by University of Exeter Credit: CC0 Public Domain People with dementia who see the same GP each time have lower rates of health complications and fewer emergency hospital admissions, according to a new study. The research, led by the University of Exeter and published in the British Journal of General Practice (BJGP) analyzed more than 9,000patient records...
Category: <span>Alzheimer’s</span>
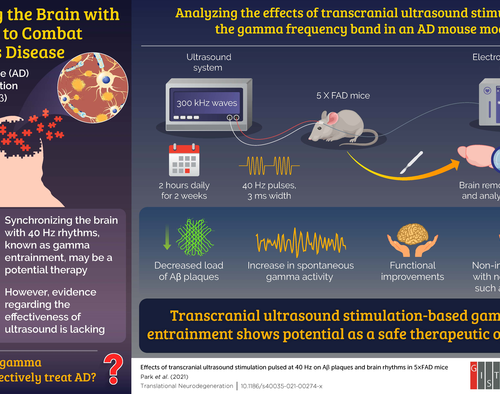
Researchers from the GIST propose ultrasound stimulation as an effective therapy for Alzheimer’s disease in new study
GIST (GWANGJU INSTITUTE OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY) IMAGE: ULTRASOUND STIMULATION AS AN EFFECTIVE THERAPY FOR ALZHEIMER’S DISEASE CREDIT: GWANGJU INSTITUTE OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY With the increase in average life expectancy in many parts of the world, certain age-related diseases have become more common. Alzheimer’s disease (AD), unfortunately, is one of them, being extremely prevalent...
A cure for Alzheimer’s is taking longer than expected; here’s why
by Carnegie Mellon University, Department of Chemical Engineering Anne Robinson, head of Carnegie Mellon’s Chemical Engineering Department, conducts research in her lab. Credit: Carnegie Mellon Chemical Engineering In her latest research paper, published in the Journal of Molecular Neuroscience, Anne Robinson, Head of Carnegie Mellon’s Department of Chemical Engineering, explains why understanding the progression of neurodegeneration...
Heart disease causes early brain dysfunction and can treble key Alzheimer’s protein
UNIVERSITY OF SHEFFIELD • Scientists have discovered that heart disease causes brain dysfunction that could lead to dementia before the buildup of plaque in blood vessels of the brain• Heart disease causes problems in the brain that causes less blood to reach the neurons that need it • Findings also show that a combination of...
A new method for treating Alzheimer’s disease
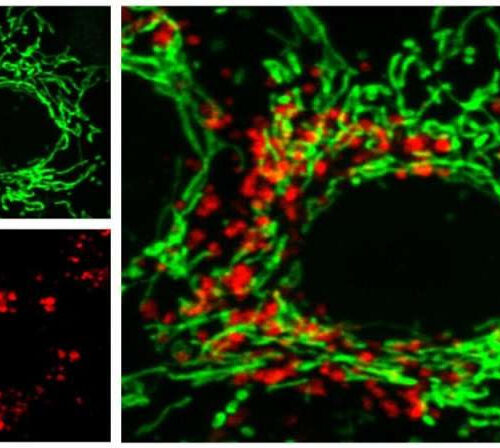
by Thomas Olafsen and Elin Doeland, University of Oslo The green colors show healthy mitochondria while the red ones are damaged mitochondria undergoing “clearance” by mitophagy. Credit: Xu-xu Zhuang One in six Norwegians over 80 is affected by Alzheimer’s disease. Numbers are even higher worldwide, and there is still no cure available. Researchers at the...
Findings open the way to more precise diagnoses and treatments of Alzheimer’s disease
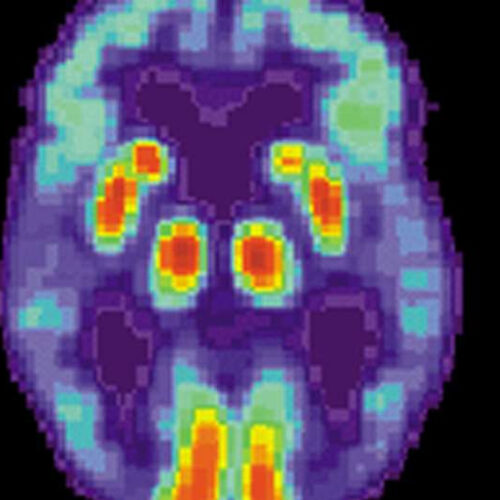
by Case Western Reserve University PET scan of a human brain with Alzheimer’s disease. Credit: public domain An international team led by Case Western Reserve University’s School of Medicine has made a significant breakthrough in understanding why Alzheimer’s disease progresses so rapidly in some people that they die within three years. The researchers found a...
Neuroprotective mechanism altered by Alzheimer’s disease risk genes
by Molly Chiu, Baylor College of Medicine Credit: Baylor College of Medicine The brain has a natural protective mechanism against Alzheimer’s disease, and researchers at Baylor College of Medicine, Texas Children’s Hospital, and collaborating institutions have discovered that gene variants associated with risk of developing the disease disturb the protective mechanism in ways that can...
Greater exposure to nitrogen dioxide linked to higher levels of biomarkers of Alzheimer’s disease in the brain
BARCELONA INSTITUTE FOR GLOBAL HEALTH (ISGLOBAL) Investigators from the Barcelonaβeta Brain Research Center (BBRC), the research arm of the Pasqual Maragall Foundation, in collaboration with ISGlobal, have found an association between exposure to air pollution and higher levels of biomarkers of Alzheimer’s disease, particularly in individuals with elevated beta-amyloid deposition in the brain. The results...
Cleveland Clinic research identifies sildenafil as candidate drug for Alzheimer’s disease
CLEVELAND CLINIC IMAGE: ACCORDING TO FINDINGS PUBLISHED IN NATURE AGING, THE RESEARCH TEAM, LED BY FEIXIONG CHENG, PH.D., OF CLEVELAND CLINIC’S GENOMIC MEDICINE INSTITUTE, DETERMINED THAT SILDENAFIL IS ASSOCIATED WITH 69% REDUCED INCIDENCE OF ALZHEIMER’S DISEASE. CREDIT: CLEVELAND CLINIC December 6, 2021, CLEVELAND: A new Cleveland Clinic-led study has identified sildenafil – an FDA-approved therapy for erectile...
Three-dimensional X-ray image spotlights neurodegenerative disease
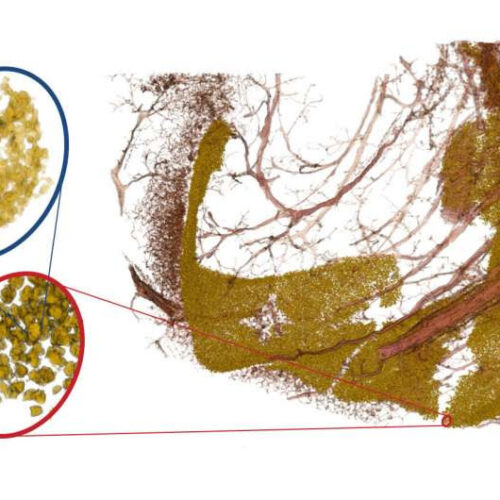
by Göttingen University The image shows neuronal cell nuclei of the dentus gyratus (yellow) and associated blood vessels (red). By varying the magnification of the X-ray optics, one can “zoom in” on the densely packed band of neurons (in the red oval) and also resolve the substructure of the cell nucleus (blue oval). The study...