by Monash University Credit: Pixabay/CC0 Public Domain As little as 1% reduction in deep sleep per year for people over 60 years of age translates into a 27% increased risk of dementia, according to a study which suggests that enhancing or maintaining deep sleep, also known as slow wave sleep, in older years could stave off...
Category: <span>Alzheimer’s</span>
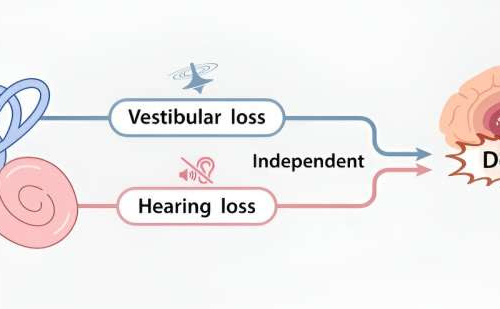
New large-scale study results add to evidence that vestibular loss increases dementia risk
by Stephanie Baum , Medical Xpress The relationship between vestibular loss and the risk of dementia. Credit: Scientific Reports (2023). DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-42598-wExisting research shows a link between hearing loss and the risk of dementia, and a new study adds to growing evidence that vestibular loss can increase dementia risk as well. Results from this work,...
How a Candida infection could trigger mechanisms tied to Alzheimer’s
A study in mice and cell cultures suggests that Candida albicans can infect the brain and trigger Alzheimer’s-like mechanisms. Image credit: Paul Campbell/Getty Images.Researchers have uncovered how a common fungus enters the brain and generates toxic proteins implicated in Alzheimer’s disease.By studying animal models, the team found that the fungus Candida albicans uses enzymes to...
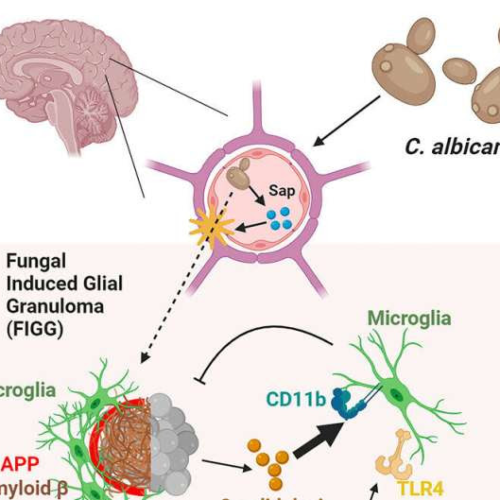
Brain fungal infection produces Alzheimer’s disease-like changes, says new study
by Homa Warren, Baylor College of Medicine Graphical abstract. Credit: Cell Reports (2023). DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2023.113240Previous research has implicated fungi in chronic neurodegenerative conditions such as Alzheimer’s disease, but there is limited understanding of how these common microbes could be involved in the development of these conditions. Working with animal models, researchers at Baylor College of Medicine...
Stem cell research sheds light on new ‘molecular road’ to Alzheimer’s disease
by Mass General Brigham Credit: Pixabay/CC0 Public Domain Alzheimer’s disease (AD) varies widely in its age of onset, presentation and severity. Recently, the SORL1 gene has received increased attention since variations in this gene have been associated with both early and late onset AD. However, little is known about how damage to SORL1 leads to disease....
Intermittent fasting improves Alzheimer’s pathology
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA – SAN DIEGO IMAGE: THIS CONFOCAL MICROSCOPY IMAGE SHOWS AMYLOID PLAQUES (BLUE AND RED) IN THE BRAIN OF A MOUSE. THE ACCUMULATION OF AMYLOID PLAQUES IS THE MOST WELL-DOCUMENTED BIOCHEMICAL HALLMARK OF ALZHEIMER’S DISEASE. CREDIT: UC SAN DIEGO HEALTH SCIENCES One of the hallmarks of Alzheimer’s disease is disruption to the body’s circadian...
Brains with Alzheimer’s disease have subnormal levels of important dietary antioxidants
by Josh Meyer, Virginia Tech Credit: Unsplash/CC0 Public Domain Alzheimer’s disease is a progressive neurodegenerative disease estimated to affect 6 million Americans and 33 million people worldwide. Large numbers of those affected have not yet been diagnosed. A new study published in the Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease by a Virginia Tech Carilion School of Medicine faculty member shows...
Novel vaccine targets inflamed brain cells in Alzheimer’s to modify the course of disease
Reviewers’ NotesReviewed by Danielle Ellis, B.Sc.Jul 31 2023 A novel vaccine that targets inflamed brain cells associated with Alzheimer’s disease may hold the key to potentially preventing or modifying the course of the disease, according to preliminary research presented at the American Heart Association’s Basic Cardiovascular Sciences Scientific Sessions 2023. The meeting is in Boston, July...
Phyllodulcin could be a potential candidate for treating Alzheimer’s disease
by Sahmyook University Researchers from Korea have now identified phyllodulcin, a major component of hydrangeas, as a potential candidate for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. In this animal model study, phyllodulcin controlled the formation and degradation of amyloid aggregates, thereby targeting the main cause of AD. It also reduced memory impairment and improved memory formation processes...
AI Unlocks Olive Oil’s Potential in Alzheimer’s Battle
Summary: Researchers have utilized artificial intelligence to uncover the promising potential of extra virgin olive oil (EVOO) in combating Alzheimer’s disease (AD). By integrating AI, chemistry, and omics research, the study identified specific bioactive compounds in EVOO that could contribute to the treatment and prevention of AD. Ten phytochemicals within EVOO, such as quercetin, genistein, luteolin, and kaempferol,...