The accumulation of amyloid-beta and tau proteins in the brain is linked to Alzheimer’s disease, and now research shows that such accumulation can disrupt connections between brain structures important for memory. The new study, led by investigators at Harvard Medical School and Massachusetts General Hospital and published in PNAS, revealed that these disrupted connections were present years before...
Category: <span>Alzheimer’s</span>
‘Stressed’ cells offer clues to eliminating build-up of toxic proteins in dementia
by University of Cambridge It’s often said that a little stress can be good for you. Now scientists have shown that the same may be true for cells, uncovering a newly-discovered mechanism that might help prevent the build-up of tangles of proteins commonly seen in dementia. A characteristic of diseases such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s—collectively...
Study preserves memory in mice, offering promising new basis for active immunization against Alzheimer’s disease
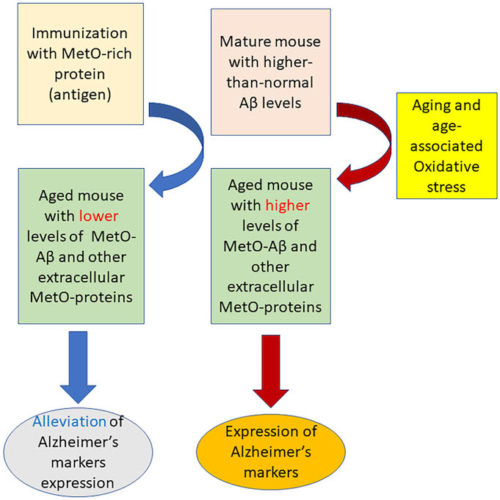
UNIVERSITY OF KANSAS IMAGE: IN A SERIES OF TESTS, KU RESEARCHERS ASSESSED THE MEMORY OF INJECTED MICE AGAINST SIMILAR MICE THAT DIDN’T RECEIVE THE CORN-BASED METHIONINE SULFOXIDE. CREDIT: SMITH, ET AL. LAWRENCE — During experiments in animal models, researchers at the University of Kansas have discovered a possible new approach to immunization against Alzheimer’s disease (AD)....
Study of promising Alzheimer’s marker in blood prompts warning about brain-boosting supplements
by University of California – San Diego Credit: Unsplash/CC0 Public Domain Elevated levels of an enzyme called PHGDH in the blood of older adults could be an early warning sign of Alzheimer’s disease, and a study led by the University of California San Diego provides new evidence to support this claim. In analyzing brain tissue,...
How the Discovery of an Alzheimer’s Tipping Point Could Improve Drug Trials
Researchers have known for many years that Alzheimer’s disease involves two proteins called amyloid-beta and tau, and that interaction drives the spread of neurodegeneration. What hasn’t been clear is where and how those interactions occur over time as the disease progresses. In a study published in the journal Neuron, neurologist William Seeley, MD, and his colleagues at...
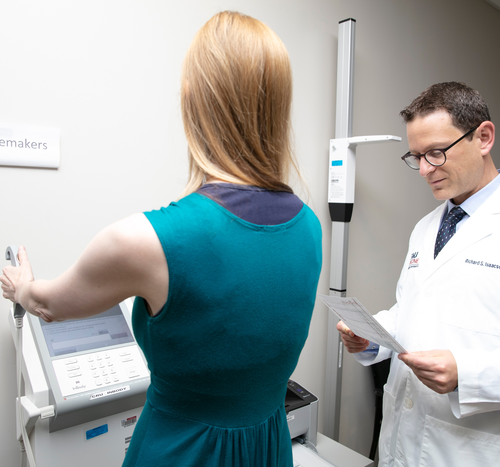
When it comes to preventing Alzheimer’s, women and men are not created equal
FLORIDA ATLANTIC UNIVERSITY IMAGE: RICHARD ISAACSON, M.D., DIRECTOR, ALZHEIMER’S PREVENTION CLINIC IN THE CENTER FOR BRAIN HEALTH AT FAU’S SCHMIDT COLLEGE OF MEDICINE, MEASURES A PATIENT’S PERCENTAGE OF BODY FAT AND MUSCLE MASS OVER TIME TO EVALUATE RESPONSE TO THERAPIES AND HELP REFINE EXERCISE AND NUTRITION PLANS. CREDIT: FLORIDA ATLANTIC UNIVERSITY After increasing age, the...
Interferon drives cognitive impairment in Alzheimer’s disease model
by Baylor College of Medicine Credit: CC0 Public Domain Alzheimer’s disease (AD), the most common type of dementia, progressively impairs memory, concentration and the ability to learn new things and accomplish everyday activities. Although scientists do not yet fully understand the causes of cognitive impairment associated with AD, a group of researchers at Baylor College...
A potential target for Alzheimer’s treatment? Researchers unearth new immune response pathway
Lei Lei Wu News Reporter Most Alzheimer’s drugs, including Biogen’s aducanumab (Aduhelm) and Eli Lilly’s donanemab, target amyloid plaques, misfolded protein clumps that build up in the brain, which are a hallmark of Alzheimer’s disease. However, researchers from Weill Cornell have uncovered an alternate immune response pathway that could be a potential target for new...
Key signaling pathway in immune cells could be new Alzheimer’s target
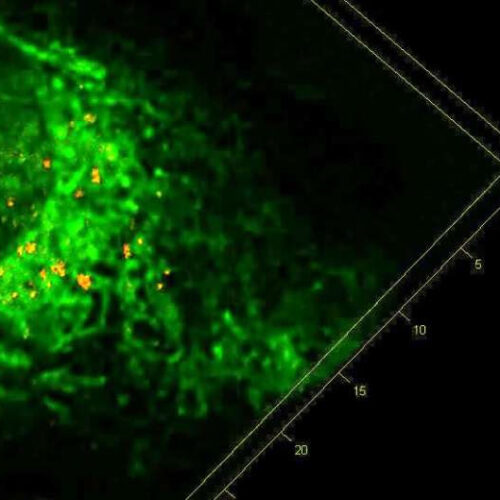
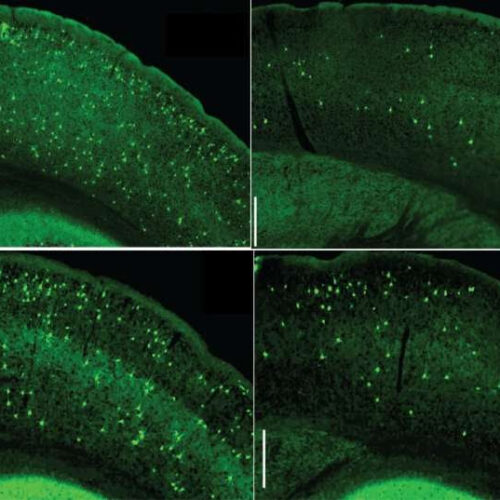
by Weill Cornell Medical College Microglial NF-kB accelerates the seeding and spread of tau aggregates in the cortex of mice inoculated with tau seeds. Depleting microglia (top right) or inhibiting microglia NF-kB (bottom right) diminished the amount of tau aggregates. (Controls are shown on the left.). Credit: Dr. Li Gan Inhibiting an important signaling pathway...
Small ‘good cholesterol’ particles may have a role in Alzheimer’s prevention
KECK SCHOOL OF MEDICINE OF USC Medical guidelines meant to reduce risk for heart disease focus on levels of cholesterol in the blood, including low-density lipoproteins (LDL), labeled “bad cholesterol,” and high-density lipoproteins (HDL), labeled as “good.” Now, a new study suggests an important connection between good cholesterol particles in cerebrospinal fluid and brain health...