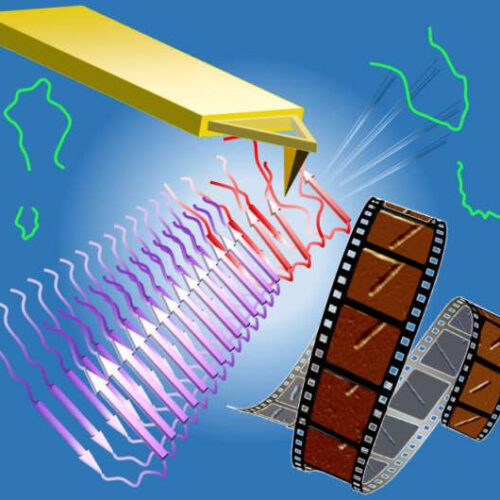
by Mike Williams, Rice University Using computational models and atomic force microscope experiments, researchers at the University of Houston and Rice University have identified a possible “Achilles’ heel” in the frustration of amyloid beta peptides as they dock to the fibrils that form plaques in patients with Alzheimer’s. The frustrated steps could open a window for drugs able...
Category: <span>Alzheimer’s</span>
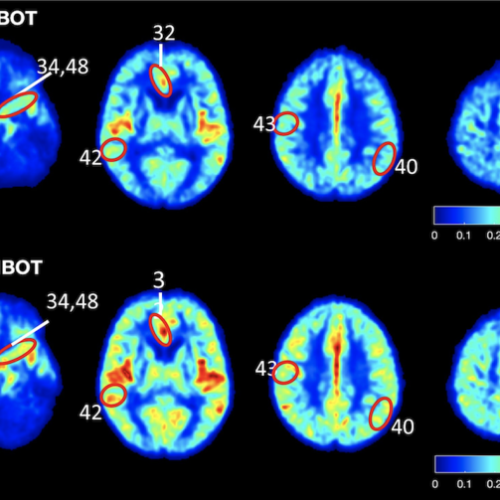
Reversal of the biological hallmarks responsible for development of Alzheimer’s disease and dementia using unique hyperbaric oxygen therapy protocol
IMAGE: STUDY RESULTS SHOW ELEVATED BLOOD FLOW AND IMPROVED OXYGENATION IN THE BRAIN OF PATIENTS SUFFERING FROM COGNITIVE IMPAIRMENT CREDIT: TEL AVIV UNIVERSITY (TAKEN FROM THE ARTICLE). Scientific Breakthrough: A team of investigators from Tel Aviv University has succeeded in restoring brain trauma by hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT). This is the first time in the...
Stopping dementia in Down syndrome patients
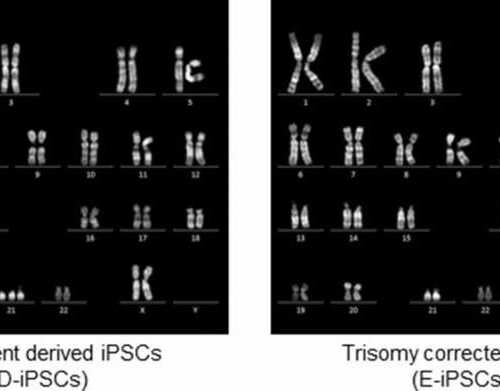
by Kyoto University Karyotype analysis of the iPSC clones. Credit: DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-96697-7 Down syndrome is mostly known for the learning disabilities it causes, but patients typically suffer from a wide number of ailments. One is the early onset of Alzheimer’s disease. Using iPS cells from Down syndrome patients, a new study by CiRA researchers suggests that the molecular...
