The immune system is complex and ages in complex ways, pressed by the lifetime burden of infection and rising levels of molecular damage that trigger many of the same innate immune responses as are produced by invading pathogens. The common innate immune cells known as macrophages play many roles in the body: defense against pathogens; destruction of errant cells; assisting in tissue maintenance...
Category: <span>Anti-aging</span>
Study suggests scientists may need to rethink which genes control aging
NIH/NATIONAL INSTITUTE OF NEUROLOGICAL DISORDERS AND STROKE IMAGE: In a study of Drosophila fruit flies, NIH scientists found that only about 30% of the genes that are hallmarks for aging may set an animal’s internal clock. The rest may reflect the body’s response to bacteria. Above is a picture of a Drosophila gut, a key source of bacteria....
Personalized medicine, not X-rays, should guide forearm fracture treatment in older adults
MICHIGAN MEDICINE – UNIVERSITY OF MICHIGAN A decade-long study of the most common forearm fracture in older adults revealed that personalized medicine catering to a patient’s individual needs and environment, not age or X-rays, should guide treatment options. Led by a Michigan Medicine physician, the research team examined treatment outcomes over two years for patients...
Cells optimised to produce substance that holds potential to improve ‘healthy ageing’
TECHNICAL UNIVERSITY OF DENMARK IMAGE: A NEW SCIENTIFIC STUDY PUBLISHED IN NATURE CATALYSIS SHOWS THAT BAKER’S YEAST CAN BE DESIGNED AND OPTIMISED TO PRODUCE POLYAMINES AND POLYAMINE ANALOGUES FOR TACKLING GRAND CHALLENGES IN BOTH THE HEALTH AND AGRICULTURAL SECTOR. CREDIT: THE NOVO NORDISK FOUNDATION CENTER FOR BIOSUSTAINABILITY The population on Earth is increasingly growing and...
Anti-aging protein in red blood cells helps stave off cognitive decline
by Public Library of Science Credit: CC0 Public Domain Research conducted by Qiang et al have discovered a link between a protein in red blood cells and age-related decline in cognitive performance. Published in the open-access journal PLOS Biology on 17th June 2021, the study shows that depleting mouse blood of the protein ADORA2B leads to...
Convergent mechanism of aging discovered
MAX-PLANCK-GESELLSCHAFT IMAGE: ANDREA ANNIBAL USES THE MASS SPECTROMETER TO INVESTIGATE VARIOUS METABOLITES IN LONG-LIVED WORMS AND MICE. CREDIT: LINK/MAX PLANCK INSTITUTE FOR BIOLOGY OF AGEING, 2021 Several different causes of aging have been discovered, but the question remains whether there are common underlying mechanisms that determine aging and lifespan. Researchers from the Max Planck Institute...
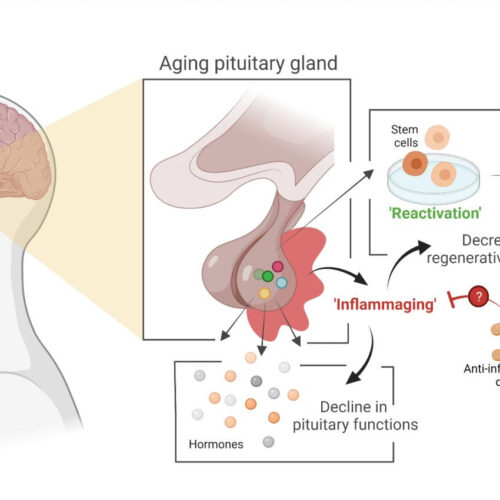
Main gland in hormonal system ages due to process that can potentially be slowed down
KU LEUVEN IMAGE: Stem cell biologist Hugo Vankelecom (KU Leuven) and his colleagues have discovered that the pituitary gland in mice ages as the result of an age-related form of chronic inflammation. It may be possible to slow down this process or even partially repair it. Vankelecom and his colleagues studied the pituitary of mice,...
What might cause head pressure and dizziness?
by Eric Swensen, University of Virginia Credit: CC0 Public Domain Researchers at the University of Virginia School of Medicine have taken a new approach to understand how our genes determine the strength of our bones, allowing them to identify several genes not previously known to influence bone density and, ultimately, our risk of fracture. The work...
A prescription to ward off cognitive decline – without medication
A clinical neuropsychologist with expertise in dementia shares what the science tells about improving memory and thinking without drugs. There’s a pill for many ailments, but aging isn’t one of them. And while some mounting difficulty in thinking and processing is expected as you grow older, cognition experts say you can take steps to slow...
Memory biomarkers confirm aerobic exercise helps cognitive function in older adults
FLORIDA ATLANTIC UNIVERSITY IMAGE: THE ENHANCED PHYSICAL ACTIVITY GROUP UNDERWENT 26 WEEKS OF SUPERVISED TREADMILL TRAINING. BLOOD SAMPLES FOR BOTH GROUPS WERE TAKEN AT BASELINE AND AFTER 26 WEEKS. CREDIT: FLORIDA ATLANTIC UNIVERSITY Increasing evidence shows that physical activity and exercise training may delay or prevent the onset of Alzheimer’s disease (AD). In aging humans,...