whole grains.
Your thyroid gland produces hormones essential for metabolism, growth, and development in your body. Several disorders might impact your thyroid’s functionality.
It’s best to visit your healthcare practitioner if you have a thyroid issue. The diagnosis and treatment of thyroid problems are simple. Additionally, it’s crucial to ensure your thyroid examination is part of your yearly physical.
How often should I test my thyroid?
If you have hyperthyroidism, it’s advised that you test your thyroid function every month and once a year if you have hypothyroidism. Regardless of your diagnosis, you can still test for thyroid disease at home using our thyroid blood test kits.

Leave a Reply