Scientists in Sweden discover a rare, aggressive form of Alzheimer’s that begins in the early 40s
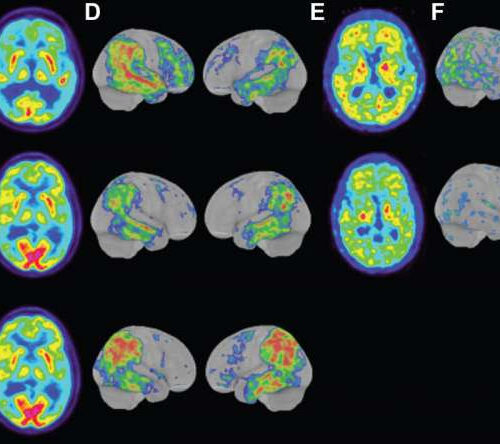
by Delthia Ricks , Medical Xpress CT images of the brain from two siblings and a cousin with familial Alzheimer’s disease who harbored the Uppsala APP mutation. Credit: M. Pagnon de la Vega et al., Science Translational Medicine (2021) A newly discovered gene mutation linked to early onset Alzheimer’s disease has been discovered by an international team...
First study to investigate the role of RNA tags in Alzheimer’s disease
by Boston University School of Medicine Credit: Pixabay/CC0 Public Domain Understanding the role of tau protein in Alzheimer’s disease (AD) has led to new ways to diagnose it as well as the creation of medicines now in clinical trials to treat it. Misfolding and aggregation of microtubule associated protein tau (MAPT) are core features of AD....
Brain tissue inflammation is key to Alzheimer’s disease progression
UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH IMAGE: ASSISTANT PROFESSOR OF PSYCHIATRY AND NEUROLOGY, UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH SCHOOL OF MEDICINE. CREDIT: THARICK PASCOAL PITTSBURGH, Aug. 26, 2021 – Neuroinflammation is the key driver of the spread of pathologically misfolded proteins in the brain and causes cognitive impairment in patients with Alzheimer’s disease, researchers from the University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine reveal in a...
Restoring “chaperone” protein may prevent plaque build-up in Alzheimer’s
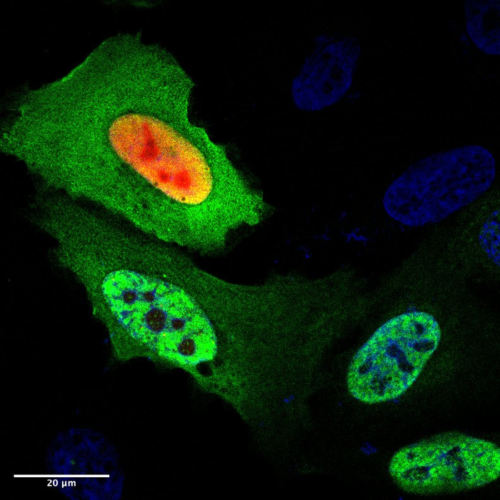
UNIVERSITY OF PENNSYLVANIA SCHOOL OF MEDICINE IMAGE: DAXX (RED COLOR AT TOP) PREVENTS THE AGGREGATION OF MUTANT P53 PROTEIN ASSOCIATED WITH CANCERS (DARK GREEN COLOR AT BOTTOM) IN CELLS. CREDIT: XIAOLU YANG, PHD PHILADELPHIA — For the first time, Penn Medicine researchers showed how restoring levels of the protein DAXX and a large group of...
No Net Benefit of Aducanumab for Alzheimer’s Disease, Expert Panel Rules
An influential, independent panel unanimously voted that aducanumab (Aduhelm) offers no benefit for patients with Alzheimer’s disease (AD), adding to growing opposition from medical experts to the US Food and Drug Administration’s (FDA’s) approval of this controversial drug. The Institute for Clinical and Economic Review (ICER) asked one of its expert panels, the California Technology Assessment Forum, to consider the available...
Waking nightmare: Disturbed circadian rhythm may be associated with Alzheimer’s disease
by Shoolini University Credit: CC0 Public Domain Our body is tuned to function in a synchronous manner with a “circadian” or day-and-night rhythm. Alterations to daily lifestyles due to the current stressful routines people follow can disrupt the body’s day-night cycle for longer periods. Recent studies in rats have shown that even chronic light exposure...
Complicating the Contribution of Persistent Infection to Neurodegeneration and Alzheimer’s Disease Risk
Researchers have in recent years put forward contradictory evidence for and against a role for persistent infection, such as by herpesviruses, in neurodegeneration and the incidence of Alzheimer’s disease. The Alzheimer’s disease scientific community is in need of a good explanation as to why only some people with the known risk factors go on to develop the condition. That disease...