by KAIST
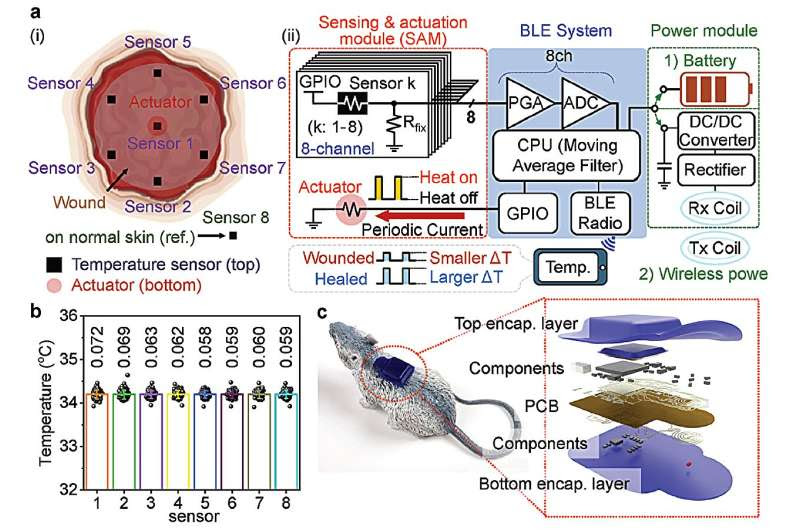
Schematic illustrations and diagrams of real-time wound monitoring systems. Credit: Advanced Healthcare Materials (2023). DOI: 10.1002/adhm.202302797
A KAIST research team has developed an effective wireless system that monitors the wound healing process by tracking the spatiotemporal temperature changes and heat transfer characteristics of damaged areas such as diabetic wounds.
The research team led by Professor Kyeongha Kwon from KAIST’s School of Electrical Engineering, in association with Chung-Ang University professor Hanjun Ryu, developed digital health care technology that tracks the wound healing process in real-time, which allows appropriate treatments to be administered.
The skin serves as a barrier protecting the body from harmful substances. Therefore, damage to the skin may cause severe health risks to patients in need of intensive care. Especially in the case of diabetic patients, chronic wounds are easily formed due to complications in normal blood circulation and the wound healing process.
In the United States alone, hundreds of billions of dollars of medical costs stem from regenerating the skin from such wounds. While various methods exist to promote wound healing, personalized management is essential depending on the condition of each patient’s wounds.
Accordingly, the research team tracked the heating response within the wound by utilizing the differences in temperature between the damaged area and the surrounding healthy skin. They then measured heat transfer characteristics to observe moisture changes near the skin surface, ultimately establishing a basis for understanding the formation process of scar tissue.
The team conducted experiments using diabetic mice models regarding the delay in wound healing under pathological conditions, and it was demonstrated that the collected data accurately tracks the wound healing process and the formation of scar tissue.
To minimize the tissue damage that may occur in the process of removing the tracking device after healing, the system integrates biodegradable sensor modules capable of natural decomposition within the body. These biodegradable modules disintegrate within the body after use, thus reducing the risk of additional discomfort or tissue damage upon device removal. Furthermore, the device could one day be used for monitoring inside the wound area as there is no need for removal.
Professor Kyeongha Kwon, who led the research, anticipates that continuous monitoring of wound temperature and heat transfer characteristics will enable medical professionals to more accurately assess the status of diabetic patients’ wounds and provide appropriate treatment.
He further predicted that the implementation of biodegradable sensors allows for the safe decomposition of the device after wound healing without the need for removal, making live monitoring possible not only in hospitals but also at home.
The research team plans to integrate antimicrobial materials into this device, aiming to expand its technological capabilities to enable the observation and prevention of inflammatory responses, bacterial infections, and other complications. The goal is to provide a multi-purpose wound monitoring platform capable of real-time antimicrobial monitoring in hospitals or homes by detecting changes in temperature and heat transfer characteristics indicative of infection levels.
The work is published in the journal Advanced Healthcare Materials.
More information: Hanjun Ryu et al, Materials and Device Designs for Wireless Monitoring of Temperature and Thermal Transport Properties of Wound Beds during Healing, Advanced Healthcare Materials (2023). DOI: 10.1002/adhm.202302797
Provided by KAIST

Leave a Reply